
As a result of blockchains, a plethora of innovative technologies are emerging that have the potential to completely change the IT industry. One such outcome of the advancements made possible by blockchain technology is NFTs. The need for digital assets is growing exponentially along with the paradigm change from a conventional to an increasingly digital environment. Tokens that aren’t fungible have shown to be a significant step in this approach.
It’s crucial to remember that these tokens are referred to be “non-fungible” since, once created, they cannot be altered or replicated. Every NFT is uniquely identified with the use of smart contracts, and all relevant data is kept on a distributed ledger known as the blockchain.
Many people are interested in NFTs because of their potential. As a result, a wide range of NFT use cases across several industries, including crypto art, gaming, banking, insurance, certifications, and licensing, are being created and tested. Today, in this blog, we will go deeply into the world of NFTs and all of its important facets.
What is a Non-Fungible Token?
Now, you must be wondering what is NFT in general. Blockchain-based tokenization of assets is known as non-fungible tokenization (NFT). Tokens are distinct identifying codes generated by an encryption mechanism from metadata. These tokens are stored on a blockchain, and the assets actually are stored somewhere else. The connection between the token and the asset is what sets them apart.
NFTs are seen as an alternative investment as they aren’t fungible, or interchangeable, with other similar assets like stocks, bonds, and other conventional investments. NFTs are as same as rare collectibles They were more and more in demand in 2020 and 2021. Due to the involvement of celebrities, content providers, auction houses, and other parties in the market, the price of digital artworks increased.
History of Non-Fungible Tokens
NFTs were developed long before they gained popularity in the mainstream. Based on sources, the first NFT sold proved “Quantum,” which was created and tokenized by Kevin McKoy in 2014 on a single blockchain (Namecoin) while being coined on Ethereum and sold in 2021.
NFTs are designed in accordance with the ERC-721 (Ethereum Request for Comment #721) standard, which specifies how ownership is transmitted, mechanisms for confirming transactions, and how apps manage safe transfers, among other criteria.
The ERC-1155 standard, established six months after ERC-721, enhances on it by batching many non-fungible tokens into a single contract, lowering transaction costs.
How Do NFTs Function?
The ownership of the NFT is established using blockchain technology. Blockchain functions as a decentralized ledger, making it possible for NFTs to have public authentication. The technique verifies the originality and ownership of the work using a digital signature. Instead of owning a work of art to display on a wall, an NFT buyer receives a digital copy of the artwork together with a digital certificate of authenticity.
The item’s trademark and copyright are not owned by the NFT buyer. NFT purchasers have an original in the virtual world, notwithstanding the possibility that there are several variations available online. It is possible to build royalties into the token so that artists will eventually get paid a percentage of sales.
Because NFTs are unique, they cannot be exchanged. This is in contrast to fungible assets, which have a predetermined value and can be exchanged for other assets, including stocks, dollar notes, gold bars, Bitcoin, and other cryptocurrencies. NFTs are not interchangeable, even if it is possible to exchange one dollar note for another or one bitcoin for another with ease.
In general, NFTs are not divisible. The token, which is the fundamental unit of the NFT, is often not convertible into lower denominations, unlike dimes, which may be split into ten. However, other platforms, like Fractional, have lately introduced the concept of fractional ownership of NFTs. An NFT may be split up into smaller NFTs and sold to different customers thanks to fractional ownership.
Characteristics of Non-Fungible Tokens
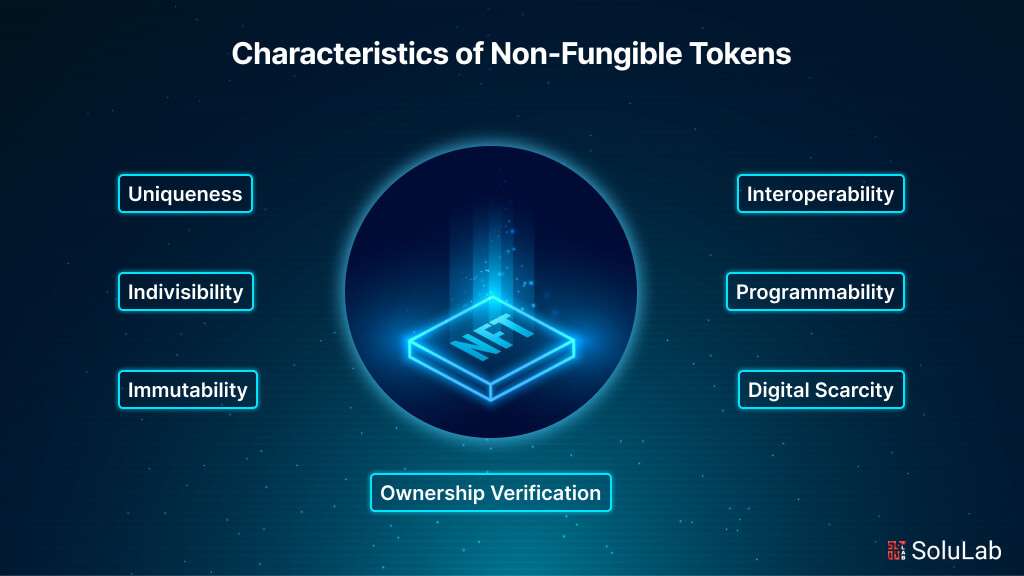
The characteristics of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) include:
- Uniqueness: Each NFT is distinct and cannot be replicated, ensuring that it represents a one-of-a-kind digital asset.
- Indivisibility: NFTs cannot be divided into smaller units like cryptocurrencies, maintaining the integrity of the digital asset they represent.
- Immutability: Once created and recorded on the blockchain, NFTs are immutable and cannot be altered or tampered with, providing a secure and transparent record of ownership.
- Ownership Verification: NFTs utilize smart contracts and distributed ledger technology to verify ownership, allowing creators and buyers to establish authenticity and provenance.
- Interoperability: NFTs can be bought, sold, and traded across different platforms and marketplaces, enabling seamless transferability of digital assets.
- Programmability: Smart contracts embedded within NFTs can include customizable rules and conditions, enabling automated processes such as royalties for creators or restrictions on resale.
- Digital Scarcity: NFTs introduce scarcity to the digital realm by creating limited editions or unique items, increasing their value and desirability among collectors and investors.
These characteristics collectively contribute to the utility and appeal of NFTs across various industries, from art and gaming to finance and digital identity.
What is NFT Marketplace?
A Non-Fungible Token (NFT) marketplace is a digital platform where users can buy, sell, and trade NFTs. These marketplaces serve as hubs for creators, collectors, and investors to interact and transact with unique digital assets represented by NFTs.
In an NFT marketplace, users can browse through a diverse range of digital items, including artwork, collectibles, virtual real estate, and more. Each item is represented by its own NFT, providing proof of ownership and authenticity. These marketplaces often feature search and discovery tools to help users find specific NFTs or explore trending collections.
One of the key features of NFT marketplaces is their support for peer-to-peer transactions. Sellers can list their NFTs for sale, setting their own prices and terms, while buyers can browse listings and make purchases directly from the platform. Some marketplaces may also facilitate auctions or bidding processes for high-value NFTs.
Additionally, NFT marketplaces often provide features to enhance the user experience and support the needs of creators and buyers. This may include integrated wallets for storing and managing NFTs, social features for connecting with other users and sharing collections, and analytics tools for tracking the performance of NFT investments.
Overall, NFT marketplaces play a crucial role in the growing ecosystem of digital assets, providing a central venue for the exchange of unique and valuable digital items powered by blockchain technology.
Read Our Blog: The Ultimate Guide to NFT Marketplace Development in 2024
Benefits of NFTs
NFTs provide a number of benefits for collectors, artists, and digital artists. Among the most significant benefits of NFTs are the following:
- Direct Monetization: With NFTs, digital artists may make money from their work without the use of galleries, auction houses, or other middlemen by selling it on online markets like Niio.
- Immutable Authenticity and Ownership: With NFTs, owners may validate the legitimacy and unchangeable ownership of a digital item. Its provenance, ownership, and transaction history are confirmed via distinctive NFT information. This guarantees that the ownership of an NFT can be quickly and simply confirmed using blockchain technology, giving owners peace of mind and trust.
- Royalties: Through NFTs, artists may include royalties into their creations, guaranteeing a portion of future revenues when the piece is resold on secondary markets. Even after the first sale, this feature allows artists to profit from the rising value of their works. Furthermore, royalties encourage collectors to help artists and further the development of the NFT marketplace ecosystem as a whole.
- Accessible Investing and Fractional Ownership: NFTs facilitate fractional ownership, allowing several people to jointly own a digital asset. Individual collectors who may not otherwise be able to buy one can participate and invest in high-value objects thanks to fractional ownership. In the NFT realm, this democratization of ownership opens up new opportunities for collectors and artists alike.
- Improved Utility and Interactivity: NFTs can include interactive components in addition to static digital data, providing collectors with a one-of-a-kind and immersive experience. Certain NFTs, for instance, provide access to special occasions, first-rate experiences, digital goods, or content associated with the artwork or collectible. This may increase the fidelity of customers.
Use Cases of the NFTs
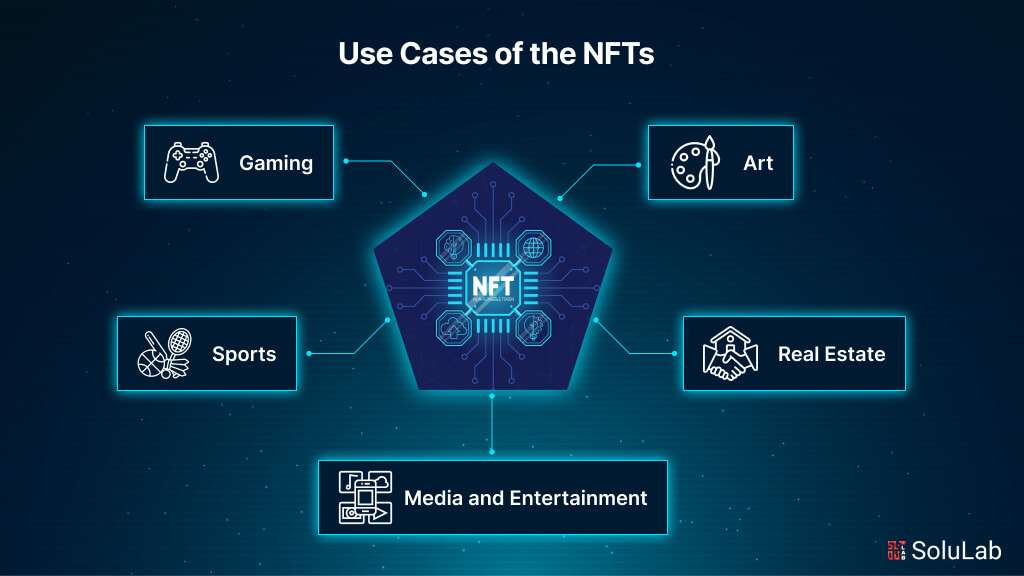
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) have exploded in popularity and brought about a wide array of potential use cases across various industries. Here are several examples of NFT use cases:
1. Gaming
The three primary market segments that make up the global gaming industry’s enormous income streams are console, mobile, and PC. In 2018, the worldwide video game business brought in 134.9 billion US dollars in sales. For a long time, the virtual economy has been growing. The staples of the worldwide gaming sector include titles like World of Warcraft and Fortnite. The primary focus of these games is still on marketplaces, currencies, and in-game objects, which players need in order to advance in the game or level up. Players may safely transfer in-game assets and offer authentication proof while using blockchain gaming. The issue of digital ownership of rare and exclusive in-game items can be resolved using NFTs. In order to influence future game improvements, users may also take part in governance.
2. Sports
In the sports sector, blockchain offers a practical way to get rid of fake tickets and goods. By utilizing NFTs, blockchain immutability prevents counterfeiting. The blockchain-issued tokenized tickets for sporting events provide an ideal application for NFTs in the sports industry. While each game gives the audience tickets that are identical to one another, each ticket has particular data about its authorized owner on the blockchain.
3. Art
Digital artists find it difficult to protect the copyright of their creations. It is feasible to fix this problem with NFTs. A work with its whole history may be purchased by a user, who can then proudly exhibit the asset in any virtual place. The copyright data may include the artist’s name, the creation date, the asset’s worth, and the names of prior owners.
4. Media and Entertainment
The entertainment business has seen a number of scams including copyright theft, content duplication, and other related issues as a result of the internet. These are problems that the entertainment business has long faced. Every movie or other work of media may now be linked to the blockchain as an NFT thanks to the development of blockchain technology and NFTs. NFTs may aid in preventing unauthorized file sharing or copying in this manner. Since NFTs offer origin verification, they are also utilized to eradicate false information.
5. Real Estate
Real-world assets, like as real estate, are tokenized on the blockchain with the use of NFTs. Without the assistance of a third party, it would guarantee seamless transactions when purchasing or selling homes. Conflicts about the ownership of lands or other assets won’t be possible with NFTs.
Read Blog: Best Real-World Use Cases of NFT Marketplace
What Makes NFTs Important?
Non-fungible tokens are becoming quite popular, and there are a few reasons why using them is crucial. NFTs provide a number of benefits in addition to resolving persistent problems with large enterprises.
- No Intermediary: The effectiveness of NFTs in cutting out middlemen and simplifying procedures is one of the main advantages. Direct communication between buyers and creators allows for more openness and a more robust relationship.
- Unique Identity: Every NFT generated is guaranteed to have a unique identifier thanks to smart contracts. Furthermore, tracking all associated data with a physical item while preserving its scarcity is facilitated by tokenizing it.
- Multiple Ownership: In terms of democratizing the digital asset market, NFTs are the most effective. Different people may now hold non-fungible tokens thanks to the fractionalization of NFTs, which benefits both purchasers and producers by giving them the ability to resell those partially held digital assets.
The Rising Acceptance of NFT Marketplaces
Non-fungible tokens provide a wide range of applications and advantages that save companies money on fraud detection, copyright problems, fake goods, and personnel handling personal and private data. NFTs have also gained a lot of popularity among digital artists, game publishers, luxury brands, and other providers of digital material as digital evidence of ownership. They are reaching out to the international market using NFTs in order to increase the monetization of their artwork. The need for NFT markets as a venue for NFT trade has grown along with NFTs’ increasing global popularity.
The NFT Marketplace’s Business Strategy
The business concept is based on commissions. NFT owners—mostly cryptocurrency enthusiasts, game producers, and digital artists—sell their NFTs in an NFT marketplace. Digital assets such as music, films, gifs, in-game goods, artwork, and other collectibles are represented by NFTs, which are tokens based on blockchain technology. These assets are verified as owned by NFTs, and NFT owners are able to trade them in an NFT marketplace for a cryptocurrency.
Regarding NFTs, there are two approaches. Let’s say you are a fan of cryptocurrencies or digital art. If so, you may create an NFT to represent your digital asset, use it to trade NFTs, and copyright your ownership. Then, by starting their own NFT markets, startups, entrepreneurs, or interested businesses may also become owners of NFT marketplaces. By setting up their own marketplace, companies may sell NFTs to users directly. Additionally, marketplace owners receive hefty commissions each time an NFT owner sells an NFT through their well-trafficked NFT marketplace.
Final Words
With their quick trading, non-fungible tokens have taken the globe by storm and caused NFT marketplaces to flourish. They are shown to be beneficial for both artists and art collectors. Users are making enormous profits while taking advantage of a variety of privileges. They also provide authors access to fresh revenue streams and distribution networks. A greater portion of the value derived from artists’ labor is now available to them. NFTs create a strong community by uniting like-minded individuals and defining the genuine worth of digital assets. NFTs will be a ubiquitous technology with a considerably larger following than they have at the moment.
At SoluLab, as a well-known NFT development company, we understand the power of NFTs and offer expert solutions for businesses looking to harness their potential. Our team of skilled NFT developers is equipped to guide you through every step of the development process, from conceptualization to implementation. Whether you’re looking to tokenize assets, create a marketplace, or integrate NFTs into your existing platform, we’re here to help. Contact us today to hire NFT developers and take your business to the next level with this transformative technology.
FAQs
1. What exactly is a Non-Fungible Token (NFT)?
A Non-Fungible Token (NFT) is a unique digital asset that is stored on a blockchain and represents ownership of a specific item or piece of content. Unlike cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, which are interchangeable and identical, each NFT has its own distinct value and properties, making it one-of-a-kind and non-interchangeable.
2. How can businesses benefit from using NFTs?
Businesses can benefit from NFTs in various ways, including monetizing digital assets, enhancing brand engagement, and creating new revenue streams. For example, artists can tokenize their artwork and sell it as NFTs, while gaming companies can offer rare in-game items as collectibles. Additionally, NFTs can be used to verify ownership of digital assets, create limited editions or exclusives, and foster community participation through tokenized governance.
3. Are NFTs secure and tamper-proof?
Yes, NFTs are secured by blockchain technology, which ensures that ownership records are transparent, immutable, and tamper-proof. Each NFT is uniquely identified and stored on a decentralized ledger, making it virtually impossible to counterfeit or alter ownership records. This level of security and authenticity is one of the key benefits of using NFTs for digital asset management.
4. How can businesses integrate NFTs into their existing operations?
Businesses can integrate NFTs into their existing operations by partnering with blockchain developers or NFT development companies. These experts can help businesses tokenize their assets, create NFT marketplaces, and implement smart contracts to automate transactions and enforce ownership rights. By leveraging NFT technology, businesses can unlock new opportunities for monetization, engagement, and innovation.
5. What industries are currently leveraging NFTs?
NFTs are being adopted across various industries, including art, gaming, collectibles, real estate, and entertainment. Artists are selling digital artwork as NFTs, gaming companies are offering rare in-game items, and real estate developers are tokenizing property ownership. Additionally, NFTs are being used in sports memorabilia, music royalties, virtual fashion, and more. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more industries leveraging the unique benefits of NFTs.






