
Asset tokenization transforms the way we invest in and trade valuable assets such as real estate, art, or company shares. The asset tokenization market is projected to reach between $5 trillion and $16 trillion by 2030, driven by demand across financial assets, real estate, and unique assets like intellectual property and carbon credits. Estimates from Citigroup and Boston Consulting Group suggest tokenized assets could represent up to 10% of global GDP by 2030.
By representing these physical assets digitally through blockchain technology, tokenization simplifies and accelerates their trading process. There are two primary approaches to asset tokenization: on-chain and off-chain. By transforming both physical and digital assets into blockchain-based tokens, new possibilities emerge for liquidity and fractional ownership. However, the approaches to asset tokenization—on-chain vs off-chain tokenization—vary considerably.
This blog will discuss the asset tokenization comparison, examining the differences between on-chain and off-chain tokenization, their specific advantages, and real-world applications.
What is Asset Tokenization?
Asset tokenization refers to the process of converting real-world or digital assets into digital tokens using Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT), typically on a blockchain. These tokens represent ownership or rights to the asset and can be traded, transferred, or held on a decentralized platform. The concept is transforming the way assets are managed, offering benefits such as improved liquidity, transparency, and security.
DLT Tokenization enables assets like real estate, fine art, commodities, or intellectual property to be digitized and traded in fractional amounts. This process democratizes access to high-value assets, allowing multiple investors to own a fraction of an asset rather than having to purchase it in full—this is known as asset fractionalization. For instance, a property worth $1 million could be tokenized into 1,000 tokens, with each token representing a fraction of ownership, making it easier for smaller investors to participate.
The key to asset tokenization is the use of smart contracts in tokenization, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. Smart contracts automate processes such as transferring ownership, distributing dividends, or handling compliance requirements, reducing the need for intermediaries and increasing efficiency.
Another essential aspect of tokenization is the adherence to specific token standards that define how these tokens behave on the blockchain. For instance, ERC-20 and ERC-721 are popular token standards on Ethereum that ensure interoperability, security, and proper functionality of tokens. These standards allow for consistent token creation and management across different platforms, enabling seamless trading and transferability.
Overall, asset tokenization via DLT creates a more accessible, efficient, and transparent system for asset ownership and exchange. By leveraging blockchain, smart contracts, and token standards, tokenization is unlocking new opportunities for investors and businesses alike, facilitating more liquid markets and reducing the complexities of traditional asset management.
The Role of Blockchain in Asset Tokenization
Blockchain plays a pivotal role in asset tokenization, serving as the underlying infrastructure that enables the digitization, security, and transfer of assets. By utilizing decentralized ledger technology (DLT), blockchain provides a transparent and immutable platform for recording asset ownership, ensuring that transactions are secure and tamper-proof. This innovation is driving a fundamental shift in how assets are managed and traded across industries.
One of the primary blockchain tokenization methods involves representing physical or digital assets as tokens on a blockchain. These tokens act as digital certificates of ownership, providing proof of stake in an asset. Blockchain ensures that the process is transparent, with all transactions recorded on a distributed ledger that can be audited and verified by all participants. This level of visibility minimizes the risks associated with fraud or disputes, making the asset tokenization process more secure than traditional methods.
Asset tokenization security is one of the biggest advantages of blockchain technology. Blockchain’s decentralized nature ensures that no single entity controls the data, reducing the risk of tampering or unauthorized changes. Additionally, cryptographic methods are used to secure tokenized assets, ensuring that only authorized parties can access and transfer ownership. This level of security is particularly important for high-value assets such as real estate, fine art, or commodities, where ownership records must be meticulously protected.
Blockchain also enables digital asset custody solutions, which are vital for the safe storage and management of tokenized assets. These custody solutions leverage smart contracts to automate the management of assets, including dividend payments, ownership transfers, and compliance with regulatory requirements. This eliminates the need for third-party intermediaries, streamlining the asset management process and reducing operational costs. Blockchain-based custody solutions also provide enhanced security by safeguarding assets through cryptographic measures, protecting against hacks or theft.
Thus, blockchain technology is the backbone of asset tokenization, providing the necessary infrastructure for secure, transparent, and efficient asset management. Through blockchain tokenization methods, enhanced security, and digital asset custody solutions, blockchain is improvising how assets are digitized, transferred, and stored, creating new opportunities in global markets.
What is On-Chain Tokenization?
On-chain tokenization is the process of converting physical or digital assets into digital tokens that are stored and managed directly on a blockchain. These tokens represent ownership or rights to the underlying asset, which can include anything from real estate and artwork to intellectual property or cryptocurrencies. By using blockchain’s decentralized ledger, on-chain tokenization ensures that transactions, ownership transfers, and records are transparent, secure, and immutable. This means that once an asset is tokenized, its ownership and transaction history are recorded permanently on the blockchain, preventing tampering or unauthorized changes.
A key feature of on-chain tokenization is the ability to fractionalize assets, making it easier for multiple people to own shares of high-value items. Through smart contracts, the transfer of ownership, regulatory compliance, and even dividend distribution can be automated, eliminating the need for intermediaries and streamlining the process. On-chain tokenization not only improves liquidity by allowing token holders to trade fractions of assets, but it also opens up global markets, enabling investors from around the world to participate in traditionally exclusive sectors, such as real estate, fine art, and commodities.
Key Features of On-Chain Tokenization
On-chain tokenization refers to the process of directly issuing and managing tokens representing assets on a blockchain. This method offers numerous advantages due to the transparent and immutable nature of blockchain technology. Below are the key features that make on-chain tokenization a powerful tool for asset management:
-
Full Transparency and Immutability
On-chain tokenization leverages the blockchain’s decentralized ledger, ensuring that all transactions, ownership transfers, and token issuance are recorded on a publicly accessible, immutable ledger. This transparency allows for easy auditing, while immutability ensures that once data is written to the blockchain, it cannot be altered or tampered with, thereby reducing fraud and increasing trust among participants.
-
Enhanced Security and Fraud Prevention
Blockchain’s cryptographic security mechanisms safeguard tokenized assets against unauthorized access and cyber threats. Each transaction and ownership change is verified and encrypted, making it nearly impossible for fraudulent activities to occur. This robust security framework is a key feature of on-chain tokenization, especially when dealing with high-value or sensitive assets.
-
Real-Time Settlement and Efficiency
On-chain tokenization facilitates real-time transaction settlement, eliminating the need for third-party intermediaries. This significantly reduces the time and cost associated with transferring ownership or managing assets, enhancing overall market efficiency. Smart contracts, which automate the execution of predefined rules, further streamline processes like ownership transfers, dividend payments, or compliance checks.
-
Regulatory Compliance Tokenization
One of the critical considerations in asset tokenization is adherence to regulatory standards. On-chain tokenization can incorporate regulatory compliance tokenization by embedding legal and regulatory requirements directly into the tokens through smart contracts. For example, restrictions on who can trade certain assets or geographic limits on investment can be coded into the token itself, ensuring that compliance is automated and enforced at the blockchain level.
-
Fractional Ownership and Liquidity
On-chain tokenization enables fractional ownership, allowing assets to be divided into smaller units and owned by multiple parties. This opens up investment opportunities for a broader range of participants who might not have the capital to purchase an entire asset. As a result, traditionally illiquid assets, such as real estate or fine art, become more liquid, with fractional shares of these assets traded on secondary markets.
-
Global Accessibility
With on-chain tokenization, assets can be accessed and traded globally without the limitations imposed by traditional borders. Blockchain platforms operate 24/7, enabling continuous trading and reducing barriers to entry for international investors. This global accessibility unlocks new markets for asset owners and enhances liquidity for previously localized assets.
In conclusion, the key features of on-chain tokenization—transparency, security, real-time settlement, regulatory compliance, fractional ownership, and global accessibility—make it an ideal solution for asset management in the modern digital economy. Through on-chain methods, asset tokenization becomes a secure, efficient, and scalable process that empowers both asset owners and investors.
How Does On-Chain Tokenization Work?
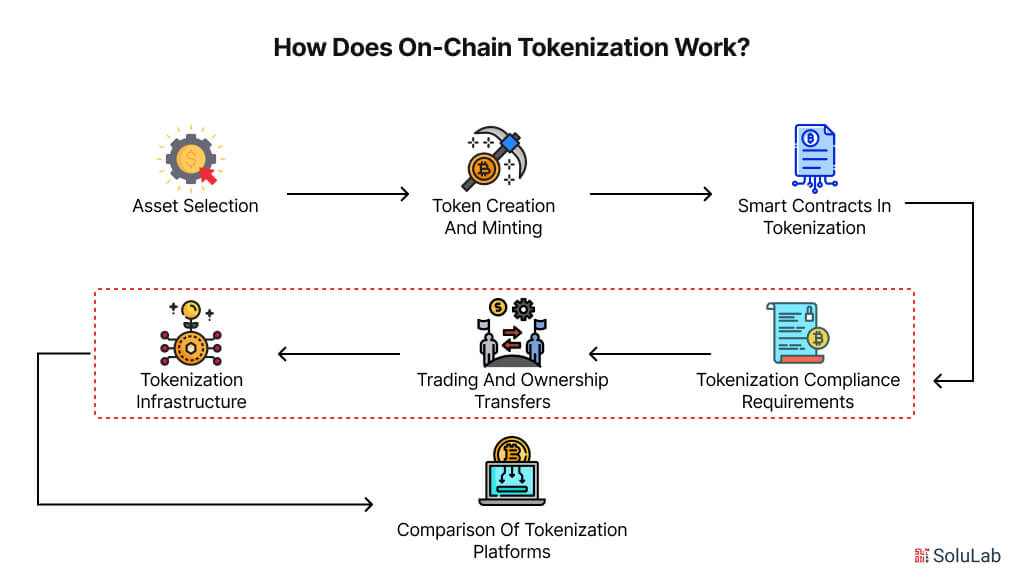
On-chain tokenization transforms physical or digital assets into digital tokens that are securely managed on a blockchain. This method allows for easier tracking, trading, and ownership transfer of assets while ensuring transparency and security. Here’s a simple breakdown of how it works, using key elements of blockchain technology.
-
Asset Selection
The first step in on-chain tokenization is deciding which asset you want to tokenize—this could be anything from real estate and art to digital intellectual property. By converting the asset into digital tokens on a blockchain, the asset becomes easier to track and trade. Tokenization platforms allow asset owners to choose different methods based on the asset type, offering comparisons between features like supported blockchain networks, ease of use, and cost efficiency.
-
Token Creation and Minting
The asset is divided into digital tokens, each representing a share of ownership. This process is known as minting. Depending on the asset, different digital asset tokenization types can be used, such as fungible tokens (which are interchangeable, like cryptocurrencies) or non-fungible tokens (unique, like Non-fungible tokens (NFTs)). Once minted, these tokens can be easily traded, tracked, and transferred on the blockchain.
-
Smart Contracts in Tokenization
Smart contracts are automated digital agreements programmed into the blockchain, and they play a crucial role in tokenization. These contracts manage the rules for token transfers, asset ownership, and compliance without the need for intermediaries. For instance, a smart contract will automatically transfer ownership of a token once certain conditions are met, such as a payment being made. This automation increases efficiency, reduces costs, and ensures transactions are secure and reliable.
-
Tokenization Compliance Requirements
For on-chain tokenization to be legally compliant, tokens must adhere to tokenization compliance requirements. These requirements often involve programming smart contracts to enforce restrictions, such as who can own the tokens or limits on the number of tokens one person can hold. This ensures that the tokenization process follows regulatory standards in various jurisdictions, making it safer for both issuers and investors.
-
Trading and Ownership Transfers
Once tokens are created and compliance is established, they can be traded or transferred between parties. The blockchain records every transaction, providing a transparent and immutable record of ownership. Tokenization increases liquidity because assets that were previously difficult to trade, like real estate, can now be easily divided into smaller, tradeable tokens. This makes fractional ownership possible and opens up new opportunities for investors.
-
Tokenization Infrastructure and Digital Asset Custody Solutions
To support the entire tokenization process, a robust tokenization infrastructure is essential. This includes the blockchain network itself, smart contract development, and platforms that facilitate token creation and trading. Additionally, digital asset custody solutions play a crucial role by securely storing these tokens. Custody solutions safeguard digital assets using advanced encryption and access control, ensuring that tokenized assets are protected from theft or fraud.
-
Comparison of Tokenization Platforms
Different tokenization platforms offer varying features such as blockchain compatibility, user interface, and fees. Some platforms are designed for specific industries, like real estate or fine art, while others offer more general solutions. A comparison of these platforms can help asset owners choose the right infrastructure based on their specific needs, including compliance capabilities, ease of token issuance, and integration with digital asset custody solutions.
Use Cases for On-Chain Tokenization
On-chain tokenization has a wide range of practical applications across different industries, thanks to its ability to make assets more accessible, liquid, and secure. By leveraging tokenization infrastructure on a blockchain, businesses and individuals can unlock new opportunities for investment and ownership. Below are some key use cases where on-chain tokenization is making a significant impact:
1. Real Estate Tokenization: One of the most prominent use cases is in real estate tokenization. Property can be tokenized, allowing it to be divided into smaller, tradable units. This concept, known as asset fractionalization, enables multiple investors to own fractions of a property, lowering the barrier to entry for real estate investments. Instead of needing millions to purchase an entire building, investors can own a portion with just a few thousand dollars. This also makes it easier to trade or sell those fractions on secondary markets, improving liquidity in the traditionally illiquid real estate market.
2. Art and Collectibles: Fine art, rare collectibles, and luxury items can also be tokenized, giving people a chance to invest in high-value assets without having to purchase the entire piece. On-chain tokenization allows investors to own a fraction of a valuable artwork or collectible, with ownership recorded securely on the blockchain. This makes it possible for art lovers and collectors to diversify their portfolios and trade ownership shares more easily.
3. Commodities and Precious Metals: Tokenization can also apply to commodities like gold, silver, or oil. Instead of physically storing these assets, ownership can be represented by digital tokens on a blockchain. This reduces the need for complicated and costly storage and transportation logistics, while still allowing investors to own a stake in these valuable resources. Fractional ownership also makes it easier for smaller investors to enter markets that were previously dominated by large players.
4. Equity and Bonds: Traditional financial assets like stocks and bonds can also benefit from on-chain tokenization. Companies can tokenize shares of their equity or debt instruments and offer these tokens to investors on the blockchain. This opens up access to a global pool of investors and simplifies the buying, selling, and transferring of ownership. Tokenized equity and bonds can also be traded on secondary markets, providing more liquidity and flexibility to investors.
5. Intellectual Property: On-chain tokenization can be used to tokenize intellectual property (IP) rights, such as patents, trademarks, and copyrights. By doing so, creators and innovators can easily license or sell fractions of their IP rights to multiple investors. Tokenizing IP ensures that ownership is clearly tracked, while tokenization infrastructure.
6. Crowdfunding and Fundraising: Tokenization has become a popular tool in crowdfunding and fundraising efforts, especially in the context of new business ventures. Startups and businesses can issue tokens to raise capital from a large number of investors, who in turn gain fractional ownership or rights associated with the project. Blockchain ensures transparency and smart contracts help streamline the distribution of funds or returns based on the token holder’s contribution.
To put it short, the use cases for on-chain tokenization are vast and varied, ranging from real estate and fine art to commodities, equity, intellectual property, and more. By leveraging the power of blockchain and tokenization infrastructure, asset fractionalization becomes possible, enabling greater access to investments, improved liquidity, and more efficient asset management. This technology is reshaping how people buy, sell, and own valuable assets across numerous industries.
Related: Real-World Asset Tokenization
Benefits of On-Chain Tokenization
On-chain tokenization offers significant advantages by leveraging blockchain technology to transform how assets are owned, traded, and managed. Key benefits include:
-
Increased Liquidity
By enabling asset fractionalization, traditionally illiquid assets like real estate or fine art can be divided into smaller, tradeable tokens, making it easier to buy, sell, and invest in them, creating more liquidity in the market.
-
Accessibility
Tokenization lowers the investment barrier, allowing more people to own a fraction of high-value assets, promoting financial inclusion, and opening up new investment opportunities.
-
Transparency and Security
Blockchain provides a transparent and immutable record of ownership and transactions. Coupled with digital asset custody solutions, tokenized assets are secured with cryptographic protection, minimizing the risk of fraud.
-
Efficiency and Automation
Smart contracts automate key processes like ownership transfers and regulatory compliance, reducing the need for intermediaries and cutting down on costs and delays.
-
Global Reach
On-chain tokenization enables assets to be traded globally, 24/7, providing asset owners with access to a broader pool of international investors, further enhancing liquidity and market opportunities.
What is Off-Chain Tokenization?
Off-chain tokenization refers to the process of representing assets as digital tokens on a blockchain but with the actual ownership and management of the asset taking place outside the blockchain. In this model, the blockchain is primarily used to track token transactions and ownership, while the legal ownership of the asset and related documentation remains stored and governed by traditional systems, such as banks, legal entities, or custodians. The tokens on the blockchain serve as a representation or certificate of ownership, but the real asset itself is not directly tied to the blockchain ledger. Off-chain tokenization is often used for assets like real estate or physical goods, where it’s challenging or impractical to store or manage everything directly on-chain.
When comparing which tokenization method is better—on-chain or off-chain—it largely depends on the use case. On-chain tokenization is more transparent and secure because all transactions and ownership data are fully recorded on the blockchain, offering immutability and reducing reliance on third parties. However, for highly regulated or complex assets, off-chain tokenization might be preferable due to the need for traditional legal frameworks to handle ownership rights, legal obligations, and regulatory compliance. While on-chain tokenization can provide more efficient and direct control over assets, off-chain models offer flexibility for dealing with real-world assets that require physical or legal oversight. Both methods have their strengths and can be suited to different industries and asset types.
Key Features of Off-Chain Tokenization
Off-chain tokenization offers a hybrid approach to managing and trading assets, combining the benefits of blockchain technology with the familiarity and regulatory compliance of traditional asset management. Below are the key features that define off-chain tokenization:
-
Asset Representation
In off-chain tokenization, tokens on the blockchain represent ownership or rights to an asset, but the asset itself—such as real estate, commodities, or securities—remains managed and stored outside of the blockchain. Legal ownership and documentation are handled by traditional systems like custodians, banks, or legal entities. This feature makes off-chain tokenization especially useful for assets that require physical or legal oversight that cannot be managed directly on a blockchain.
-
Regulatory Flexibility
One of the key advantages of off-chain tokenization is its ability to work within existing legal and regulatory frameworks. Since the assets themselves remain off-chain, organizations can adhere to local laws, industry standards, and regulatory requirements more easily than with a purely blockchain-based system. This makes off-chain tokenization an ideal choice for highly regulated industries, such as real estate, finance, or commodities, where compliance with legal systems is essential.
-
Lower Transaction Costs
Since the actual asset transfer is not recorded directly on the blockchain, off-chain tokenization can lead to lower transaction costs compared to fully on-chain solutions. This method reduces the need for high-frequency blockchain transactions, as only the token itself is transferred, while the asset remains governed by traditional contracts or entities.
-
Security and Trust
When it comes to which tokenization method is more secure, off-chain tokenization introduces a balance between blockchain security and traditional asset governance. While the blockchain provides security through cryptographic protection and an immutable ledger for token transactions, the actual asset remains governed by legal entities. This ensures that real-world processes, such as enforcing legal rights or transferring physical assets, are handled securely within existing frameworks. However, off-chain tokenization may rely more heavily on third-party custodians for security and trust, which can introduce some vulnerabilities compared to fully on-chain models.
-
Scalability
Off-chain tokenization allows for greater scalability since not every action related to the asset requires recording on the blockchain. By offloading some processes to traditional systems, it can handle a larger number of transactions without the high costs and slower transaction speeds associated with blockchain-based operations. This makes off-chain tokenization more practical for businesses that manage large volumes of assets but still want to benefit from blockchain technology for transparency and token management.
Use Cases for Off-Chain Tokenization
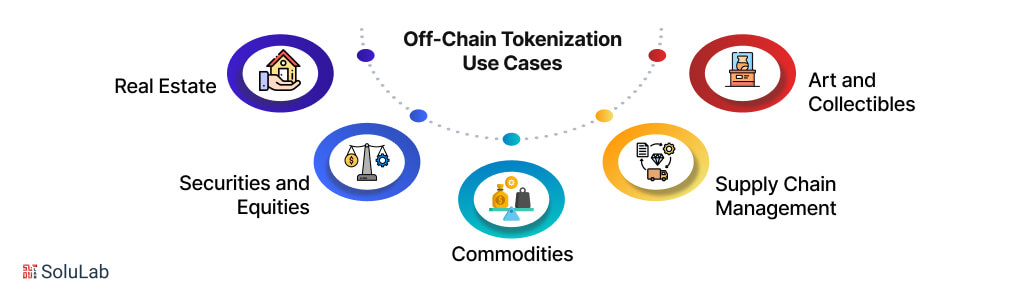
Off-chain tokenization, one of the widely used blockchain tokenization methods, is widely used in industries where physical or legal oversight is essential, but where blockchain technology can still provide efficiency and security for tracking ownership and transactions. Below are some key use cases where off-chain tokenization proves valuable:
1. Real Estate: Real estate is one of the most common applications of off-chain tokenization. High-value properties can be tokenized, allowing investors to own a fraction of a building or piece of land. While the tokens that represent ownership are traded on the blockchain, the actual property remains governed by traditional legal frameworks and custodianship. This balance allows for fractional ownership and global investor participation, while still adhering to local property laws and regulations. The tokenization infrastructure supports tracking and trading ownership through blockchain, but the actual asset management is handled off-chain, ensuring compliance with real estate laws.
2. Securities and Equities: Off-chain tokenization is also used in the securities and equities markets, where compliance with financial regulations is critical. Stocks, bonds, and other financial instruments can be tokenized, enabling faster and more secure trading of ownership. However, because of regulatory requirements around securities, the assets themselves and legal rights are managed off-chain, ensuring that they remain within the scope of the law. Token standards, such as ERC-20 for fungible tokens, are used to create and manage these digital tokens, while traditional financial systems handle actual ownership rights and dividends.
3. Commodities: Physical commodities like gold, silver, oil, or agricultural products can be represented by tokens on a blockchain while being stored and managed off-chain. Off-chain tokenization enables fractional ownership of these commodities, allowing investors to easily buy, sell, and trade shares of these assets. The tokenization infrastructure tracks the tokens on the blockchain, providing transparency, while the physical commodities remain securely stored and governed by traditional custodians. This makes it easier for smaller investors to access commodity markets while maintaining the security and stability of the underlying assets.
4. Supply Chain Management: In supply chain management, off-chain tokenization can be used to represent the ownership and tracking of goods. For example, companies can tokenize shipments or products, creating a transparent record of their movement through the supply chain. However, because the goods themselves are physical items that require real-world management, the actual logistics and transfer of goods are handled off-chain. This creates a tokenization infrastructure that improves visibility and traceability without disrupting traditional supply chain operations.
5. Art and Collectibles: Off-chain tokenization is also applicable to high-value art and collectibles. By tokenizing a piece of artwork or a collectible, fractional ownership can be distributed among multiple investors. While the tokens are traded on the blockchain, the artwork itself remains stored and managed by a custodian. This provides the security and transparency of blockchain while ensuring the physical asset remains safe and properly managed. On-chain vs off-chain tokenization, in this case, depends on whether the asset is entirely digital (which could be fully on-chain) or a physical item requiring traditional oversight (which would benefit from off-chain management).
Benefits of Off-Chain Asset Tokenization
Off-chain asset tokenization offers a unique set of benefits by combining the transparency and security of blockchain technology with the practicality of traditional asset management. This hybrid approach is particularly useful for industries that require legal oversight or physical management of assets, such as real estate, commodities, and art. Here are the key benefits of off-chain asset tokenization:
- Lower Blockchain Tokenization Costs: One of the major advantages of off-chain tokenization is the reduction in blockchain tokenization costs. Since the actual asset is managed off the blockchain, the number of transactions recorded on-chain is minimized, lowering the associated gas fees and transaction costs. This can make off-chain tokenization more cost-effective compared to fully on-chain models, especially when dealing with large or complex assets like real estate or commodities.
- Regulatory Compliance and Legal Oversight: Off-chain tokenization is ideal for industries that require adherence to strict regulatory frameworks. For example, in real estate tokenization, while the tokens representing ownership can be traded on a blockchain, the legal management and compliance of the property remain off-chain, ensuring that local real estate laws are followed. This feature allows asset owners to benefit from blockchain’s efficiency and transparency while still complying with traditional legal requirements. When comparing on-chain vs off-chain real estate tokenization, off-chain models offer greater flexibility for dealing with physical assets that require legal or regulatory management.
- Improved Scalability and Flexibility: Since the asset itself is not directly recorded on the blockchain, off-chain tokenization allows for greater scalability. This approach reduces the number of on-chain transactions required, enabling the system to handle a larger volume of assets and trades without incurring high blockchain fees or experiencing slow transaction times. This makes off-chain tokenization ideal for large-scale projects like real estate, commodities, or high-volume securities trading, where scalability and flexibility are key.
- Enhanced Security with Custodianship: With off-chain tokenization, assets are often managed by trusted custodians, ensuring that physical items like real estate, art, or commodities are securely stored and managed. While the blockchain provides transparency and security for the tokens, the physical asset remains under the protection of established legal and custodial systems. This dual approach ensures both digital and physical security, making off-chain tokenization a practical solution for high-value, tangible assets.
- Tokenization Platforms Comparison: Off-chain tokenization offers more options when it comes to choosing the right tokenization platform. Different platforms specialize in on-chain or off-chain tokenization, with off-chain models providing more flexibility for industries like real estate and art, where assets require physical management. Tokenization platforms comparison can help businesses select platforms that align with their needs, such as regulatory support, low transaction costs, and secure custodial services, all while benefiting from the transparency and efficiency of blockchain technology.
Difference Between On-Chain and Off-Chain Tokenization
The following table summarizes the key differences between on-chain and off-chain tokenization, focusing on aspects like real estate tokenization, blockchain tokenization costs, and DLT tokenization.
| Aspect | On-Chain Tokenization | Off-Chain Tokenization |
| Definition | Assets and their ownership details are fully recorded and managed directly on the blockchain. | Assets are represented as tokens on the blockchain, but the actual assets and legal rights are managed off-chain. |
| Real Estate Tokenization | Full ownership and transaction details of real estate are recorded on the blockchain. This method is best for tokenizing fully digital real estate or land that doesn’t require traditional legal systems. | Tokenized real estate is represented on-chain, but actual property ownership and legal processes remain managed by traditional entities, such as real estate firms or custodians. |
| Blockchain Tokenization Costs | Higher transaction costs due to more frequent blockchain interactions, such as gas fees and transaction processing. | Lower blockchain tokenization costs, as fewer on-chain transactions are required, with much of the asset management taking place off-chain. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Regulatory rules and compliance can be automated with smart contracts directly on the blockchain, but integrating local legal frameworks may be challenging. | Easier to integrate with existing legal and regulatory frameworks, as the asset itself is governed off-chain, allowing for compliance with real-world laws. |
| DLT Tokenization | The asset is fully integrated into Distributed Ledger Technology, with full transparency and decentralization. | Only the token representation of the asset is recorded on DLT, while the actual asset remains within traditional legal and custodial systems. |
| Security | Provides high transparency and security through blockchain immutability and decentralized verification. | Offers security through blockchain transparency for token trading, but relies on off-chain custodians for asset protection, introducing some third-party risk. |
| Liquidity and Trading | High liquidity potential, as assets, are fully tradeable on decentralized exchanges without needing third-party intermediaries. | Moderate liquidity, as the tokens can be traded on blockchain platforms, but actual asset transfers depend on off-chain legal and custodial systems. |
| Scalability | Less scalable due to high costs and slower processing speeds associated with recording all transactions on-chain. | More scalable as fewer blockchain interactions are needed, making it suitable for large-scale projects and high-volume trades. |
| Use Case Example | Ideal for fully digital assets like cryptocurrencies, digital art (NFTs), or certain tokenized financial instruments. | Best suited for physical assets like real estate, fine art, or commodities that require off-chain legal management and oversight. |
How to Choose Between On-Chain and Off-Chain Tokenization?
Choosing between on-chain and off-chain tokenization depends on asset type, security needs, regulatory requirements, and cost considerations. Here’s a quick guide:
-
Asset Type and Fractionalization
For digital assets like cryptocurrencies or NFTs, on-chain tokenization is ideal for seamless asset fractionalization and global trading. For physical assets, such as real estate, off-chain tokenization is better, allowing traditional management while still enabling token-based fractional ownership.
-
Security
On-chain tokenization offers higher transparency and security, with all transactions recorded immutably on the blockchain. For physical assets requiring custodianship, off-chain tokenization balances blockchain transparency with secure asset handling by trusted parties.
-
Regulatory Compliance
If your asset requires strict regulatory adherence, off-chain tokenization is more practical, as traditional legal frameworks can handle compliance easier than on-chain smart contracts. On-chain tokenization can automate compliance but may struggle with integrating existing legal systems.
-
Costs and Scalability
On-chain tokenization often has higher blockchain tokenization costs due to frequent transaction fees, making off-chain tokenization a more cost-effective and scalable option for large-scale projects with lower on-chain interactions.
Now you may choose on-chain tokenization for digital assets and global liquidity, and off-chain tokenization for physical assets requiring legal oversight and regulatory compliance.
How SoluLab Can Help in On-Chain and Off-Chain Asset Tokenization?
SoluLab offers end-to-end solutions for both on-chain and off-chain asset tokenization, leveraging our expertise in blockchain development to transform how assets are managed and traded. Whether you’re looking to tokenize digital assets like cryptocurrencies and NFTs or physical assets such as real estate and commodities, our asset tokenization development company can design a customized tokenization platform tailored to your needs. We provide seamless integration of smart contracts for on-chain tokenization, ensuring secure, transparent, and automated asset management. For off-chain tokenization, we develop hybrid solutions that allow for regulatory compliance and traditional asset oversight, balancing blockchain transparency with legal and custodial requirements.
Our tokenization services include developing blockchain infrastructure, ensuring asset fractionalization, integrating tokenization compliance requirements, and implementing secure digital asset custody solutions. Whether you’re exploring real estate tokenization on-chain vs off-chain or any other asset class, we provide a scalable and efficient solution. Let SoluLab guide you through the tokenization process with innovative blockchain technologies to unlock liquidity and expand your market reach. We launched Borrowland, a crypto borrowing and lending platform that enhanced traditional financial services through blockchain technology. The platform enabled users to easily borrow, lend, swap, and manage crypto assets, providing them with secure, global access and the ability to earn interest on their holdings.
Ready to transform your assets with blockchain? Contact us today to learn more about how SoluLab can help with your on-chain and off-chain tokenization needs.
FAQs
1. What is the main difference between on-chain and off-chain tokenization?
The main difference lies in how assets are managed. In on-chain tokenization, both the asset and ownership are fully recorded and managed on the blockchain. In off-chain tokenization, only the token representing the asset is on the blockchain, while the asset itself and legal ownership remain managed off the blockchain.
2. Which tokenization method is more secure: on-chain or off-chain?
On-chain tokenization typically offers more transparency and security, as all transactions are immutably recorded on the blockchain, minimizing fraud risk. However, off-chain tokenization provides security for physical assets through trusted custodians while still utilizing blockchain for transparency in token trading.
3. How does off-chain tokenization handle regulatory compliance?
Off-chain tokenization makes it easier to adhere to existing legal and regulatory frameworks because the actual asset remains governed by traditional legal systems. This flexibility ensures that assets like real estate and securities comply with local laws while using blockchain for trading the tokens.
4. What types of assets are best suited for on-chain tokenization?
On-chain tokenization is ideal for digital assets like cryptocurrencies, NFTs, and digital intellectual property, where all ownership and transactions can be securely managed on the blockchain without the need for physical oversight.
5. Which tokenization method is more cost-effective?
Off-chain tokenization is generally more cost-effective for high-volume or large-scale projects because fewer blockchain interactions are required, reducing blockchain tokenization costs. On-chain tokenization, while offering enhanced security, can have higher transaction fees due to frequent on-chain activity.






