A key idea in Web3’s development is chain abstraction, which aims to connect users with decetrnalized apps (dApps) easier. As blockchain technology spreads by 2030 technology will be worth $3.1 trillion, with 10% and 20% of the world’s economic infrastructure. users frequently encounter challenges, such as juggling multiple wallets, accessing different networks, and paying gas fees. Creating a smooth experience similar to typical web applications is essential because this fragmentation may discourage widespread adoption.
Chain abstraction can help with many issues by offering an integration layer that makes transactions between various blockchains more efficient. This strategy not only improves user experience but also promotes interoperability across various blockchain ecosystems. Blockchain Abstraction makes it possible for consumers to interact with dApps similarly how to they already use traditional apps by abstracting away the underlying complexity. We will examine how chain abstraction can transform the decentralized environment and make it more approachable and user-friendly for all as we dig deeper into what it means.
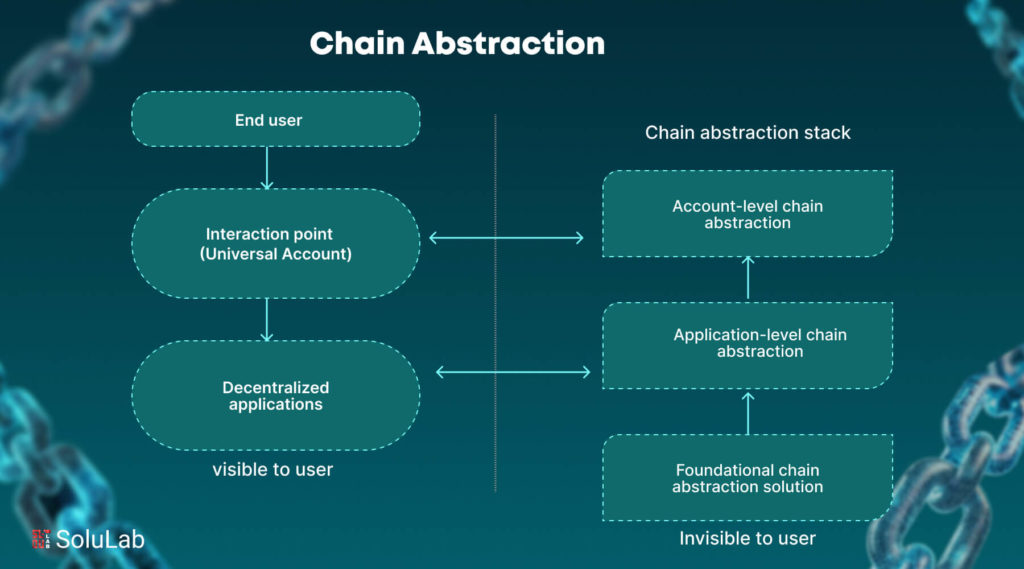
What is Chain Abstraction?
It is important to understand what is chain abstractions before getting into it. By addressing the fragmented characteristics of many blockchains (liquidity, user experience, etc.) It is a proposal to make integrating with them easier. It facilitates the easy access of cross-chain applications by consumers and the development of such applications by developers.
Chain abstraction makes Web3 more accessible by improving the user experience overall and removing obstacles to widespread adoption by removing away technical concerns. Abstraction in Blockchain eliminates the hassle of handling numerous gas tokens, wallets, and accounts as well by combining several blockchains under a single interface. Although several initiatives take different approaches to chain abstraction, they resolve the issues of fragmented ecosystems by facilitating smooth communication and interoperability. Additionally, chain abstraction improves developer efficiency by offering a uniform development environment across chains.
What is the Role of Multi-Chain in Abstraction?
In blockchain ecosystems, cross-chain abstraction is essential to the abstract notion. The complexity of communicating across these platforms rises dramatically as the amount of blockchains keeps expanding, each with distinct protocols and features. This problem is solved by multi-chain abstraction, which offers a stable framework that improves interoperability and streamlines user interactions. Here is your Multi-chain Abstraction Guide :
1. User Experience Simplified
Simplifying the user experience is one of the multi-chain abstraction’s main purposes. Users may manage assets and complete transactions without having to learn the nuances of each blockchain by using one interface that combines features from several blockchains. For example, users can manage Bitcoin assets and Ethereum-based NFTs from a single platform, removing the need for various interfaces.
2. Improved Interoperability
Chain Interoperability explained across several blockchain networks is also improved by multi-chain abstraction. It facilitates smooth communication and transactions, removing the need for manual bridging or handling several transaction formats for tasks like asset exchanges between blockchains. These interactions are made possible by technologies like cross-chain bridges which guarantee that users may take advantage of various blockchains.
3. Simplified Development
Multi-chain abstraction has several benefits from a development standpoint. Without being constrained by the limitations of a single ecosystem, developers can produce decentralized apps (dApps) that leverage several blockchains. This adaptability enables the greatest characteristics of several platforms to be utilized, resulting in increased performance and cost-effectiveness.
What is the Aim of Chain Abstraction?
This is your ultimate Guide to Blockchain Abstraction. The goal of chain abstraction is to address the fragmented Web3 user experience caused by the growth of public blockchains such as L2s and even L3s. This fragmentation hinders Web3’s adoption because it demands strongly sophisticated and active users in liquidity spread across multiple blockchains, and dApps within an increasing number of ecosystems. It also causes many user experience issues for users, including costly and lengthy cross-chain operations, the need to hold multiple gas tokens, etc. To put it simply, within a chain-abstracted world, top blockchain development companies connect to dApp and sign an operation that may span many blockchain networks using a single interface.
To formulate a more elaborative definition two points can be deduced from this which are as follows:
- It is more beneficial to think about chain abstraction more as a group objective when opposed to a particular service or technology. Therefore, chain abstraction can be viewed as a kind of vision, flow, or user experience that exists in some domains.
- Any element that contributes to achieving the type of user experience that chain abstraction can generally refer to can be seen as enabling or powering chain abstraction.
How Does Chain Abstraction Work?
Fundamentally chain abstraction is a sophisticated fusion of communication protocols, smart contracts, and middleware that allows for smooth communication with several different blockchains via a single interface. Here are the points that explain how chain abstraction works:
1. The Abstraction Layer
The Abstraction Layers in Blockchain is a distinct blockchain or layered solution that is placed on top of the other background that it seeks to abstract. The smart contracts that serve as the bridge between the underlying blockchain and the user’s dApp are stored at this layer.
These smart contracts can comprehend unique transaction formats and protocols of every linked blockchain. By translating user requests into a language that the target blockchain can comprehend, they serve as translators.
2. Protocols for Messaging
The abstraction layer requires a strong communication channel to communicate with the underlying blockchains. Message protocols are used in this situation. Between the many blockchains and the abstraction layer, these protocols allow for safe and dependable message transfer. Several widely used communication protocols in chain abstraction are as follows:
- Inter-blockchain communication protocol called IBC is a standardized interface for blockchain interoperability.
- LayerZero is an omnichain integration protocol that makes asset transfers and cross-chain messaging possible.
- A wormhole is a kind of message-passing mechanism used to link different blockchains.
These protocols provide accurate relaying and execution of transactions started on the abstraction layer that resides on the target blockchains, as well as communication of the outcomes.
Related: What is Cross-Chain Compatibility?
3. Middleware
As it offers extra features and services that improve the system as a whole, middleware is essential to chain abstraction. It may consist of the following:
- Relayers are outside of the chain services that keep an eye for fresh transactions at the abstraction layer and forward them to to relevant blockchain.
- Validators guarantee the system’s security and integrity and confirm the legitimacy of transactions.
- Oracles provide smart contracts access to real-world data so that they can communicate with outside sources.
The abstraction layer, messaging protocols, and middleware components collaborate to establish a smooth and effective cross-chain communication channel.
4. The Process
- User Interaction: Using a dApp based on the chain abstraction layer, the user requests a token transfer.
- Request Translation: After receiving the request, the abstraction layer’s smart contract converts into the format that the destination blockchain needs.
- Messay Relay: The relayer network receives the translated message and forwards it to the relevant blockchain.
- Transaction Execution: After receiving the message, the token transfer is carried out on the target blockchain.
- Confirmation Relay: The transaction confirmation is sent back to the abstraction layer via the relayer network.
- UI Update: To indicate an effective token transfer, the abstraction layer modifies the dApp’s user interface.
Major Benefits of Chain Abstraction
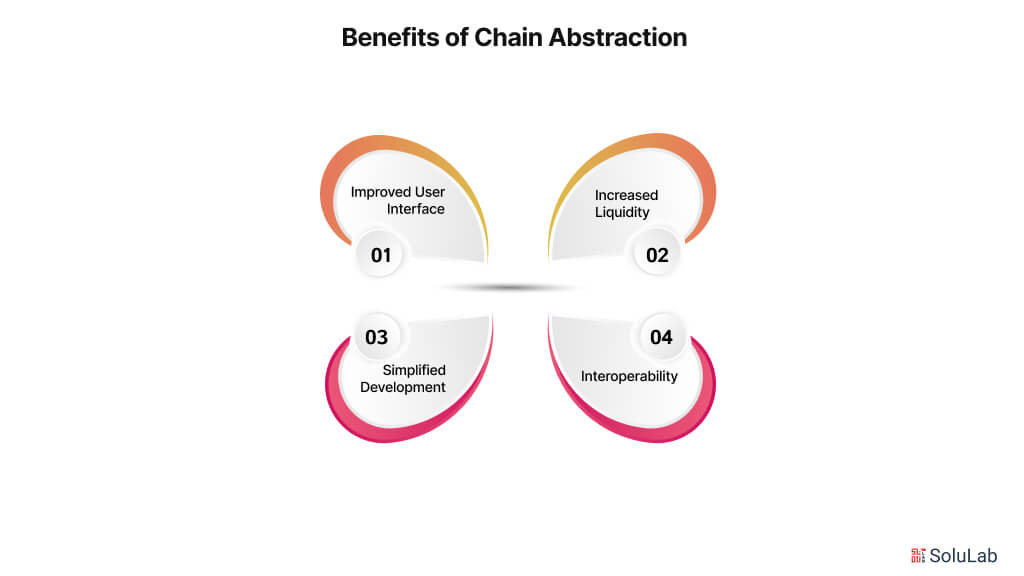
When these various services are combined, a seamless user experience is produced, enabling consumers to utilize blockchain-based apps without being aware that blockchain is being utilized. Here are the major chain abstraction benefits you must know before getting into it:
-
Improved User Interface
Chain abstraction facilitates user interaction with dApps and digital asset management by concealing the intricacies of various blockchains. This is comparable to how individuals can browse without being concerned about the supporting protocols.
-
Increased Liquidity
Chain abstraction aids in the procedure of separate liquidity pools within certain blockchains. A wider variety of liquidity choices are available to users and developers, which improves the overall effectiveness of financial apps and makes it simpler to locate competitive prices.
-
Simplified Development
Without being constrained by the constraints of a single blockchain, developers are free to design dApps. They can maximize performance and cost-effectiveness by utilizing the advantages of several blockchains such as Ethereum’s smart contract and Polygon’s lower transaction fees in a single application.
-
Interoperability
By enabling smooth transactions and integration between blockchain networks, chain abstraction improves their interoperability. This feature, which encourages a more flexible and integrated blockchain environment, is essential to the development of the decentralized system.
Limitations and Challenges in Chain Abstraction
Although chain abstraction has several advantages there are a few challenges associated with it as well:
1. Risk of Centralization
Gathering several blockchains in one window can cause the problem of having an area of weakness. It is pivotal to ensure a secure and decentralized network and to reduce the overall risks inherent to centralized protocols.
2. Security Issues
There are always security features that are exclusive to every blockchain. A major concern that arises is to ensure that protocols embraced and abide by the various links of chain abstraction do not get compromised. For instance, defects in one blockchain can cause an impact on the chain abstraction system, and if not well managed.
3. Interoperability
This is because different blockchains use different standard smart contract language and consensus algorithms. Thus, to achieve valid chain abstraction it is necessary to create a robust and flexible chain, capable of handling these fluctuations.
4. Performance Overheads
Having a single interface and managing cross-chain transactions brings performance overheads along with it. This procedure, of course, has to be optimized to ensure that they are fully effective and do not slow down the processes.
Real-World Services Use Cases of Chain Abstraction
Here are the major real-time use cases of chain abstraction to help you better understand them:
- Multi-Chain Asset Management
To provide customers hassle-free experience, chain abstraction is currently being adopted by applications such as asset managers and multi-chain wallets. The general usability of the decentralized ecosystem is facilitated due to the possibilities to manage, trade, and stake assets across several blockchains through a single interface.
-
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Chain abstraction can greatly improve Defi Development which gives consumers the possibility to use financial services and liquidity in several blockchains. Solutions to problems related to finances coupled with more attractive interest rates are often the effects of it.
-
Gaming and NFTs
The cross-game and cross-platform portability of digital assets is made possible through chain abstraction in the gaming and NFT spaces. Enabling integrated digital assets allows cross-platform use to enhance usability and perceived value by the user. The gaming NFT industry is expected to develop between 2024 to 2032 with a CAGR of more than 60% mainly due to the growth of adoption of blockchain technology.
How Are Multi-Chain Interactions Better Than Single Chain?
| ASPECTS | MULTI-CHAIN | SINGLE-CHAIN |
| Scalability | High scalability by handling transactions concurrently, several chains can ease congestion. | Congestion is likely to occur when transaction volumes are larger due to limited scalability. |
| Performance | Enhanced efficiency as a result of cross-chain parallel processing. | Performance time often gets slowed down when the network is crowded. |
| Customization | Extremely adaptable, enables the development of customized chains for certain use cases or legal requirements. | No room for customization and a one-size-fits-all strategy. |
| Risk Mitigation | Enhances resilience, and better availability are ensured by the ability of other chains to continue operating even in the event of chain failure. | Susceptible to systematic failures, problems throughout the chain have the potential to stop all activities. |
| Complexity | Less complicated development but less adaptability to changing requirements. | Cross-chain communication necessitates more sophisticated development, but it also provides more flexibility and chances for creativity. |
| User Experience | User may result in longer wait times during bust times and increased transaction fees. | Reduced fees and quicker transactions as a result of the spread load improve the user experience. |
How is SoluLab Developing Ease Within Chain Abstraction Operations?
SoluLab as a blockchain development company has the ability can be demonstrated by NovaPay Nexus, which shows that multi-chain interactions are transforming the blockchain environment by offering increased flexibility and efficiency. Businesses can function with several currencies according to their unique demands thanks to this platform’s ability to enable users to create and administer many stores, each featuring its wallets and settings. Without the need for technical knowledge or dependence on outside services, NovaPay Nexus also makes it easier to create a variety of applications for any store, including crowdfunding tools, payment buttons, and point-of-sale systems.
To sum up, NovaPay Nexus serves as a Cross Chain Multi-Asset Management Platform and simplifies chain abstraction framework activities, improving user experience and process efficiency within the blockchain ecosystem. Investigating platforms like NovaPay Nexus Nexus may be a modern context for companies wishing to adopt these developments in terms of operational effectiveness.
Contact SoluLab as your Blockchain consulting company today to indulge in modern developments of Blockchain-as-a-Service and you can read more developments offered by SoluLab.
FAQs
1. What are the major differences between Multi-Chain and cross-chain?
Multi-chain vs. cross-chain is a wide concept in terms of similarities and differences. When several blockchain networks are utilized along with their distinct features under a multi-chain, on the other hand, cross-chain enhances scalability and utility by facilitating the transfer of assets between several blockchain networks.
2. What are the main blockchain use cases?
Accurate asset testing, improved software, service licensing, and transparency regarding the origin of consumer goods from sourcing to consumption can all be made possible with the utilization of blockchain technology.
3. What does Layer 1 and Layer 2 stand for?
Updates such as altering block sizes, consensus procedures, and sharing the division of the database into several actions are included in Layer 1. Side chains, roll-ups, and parallel blockchains along with off-chain transactions processing come under layer 2.
4. What role does the abstraction layer play in chain abstraction?
The abstraction layer creates a framework that makes it simple to integrate many services to offer a more transparent and comprehensive business analytics query interface. Also, have the ability to mask the difficulties associated with blockchain networks.
5. Can SoluLab transform blockchain experiences using chain abstraction?
Chain abstraction is one of the ways using which SoluLab can transform blockchain technology experiences. It improves user experiences, lowers development costs, and increases interoperability by streamlining interactions across various blockchains.






