
In an era defined by digital transformation and the relentless pursuit of efficiency, the fusion of two groundbreaking technologies is reshaping the way we connect, communicate, and conduct business. The Internet of Things (IoT), a network of interconnected devices, sensors, and systems, has rapidly evolved from a futuristic concept to a fundamental pillar of modern industry. In parallel, smart contracts, the self-executing, tamper-proof agreements rooted in blockchain technology, have sparked a revolution in how we conduct transactions and automate processes.
The convergence of these two technological powerhouses—IoT and smart contracts—opens up a world of possibilities, promising to revolutionize the way we manage, secure, and leverage IoT networks. By seamlessly integrating smart contracts into IoT ecosystems, we empower devices to make autonomous decisions, streamline data exchange, and minimize the need for intermediaries.
In this blog, we embark on a journey to explore the synergy between Smart Contracts and Internet of Things. We’ll delve into the core concepts, examine the real-world applications, dissect the challenges and considerations, and peer into the promising future where the marriage of these technologies will continue to redefine industries. Whether you’re a technology enthusiast, a business leader, or simply curious about the future of interconnected devices, this blog will shed light on the exciting fusion of Smart Contracts and IoT that is driving the next wave of innovation.
So, let’s dive in and discover how this dynamic duo is reshaping the way devices communicate, transact, and evolve in our increasingly interconnected world.
Understanding IoT and its Applications
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a transformative technology paradigm that represents the interconnection of everyday objects and devices to the internet. It’s about enabling these objects to collect, transmit, and exchange data, thereby extending their functionality beyond their original design and transforming them into “smart” devices.
At the heart of IoT are sensors, embedded systems, and communication technologies that allow devices to gather and share data. These devices can be as varied as household appliances, industrial machines, vehicles, wearable gadgets, environmental sensors, and even entire smart cities.
Read Our Blog: Top 10 Smart Contract Development Companies in 2023
Applications of IoT in Different Fields
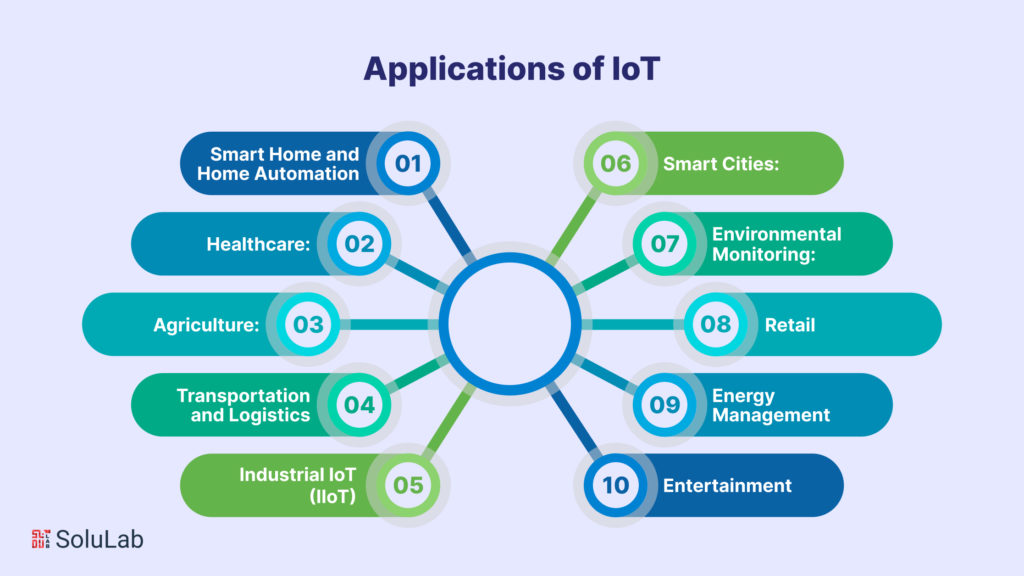
- Smart Home and Home Automation: IoT enables homeowners to control and automate various aspects of their homes, including lighting, heating, security systems, and appliances. Smart speakers and connected thermostats are examples of popular IoT devices in this context.
- Healthcare: IoT is revolutionizing healthcare through wearable devices like fitness trackers and smartwatches, which can monitor vital signs, track physical activity, and transmit health data to healthcare providers. Additionally, IoT is used for remote patient monitoring and medication adherence.
- Agriculture: IoT plays a vital role in precision agriculture. Sensors in the field measure soil conditions, weather, and crop health, allowing farmers to make data-driven decisions about irrigation, fertilization, and pest control, ultimately improving crop yields and sustainability.
- Transportation and Logistics: In the logistics and transportation industry, IoT is used for real-time tracking of goods, vehicle maintenance, and route optimization. It enhances supply chain efficiency and provides consumers with accurate delivery information.
- Industrial IoT (IIoT): In manufacturing and industrial settings, IoT devices and sensors monitor equipment, predict maintenance needs, and optimize production processes. This leads to increased productivity, reduced downtime, and cost savings.
Read Also: Top IoT Development Companies 2023
- Smart Cities: Smart city initiatives utilize IoT for various applications, including traffic management, waste management, energy efficiency, and public safety. Sensors and data analysis enable city planners to create more sustainable and livable urban environments.
- Environmental Monitoring: IoT helps monitor and combat environmental issues. For example, it’s used in weather forecasting, air and water quality monitoring, and early detection of natural disasters.
- Retail: In the retail industry, IoT is used for inventory management, personalized marketing, and improving the shopping experience. Smart shelves, beacons, and customer tracking systems are common IoT applications.
- Energy Management: IoT plays a critical role in energy conservation and management. Smart meters and home energy management systems help consumers monitor and reduce their energy consumption.
- Entertainment: IoT is integrated into entertainment systems, such as smart TVs and streaming devices, to provide a more personalized and interconnected media experience.
The applications of IoT are diverse and continue to expand into new domains as technology evolves. Its ability to gather and analyze data from various sources in real time empowers businesses and individuals to make informed decisions, automate processes, and enhance their quality of life. This transformative IoT development technology is at the forefront of the digital revolution, ushering in an era where virtually everything is connected and communicating.
Understanding Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are a fundamental component of blockchain technology that enable automated, self-executing agreements. These digital contracts have gained significant attention and have the potential to revolutionize various industries. To understand smart contracts better, let’s break down the concept and their key attributes:
- Smart contracts are self-executing computer programs that automatically enforce and execute the terms of an agreement when predefined conditions are met.
- They are designed to eliminate the need for intermediaries, such as banks or legal entities, by facilitating trust through code and cryptography.
Check Our Blog Post: Ultimate Checklist For Smart Contract Audit
How Do Smart Contracts Work?
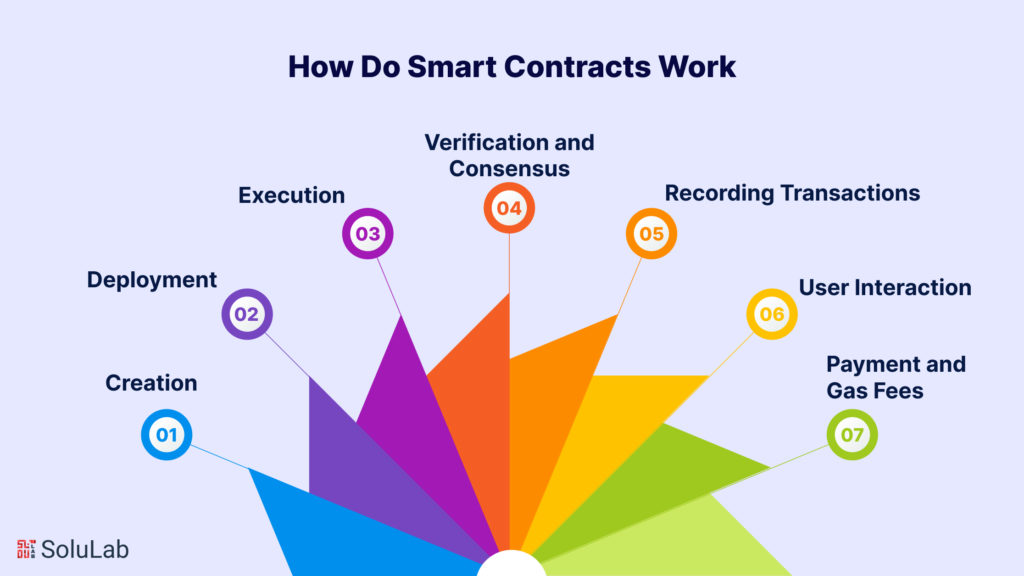
Smart contracts are self-executing digital agreements that run on blockchain technology. They work by automating the execution and enforcement of predefined conditions and actions without the need for intermediaries. To understand how smart contracts work, let’s break down the process:
Creation
- Smart contracts are created using programming languages specifically designed for blockchain platforms. For example, Ethereum, one of the most popular blockchain platforms for smart contracts, uses a language called Solidity.
- The contract’s terms and conditions are coded into the smart contract. These terms can cover various agreements, such as financial transactions, supply chain operations, legal agreements, and more.
Deployment
- Once the smart contract is coded and tested, it is deployed onto a blockchain platform. The most common platform for smart contracts is Ethereum, although others like Binance Smart Chain, Cardano, and Polkadot also support them.
- The smart contract is stored on the blockchain, and its code becomes immutable, meaning it cannot be altered once deployed. This immutability ensures that the terms of the contract remain tamper-proof.
Execution
- Smart contracts rely on predefined conditions, also known as “if-then” statements. These conditions are specified in the contract’s code.
- When the conditions are met, the smart contract self-executes without the need for human intervention. For example, if the contract is a payment agreement, the contract will automatically release the payment to the specified recipient when the conditions are fulfilled.
Verification and Consensus
- Smart contracts run on a decentralized network of computers (nodes) that validate and record transactions. These nodes reach consensus to ensure the accuracy of transactions.
- Once a transaction triggers a smart contract, it is broadcast to the network for validation. The majority of nodes on the network must agree that the transaction is valid for it to be added to the blockchain.
Recording Transactions
- All transactions related to a smart contract are recorded on the blockchain. This creates an immutable and transparent ledger of all activities associated with the contract.
- Users can access the blockchain to verify transactions and view the contract’s history, providing a high level of transparency and security.
User Interaction
- Users interact with smart contracts by sending transactions to the contract’s address on the blockchain. These transactions include data and instructions.
- The smart contract processes these interactions according to its predefined code.
Payment and Gas Fees
- In most blockchain networks, including Ethereum, executing smart contracts requires a fee known as “gas.” Gas fees are paid in cryptocurrency and cover the computational resources needed to execute the contract.
- For example, when you send a transaction to a smart contract, you’ll need to include a certain amount of cryptocurrency to cover the gas fees.
In summary, smart contracts work by encoding the terms and actions of an agreement into self-executing, tamper-proof code. They are deployed on a blockchain network, where they automatically execute when predefined conditions are met. This automation eliminates the need for intermediaries, enhances security, and increases the efficiency and transparency of agreements and transactions.
The Convergence of Smart Contracts and IoT
The convergence of Smart Contracts and the Internet of Things (IoT) represents a powerful synergy that has the potential to transform how devices interact and exchange data in a highly efficient and secure manner. In this discussion, we explore the exciting intersection of these two cutting-edge technologies and the possibilities it presents:
1. Automation of IoT Processes
- The role of Smart contracts in IoT devices is to interact autonomously, executing predefined actions based on specific conditions or triggers. For example, a smart thermostat could automatically adjust the temperature when it senses occupancy or receives weather data.
2. Decentralized Decision-Making
- IoT devices are often distributed across a network, and smart contracts operate in a decentralized blockchain environment. This decentralization ensures that decision-making and data exchange can occur without a central authority, enhancing the trust and reliability of IoT systems.
3. Improved Security
- Smart contracts bring a layer of security to IoT. Transactions and interactions between IoT devices are recorded on a tamper-proof blockchain, reducing the risk of data tampering or hacking.
Read Our Blog: Creating the Next Decentralized Application: A Step-by-Step Blockchain Development Guide
4. Supply Chain and Asset Management
- IoT sensors can be integrated with smart contracts to automate supply chain processes. For instance, a shipment can trigger payments automatically as it reaches predefined checkpoints, providing transparency and efficiency in logistics.
5. Conditional Access Control
- Smart contracts in IoT can enforce access control based on certain conditions. For instance, access to a secure facility can be granted only if a person has a specific biometric reading on their IoT device.
6. Cost Reduction and Efficiency
- Through automation and the elimination of intermediaries, the intersection of Smart Contracts and IoT can significantly reduce operational costs and increase efficiency across various industries, such as agriculture, healthcare, and manufacturing.
Benefits of Combining Smart Contracts and IoT
The pros of Smart Contracts in IoT hold tremendous potential and offer a wide array of benefits across multiple industries. This synergy brings about efficiencies, security, and innovative solutions that have the capacity to revolutionize the way we interact with devices and manage data. Here are some of the key benefits of combining Smart Contracts and IoT:
- Efficiency and Automation: Smart Contracts automate processes in IoT. Devices can interact and execute actions autonomously based on predefined conditions, reducing the need for manual intervention. This leads to increased operational efficiency.
- Cost Reduction: Automation and the elimination of intermediaries lead to cost savings. For example, in supply chain management, smart contracts can streamline processes, reducing administrative and logistics costs.
- Enhanced Security: Data integrity and security are improved through the use of blockchain technology. Smart Contracts ensure that transactions and data exchanges are tamper-proof and transparent, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
Check Our Blog Post: How Do Smart Contract Applications Actually Work
- Trust and Transparency: The decentralized nature of Smart Contracts and IoT interactions enhances trust among stakeholders. Transactions and actions are recorded on the blockchain, providing transparency and auditability.
- Conditional Access Control: Smart Contracts can enforce access control based on specific conditions. For instance, IoT devices can grant access to secure facilities only if certain criteria are met, enhancing physical security.
- Real-time Data and Decision-making: IoT devices provide real-time data, and smart contracts can process this data instantaneously. This enables rapid decision-making and the ability to respond to changing conditions in real time.
Challenges and Concerns in Combining Smart Contracts and IoT
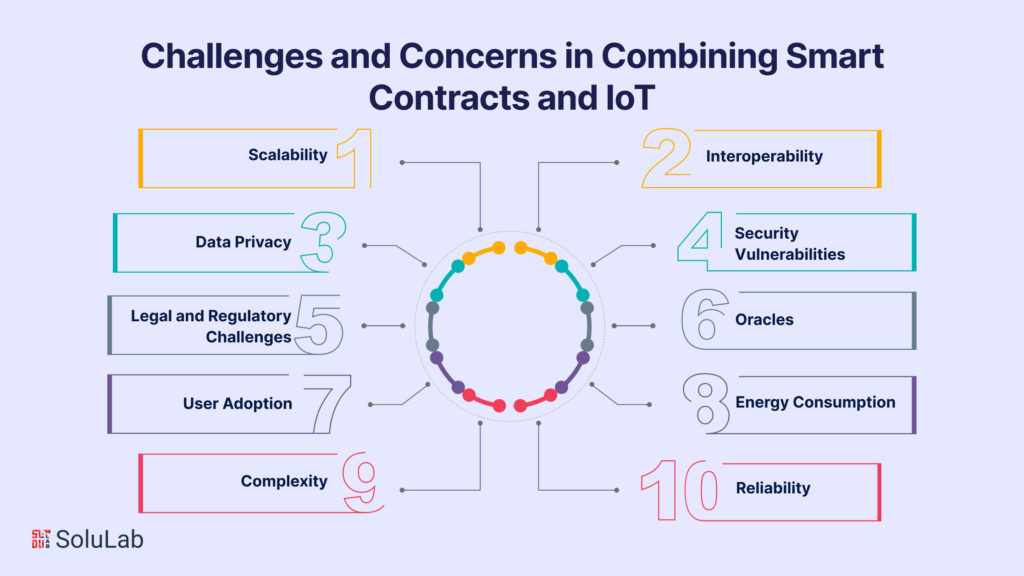
While the convergence of Smart Contracts and the Internet of Things (IoT) offers numerous benefits, it also presents several challenges and concerns that need to be addressed for successful implementation. Here are some of the key challenges and concerns in combining these two transformative technologies:
- Scalability: As IoT networks expand and the number of devices increases, scalability becomes a significant concern. Ensuring that the blockchain network can handle a growing volume of transactions and smart contracts is a technical challenge.
- Interoperability: IoT devices often use different communication protocols and standards. Ensuring compatibility and interoperability between these devices and blockchain platforms can be complex.
- Data Privacy: Smart Contracts on a public blockchain are inherently transparent, and this transparency may conflict with data privacy regulations, especially in sensitive sectors like healthcare. Striking a balance between transparency and data privacy is a concern.
- Security Vulnerabilities: While blockchain technology enhances security, it is not immune to vulnerabilities. Smart contracts are at risk of exploitation if not coded and audited correctly. IoT devices can also be vulnerable to cyberattacks, and combining them with smart contracts introduces additional risks.
- Legal and Regulatory Challenges: The legal and regulatory landscape for Smart Contracts and IoT is still evolving. Compliance with existing and emerging regulations can be complex, particularly in industries like finance, healthcare, and transportation.
Read Also: Importance of Economic & Game Theory Audits in Smart Contracts
- Oracles: Smart Contracts require real-world data to function effectively, which is provided by oracles. The accuracy and reliability of oracles are crucial, and there is a need to address the trustworthiness of data sources.
- User Adoption: The integration of these technologies may require changes in user behavior and business processes. Achieving user adoption and ensuring that users can effectively interact with these systems is a significant concern.
- Energy Consumption: Many blockchain networks, such as Ethereum, rely on energy-intensive consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work. This can raise concerns about the environmental impact and sustainability of such systems, particularly when applied to IoT devices with limited power resources.
- Complexity: Combining Smart Contracts and IoT can introduce a level of complexity that may be challenging for developers, businesses, and end-users to navigate and manage.
- Reliability: The reliability of IoT devices can vary, and not all devices are created equal. Ensuring that smart contracts can trust the data generated by these devices and the actions they take is a concern.
Future Trends and Developments in the Intersection of Smart Contracts and IoT
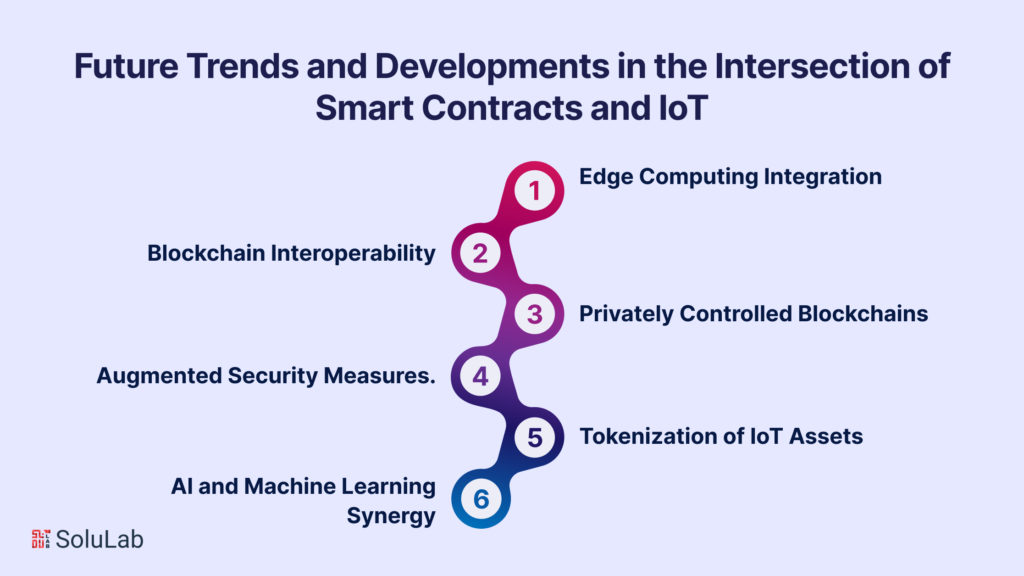
The intersection of Smart Contracts and the Internet of Things (IoT) is a dynamic space, poised to lead technological advancements and redefine how industries, businesses, and individuals interact with the digital and physical worlds. As these two transformative technologies continue their journey of innovation, a host of compelling future trends and developments is set to emerge, shaping the course of automation, connectivity, and data management in the years ahead.
- Edge Computing Integration: The fusion of Smart Contract development services and IoT will see seamless integration with edge computing, enabling real-time data processing and decision-making closer to the data source. This promises to reduce latency and enhance responsiveness in IoT applications, especially in scenarios where instant decisions are crucial.
- Blockchain Interoperability: The evolution of blockchain technology will witness a greater emphasis on interoperability, enabling diverse blockchains to communicate and collaborate. This blockchain trend will provide flexibility in selecting the most suitable blockchain platform for specific IoT applications, taking into account factors such as scalability, privacy, and consensus mechanisms.
- Privately Controlled Blockchains: Private and consortium blockchains will become more prominent for IoT use cases, catering to industries where data privacy and control are paramount. These blockchains offer a secure and flexible environment for businesses and consortia to leverage Smart Contracts and IoT without compromising sensitive information.
- Augmented Security Measures: The integration of advanced cryptographic techniques, secure hardware, and innovative security protocols will be at the forefront of Smart Contracts and IoT. This ongoing development will not only bolster the security of transactions and data exchanges but also address potential vulnerabilities, ensuring the trust and integrity of these systems.
- Tokenization of IoT Assets: IoT devices and their associated data may be tokenized, creating a digital representation of physical and digital assets. This opens the door to efficient management and monetization, enabling new business models and decentralized marketplaces for IoT-specific tokens.
- AI and Machine Learning Synergy: Artificial intelligence and machine learning will be seamlessly integrated with Smart Contracts and IoT, empowering devices to make informed, data-driven decisions. This convergence will facilitate advanced data analysis, enabling devices to adapt and optimize their functions based on patterns and real-time data.
Conclusion
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, the convergence of Smart Contracts and the Internet of Things (IoT) presents an extraordinary union of innovation and promise. As we conclude this exploration of Smart Contracts and IoT, we find ourselves at the threshold of a transformative era, where digital agreements and interconnected devices have the power to reshape industries, enhance efficiency, and secure transactions like never before. The benefits of automation, security, and transparency that arise from this combination promise to unlock a new realm of possibilities in areas ranging from healthcare and supply chain management to smart cities and environmental conservation.
As we look ahead, the future of Smart Contracts and IoT is rife with exciting developments, but it also poses a series of challenges that require careful consideration and solution. Scalability, interoperability, and data privacy will be focal points in the journey to harness the full potential of these technologies. Moreover, the need for regulatory clarity, education, and the enhancement of user-friendly interfaces is paramount for widespread adoption and seamless integration. The road ahead is undoubtedly marked by innovation, and as we navigate this intersection, it is imperative to balance the drive for progress with the commitment to address the complexities and concerns that arise. The convergence of Smart Contracts and IoT is a remarkable testament to our relentless pursuit of a smarter, more connected, and secure future, where devices and data exchanges operate in harmony, transcending the boundaries of our imagination.
SoluLab, as an established IoT development company, and a proficient smart contract development company, can play a pivotal role in bringing the concepts discussed in this blog on Smart Contracts and IoT to fruition. They offer comprehensive IoT development services, enabling the seamless integration of IoT devices and the implementation of secure and efficient data exchange protocols. Additionally, their smart contract development services empower businesses to leverage blockchain technology for enhanced security and automation, aligning perfectly with future trends and developments of IoT and Smart Contracts. Ready to explore the boundless possibilities of Smart Contracts and IoT? Contact SoluLab today to embark on your journey toward seamless automation, security, and innovation.
FAQs
1. How do Smart Contracts enhance security in IoT applications?
Smart Contracts enhance security in IoT by using blockchain technology, which offers transparency, immutability, and cryptographic security. This ensures that data exchanges and device interactions are tamper-proof and free from unauthorized access, reducing security risks associated with centralized systems.
2. Can Smart Contracts be customized to specific IoT use cases?
Yes, Smart Contracts are highly customizable to suit a wide range of IoT applications. Their code can be tailored to accommodate specific conditions, actions, and requirements unique to each use case, making them adaptable to the diverse needs of different industries.
3. What are the challenges in achieving regulatory compliance for IoT and Smart Contracts integration?
Achieving regulatory compliance for IoT and Smart Contracts can be challenging due to evolving and sometimes ambiguous legal frameworks. Challenges include data privacy regulations, cross-border issues, and adherence to industry-specific laws. Businesses must navigate these complexities to ensure compliance.
4. How can businesses prepare for the adoption of Smart Contracts and IoT?
Businesses can prepare for the adoption of Smart Contracts and IoT by first conducting a thorough assessment of their specific needs and objectives. They should invest in employee training, understand the regulatory landscape, and identify strategic use cases. Collaborating with experienced IoT development and Smart Contract companies can streamline the adoption process.
5. What are the environmental implications of Smart Contracts and IoT in conservation efforts?
Smart Contracts and IoT offer significant environmental benefits for conservation efforts. They enable the real-time monitoring of ecosystems, wildlife, and natural resources. Automated responses to environmental threats, such as pollution and resource depletion, can help reduce environmental impact and promote sustainability and conservation.
6. How can SoluLab assist in implementing Smart Contracts and IoT solutions for my business?
SoluLab offers comprehensive IoT development services and specializes in Smart Contract development. They can provide tailored solutions for your specific needs, ensuring a seamless integration of IoT devices and the deployment of secure, efficient Smart Contracts. Our expertise and experience make us a valuable partner in harnessing the full potential of Smart Contracts and IoT for your business.






