Industry analytics group DappRadar found that 312 hacks and vulnerabilities affected dApps in 2022, leading to losses of around $48 billion. Financial losses decreased by 96% to $1.9 billion in 2023, but the frequency with which hacks and exploits were used increased by 17.3%. In the first quarter of 2024, losses increased by 9% to $407 million compared to Q1 2023’s $373 million.
DApp development, on the other hand, came into play with the emergence of blockchain technology and Peer-to-peer (P2P) file sharing. Most startups today are coming up with decentralized software that utilizes the native properties of blockchain and offers a secure and transparent operational environment for businesses.
What Are Decentralized Applications (dApps)?
Decentralized applications, commonly known as dApps, are innovative software programs that operate on a blockchain or a peer-to-peer (P2P) network of computers, rather than being confined to a single device. Unlike traditional applications controlled by a central authority, dApps are distributed across the network, enabling their users to collectively govern them. Often developed on the Ethereum platform, dApps encompass a wide range of applications, including secure wallets, digital asset exchanges, captivating games, personal finance management tools, and immersive social media experiences.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Decentralized applications (dApps) are digital applications that operate on a blockchain network of computers rather than relying on a single centralized server.
- DApps are not subject to the control or interference of any single authority, ensuring greater autonomy and independence.
- The advantages of dApps include enhanced user privacy protection, resistance to censorship, and increased flexibility in development.
- Potential challenges associated with dApps include scalability limitations, user interface development complexities, difficulties in making code modifications, and potential security vulnerabilities.
Understanding Decentralized Applications (dApps)
In contrast to web applications like Uber or X (formerly Twitter), which are run on a centralized computer system owned and controlled by a single company, DApps (Decentralized applications) operate on a peer-to-peer (P2P) or blockchain network.
Examples of P2P applications include BitTorrent, Tor, and Popcorn Time, which run on computers that are part of a P2P network, allowing multiple participants to consume, feed, or seed content.
DApps, on the other hand, run on a blockchain network in a public, open-source, and decentralized environment. This means that they are free from the control and interference of any single authority.
For instance, a developer can create a decentralized application similar to X and deploy it on a blockchain where any user can publish messages. Once a message is posted, it cannot be deleted by anyone except the original author, ensuring the immutability and transparency of the data.
Difference Between a Centralized and Decentralized Apps
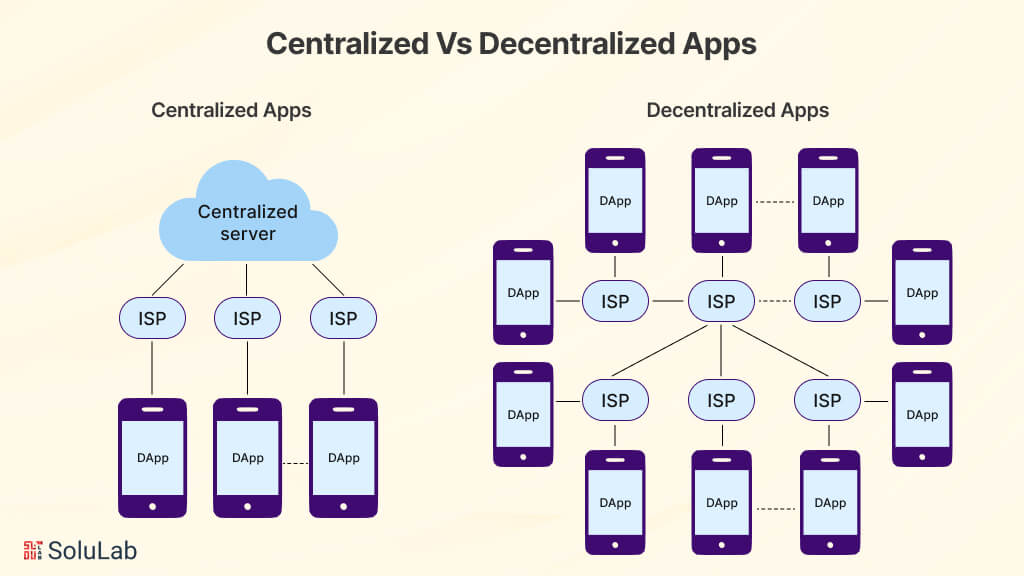
Before we into how dApps function differently from regular mobile or desktop apps, let’s first clarify some key concepts.
Centralized App:
- Owned by a single entity.
- Application software resides on servers controlled by the owner.
- Users download a copy of the app and interact with it, sending and receiving data to and from the company’s server.
Decentralized App (dApp):
- Operates on a blockchain or peer-to-peer network of computers.
- Users engage in transactions directly with each other without relying on a central authority.
- May be free or require payment to the developer in cryptocurrency to download and use the source code.
- Source code often utilizes smart contracts, which automatically execute transactions between parties, eliminating the need for trust.
- dApps rely on blockchain protocols that safeguard personal information.
Importance of dApps
There are several dApp features that can dramatically change the facilitation of information or resources.
1. Cost and Efficiency
Due to their operation on decentralized networks, Decentralized applications (dApps) eliminate the requirement for intermediaries. This can result in substantial cost reductions, enhanced efficiency, and broader accessibility. Picture having almost complete control over every aspect of your finances without relying on a bank, for instance. This has the potential to have a significant impact on a variety of industries, particularly the financial sector. When comparing dApps vs apps, the distinction becomes clear: dApps offer a decentralized, transparent, and secure alternative to traditional applications. As industries continue to evolve, embracing the benefits of dApps will be crucial. Companies like SoluLab are at the forefront of this revolution, providing expertise and solutions to leverage the full potential of decentralized applications.
2. Security
By utilizing blockchain technology, decentralized applications (dApps) can enhance the security of various business and personal processes. Blockchains employ cryptographic techniques and distributed automated consensus mechanisms to make data immutable. The shared and compared ledger across all users ensures that data remains unalterable, providing a robust foundation for secure transactions and data storage. When comparing apps vs dApps, it’s evident that dApps offer superior security features due to their decentralized and transparent nature, making them a compelling choice for secure business and personal applications.
3. Accessibility
DApps examples are universally accessible to anyone with an internet connection, regardless of geographic location. This global reach enables individuals worldwide to access various services, digital assets, and information. This democratization of access empowers individuals, fostering inclusivity and allowing them to participate in a globally connected digital ecosystem.
4. Transparency
In blockchain-based decentralized applications (dApps), transactions are recorded transparently, allowing users to verify data integrity without relying on centralized authorities. This transparency is essential for anonymous and distributed networks because users must trust the system’s trustworthiness.
DApp Uses
To eliminate intermediaries and decentralize various functions and applications, decentralized applications (DApps) have been developed. Self-executing financial contracts, multi-user games, and social media platforms are a few decentralized applications examples.
Additionally, DApps have been created to enable secure, blockchain-based voting and governance systems. They can even be incorporated as plugins into web browsers to serve ads, monitor user behavior, or request cryptocurrency donations. This integration allows for increased security and transparency in online activities.
Some decentralized applications examples of practical uses include:
- Financial Transactions: Facilitating peer-to-peer monetary exchanges and asset transfers, such as currency conversions or the movement of stocks.
- Supply Chain Tracking: Ensuring transparency and accountability by tracking the movement of goods throughout the supply chain.
- Identity Verification: Securely storing and validating personal information, including voter rolls and passport applications.
- Real Estate Management: Enabling direct property transactions between buyers and sellers, while tracking property ownership and documentation like deeds.
- Healthcare Records: Storing and monitoring medical records, as well as facilitating communication among healthcare professionals.
- Education Platforms: Creating decentralized platforms for learning, where students and educators can collaborate without intermediaries.
- Decentralized Social Media: Establishing decentralized platforms for social interaction and content sharing, free from censorship by central authorities.
- Predictive Markets: Introducing decentralized platforms for predictive markets, enabling users to make bets on future events.
Scams Involving dApps
Malicious activities have been carried out through decentralized applications (dApps). Ponzi schemes, where early investors receive payments funded by investments from newer investors, creating an illusion of substantial profits, have been known to operate on dApps. Understanding what are decentralized apps and their functionalities can help users recognize and avoid such schemes.
Deceptive initial coin offerings (ICOs) have been employed to raise funds for purportedly developing a new cryptocurrency or dApp, with no genuine intention of fulfilling these promises by the fundraisers. Knowing what is a decentralized application and how it should legitimately operate can protect investors from falling prey to such fraudulent activities.
dApps have been targeted by phishing attacks, which employ deceptive websites or emails to deceive users into disclosing sensitive data. Some dApps examples have also been exploited to spread malware or viruses, endangering users’ devices and stealing personal information. Understanding what are dapps used for and their legitimate applications can help users navigate the ecosystem more safely.
Given the decentralized nature of dApps, it can be challenging to identify and hold the perpetrators responsible, emphasizing the need for users to exercise caution and conduct thorough research before engaging with any dApps.
Do you Know?
Industry analytics group DappRadar found that 312 hacks and vulnerabilities affected dApps in 2022, leading to losses of around $48 billion.
Financial losses decreased by 96% to $1.9 billion in 2023, but the frequency with which hacks and exploits were used increased by 17.3%.
In the first quarter of 2024, losses increased by 9% to $407 million compared to Q1 2023’s $373 million.
Advantages and Disadvantages of dApps
Before we dive into the pros and cons of decentralized applications (dApps), it’s essential to understand that they have unique advantages and disadvantages due to their decentralized nature.
Advantages
- DApps offer significant advantages, particularly in safeguarding user privacy. They utilize smart contracts to facilitate transactions between anonymous parties, ensuring the privacy and security of personal information.
- DApps have the potential to revolutionize social media platforms. Decentralized social media platforms built on dApps are resistant to censorship, as no single entity has the power to delete or block messages on the blockchain, promoting freedom of expression.
- Ethereum serves as a versatile platform for Decentralized application development. It provides the necessary infrastructure for developers to concentrate on creating innovative digital applications. This could lead to the rapid deployment of dApps in various industries, such as banking and finance, gaming, social media, and online shopping.
Do you Know?
While a graduate student at the University of Washington, American cryptographer and computer scientist Nick Szabo coined the term “smart contract” in 1996.
Disadvantages
- DApps, being in their early experimental stages, face various challenges and uncertainties. Concerns arise regarding their ability to scale effectively. Additionally, overloading a network due to numerous resource-intensive applications can result in congestion.
- Creating a user-friendly interface for dApps is crucial. Traditional centralized applications have set an ease-of-use standard that encourages user interaction. To attract users to dApps, developers must create an end-user experience and performance level comparable to established programs.
- Unlike centralized applications, dApps lack the oversight and auditing typically present. Rushed, unaudited, or sloppy programming makes dApps examples vulnerable to hacking.
- Post-deployment, ongoing changes to enhance, correct bugs, or address security risks are likely to be necessary for dApps. However, Ethereum highlights the challenge developers face in updating dApps due to the immutability of data and code published to the blockchain.
Read Also: Build a dApps on Solana
Regulatory Considerations for dApps
Regulators face a significant challenge in regulating decentralized applications (dApps) due to their decentralized nature. Conventional regulatory approaches typically rely on specific geographic locations. However, since dApps do not have a centralized structure, it becomes more complex to regulate activities based solely on the location where transactions occur.
The Emerging Centralization of dApps
In the European Union, Decentralized Applications Dapps providers who serve the EU audience must comply with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). This applies regardless of where the company is based.
In December 2023, a European subnet of the Internet Computer Protocol (ICP) was launched. ICP is a blockchain DAO that provides an infrastructure and tools for developers to create compliant dApps. While this could become the standard way of ensuring compliance, it would mean that the apps would lose their decentralized standing because the ICP is centralized. Nodes must be voted in by the DAO and can only be located in the EU.
Some dApps issue tokens or conduct token sales to raise money. This may raise regulatory concerns because authorities are working to protect investors. Regulators view this as an unregistered securities issuance. Similarly, dApps involved in financial services, such as decentralized exchanges (DEXs) or lending platforms, must adhere to anti-money laundering and know-your-client regulations to prevent money laundering and terrorist financing.
Consumer Protection
Even if there is no direct exchange of money or goods, the use of dApps still involves consumer protection concerns. This includes safeguarding personal data, privacy, and security. Users who agree to transactions by signing their signatures put themselves at risk. Platforms like MetaMask caution users that they could lose funds if they are not fully aware of the implications of their actions when using decentralized applications (dApps).
Dapps examples
One popular example of a dApp is CryptoKitties, a blockchain-based virtual game that enables players to adopt, raise, and trade virtual cats. Each CryptoKitty is unique, owned by the user, and validated through the blockchain, like other tradable assets. Its value can be appreciated or depreciated based on the market. CryptoKitties are considered “crypto collectibles” because each digital pet is one-of-a-kind and verified on a blockchain.
Another noteworthy dApp is Uniswap, a decentralized exchange protocol built on Ethereum. Uniswap allows users to trade directly with each other without relying on an intermediary like a bank or broker. This dApp utilizes automated smart contracts to establish liquidity pools that facilitate trades. Users can trade their tokens directly from their wallets, providing a seamless and secure trading experience. Again, the decentralized nature of the application makes Uniswap’s existence possible.
These decentralized applications examples illustrate the potential of dApps to disrupt traditional industries and provide users with greater control over their assets and data. As technology advances, we can expect to see even more innovative and transformative dApps emerge in the future.
The Bottom Line
In conclusion, understanding what are dApps reveals the transformative potential of decentralized applications in various industries. Unlike normal apps, dApps operate on blockchain networks, providing enhanced security, transparency, and decentralization. The comparison of dApps vs apps highlights significant differences, especially in terms of control and data integrity. Knowing what are decentralized apps and what is a decentralized application helps in recognizing their applications, from finance to gaming, as demonstrated by several decentralized applications examples. If you’re exploring what are dApps used for or are interested in what are dApps crypto, SoluLab offers expertise in developing decentralized applications (dApps) to leverage these innovations for your business needs. Partner with SoluLab to harness the full potential of dApps and stay ahead in the evolving digital landscape.
FAQs
1. What are dApps?
dApps, or decentralized applications, are software programs that run on a blockchain network instead of a centralized server, offering enhanced security and transparency.
2. dApps vs Apps: What’s the Difference?
Unlike normal apps, which run on centralized servers, Decentralized Applications Dapps operates on a decentralized blockchain, providing benefits such as improved security, transparency, and resistance to censorship.
3. What are decentralized apps used for?
Decentralized apps (dApps) are used for various purposes, including decentralized finance (DeFi), gaming, social media, and supply chain management, all leveraging blockchain’s decentralization benefits.
4. What is a decentralized application?
A decentralized application (dApp) is software that interacts with a blockchain network, ensuring that the app operates without a central point of control or failure.
5. What are some decentralized applications (dApps) examples?
Decentralized Applications Examples include Ethereum-based DeFi platforms like Uniswap, decentralized storage solutions like IPFS, and blockchain-based games like CryptoKitties.
6. What are dApps in crypto?
In the crypto space, dApps refers to applications built on blockchain networks that use cryptocurrencies for transactions and smart contracts for automated, trustless operations.





