AI agents are changing the way software projects manage resources. These intelligent systems predict demands, streamline timetables, and effectively distribute resources. IT departments encounter a variety of difficulties that might reduce their effectiveness and productivity. These issues involve controlling the rising complexity of IT infrastructures, responding to expanding cybersecurity threats, assuring compliance with ever-changing legislation, and maintaining high system stability and availability. Furthermore, IT teams frequently require assistance with repetitive operations that occupy significant time and resources, restricting their capacity to focus on strategic projects and innovation. AI agents play a crucial part in this scenario. By using powerful algorithms and machine learning, AI agents have transformational capabilities that may greatly improve IT processes.
Financial institutions have experienced a 38% increase in profitability by integrating AI agents for tasks such as fraud detection and risk assessment. AI agents in IT play a vital role in transforming operations, particularly in cybersecurity. They continuously monitor systems, detect threats, and respond swiftly to potential breaches. By automating regulatory checks and generating detailed reports, they also simplify compliance efforts. Furthermore, their ability to analyze large datasets provides actionable insights, enabling smarter, data-driven decisions.
More than just tools, AI agents for IT act as strategic partners, helping IT teams tackle challenges, optimize operations, and drive innovation. In this article, we will explore their transformative role, key use cases of AI agents in IT, benefits, and different types, setting a new benchmark for IT excellence in the digital age.
What are AI Agents?
An AI agent is a high-performance virtual assistant that uses artificial intelligence to complete tasks independently. Its primary duties include perceiving the environment, processing facts, making educated judgments, and carrying out actions to attain predetermined goals.
One important characteristic of AI agents is their ability to adapt and increase their skills over time. Using technologies such as Large Language Models (LLMs), these agents constantly improve their abilities via continuing interactions, becoming more complex and effective.
Multi-agent collaboration is critical in autonomous AI systems. Each agent provides specialized knowledge, working toward shared goals to simplify difficult problem-solving methods.
The Working of AI Agents
IT operations management AI agents function through a combination of advanced technologies and methodologies, allowing them to operate autonomously or semi-autonomously. Here’s how they work:
1. Environmental Perception: These agents continuously monitor and analyze their operational environment to adapt to new data in real-time. By leveraging advanced large language models (LLMs), they understand instructions and contexts with precision, enabling efficient operations.
2. Tool Utilization: AI agents use a variety of tools, including APIs, calculators, and search engines, to gather essential information for executing tasks and making informed decisions.
3. Decision-Making: Equipped with data-driven insights, AI agents align their decisions with business objectives. LLM-powered agents excel in interpreting complex instructions and contexts, enabling them to execute tasks autonomously while supporting strategic goals.
4. Adaptive Learning: These agents learn from past outcomes to improve efficiency and refine their strategies over time. Advanced reasoning techniques, like chain-of-thought and tree-of-thought reasoning, enhance their ability to establish logical connections and solve complex problems.
5. Problem Resolution: AI agents identify solutions to emerging challenges and proactively address potential issues. Their capabilities are amplified by LLMs, which allow them to generate specific outputs, such as detailed reports or emails, to facilitate problem-solving.
6. Strategic Planning: By forecasting trends and planning, AI agents support long-term strategies and optimize resource allocation, ensuring that businesses stay agile and prepared for future challenges.
These core functions make AI agents indispensable for managing IT operations efficiently, driving innovation, and enhancing overall organizational performance.
Types of AI Agents
AI agents are digital systems that are intended to perceive their surroundings, process data, and implement actions to accomplish specific objectives. Depending on their capabilities and applications, they can be categorized into various types:
1. Reactive Agents: Reactive agents respond directly to inputs from their environment without storing past experiences. These agents are ideal for straightforward tasks like playing games or controlling basic robotics. While efficient, they lack memory or learning capabilities, limiting their ability to handle complex, evolving scenarios.
2. Goal-Based Agents: These agents work toward achieving specific objectives. They evaluate different actions based on their impact on achieving the goal. Goal-based agents are often used in navigation systems or decision-making processes, where prioritizing tasks is essential.
3. Utility-Based Agents: Utility-based agents assess different outcomes and select the one that maximizes utility or satisfaction. They not only aim to achieve a goal but also consider the most efficient or beneficial way to reach it. These agents are commonly used in industries like logistics, where optimizing processes is critical.
4. Learning Agents: By learning from their prior experiences, learning agents evolve and enhance their capabilities over time. They include components for exploration, feedback, and optimization, making them suitable for dynamic environments like autonomous vehicles or personalized recommendation systems.
5. Social Agents: Social agents are designed to interact effectively with humans or other agents, often simulating human-like behaviors. AI agents for customer service include chatbots, virtual assistants, and collaborative robots that need to work alongside people.
6. Collaborative Agents: These agents work as part of a team, either with humans or other agents, to achieve shared objectives. They are commonly used in multi-agent systems for applications like supply chain management and swarm robotics.
7. Autonomous Agents: Autonomous agents operate independently without continuous human guidance. They make decisions, learn from their environment, and adapt to changes. Examples include self-driving cars and drones that can navigate and execute tasks on their own.
8. Intelligent Agents: Intelligent agents combine several capabilities, such as perception, reasoning, learning, and acting, to solve complex problems. They are used in advanced AI systems like smart assistants, healthcare diagnostics, and predictive analytics.
Each type of AI agent uniquely enhances efficiency, solves problems, and drives innovation across industries. By choosing the right type of AI agent, businesses can address specific challenges and achieve their goals more effectively.
Key Components of AI Agents in IT
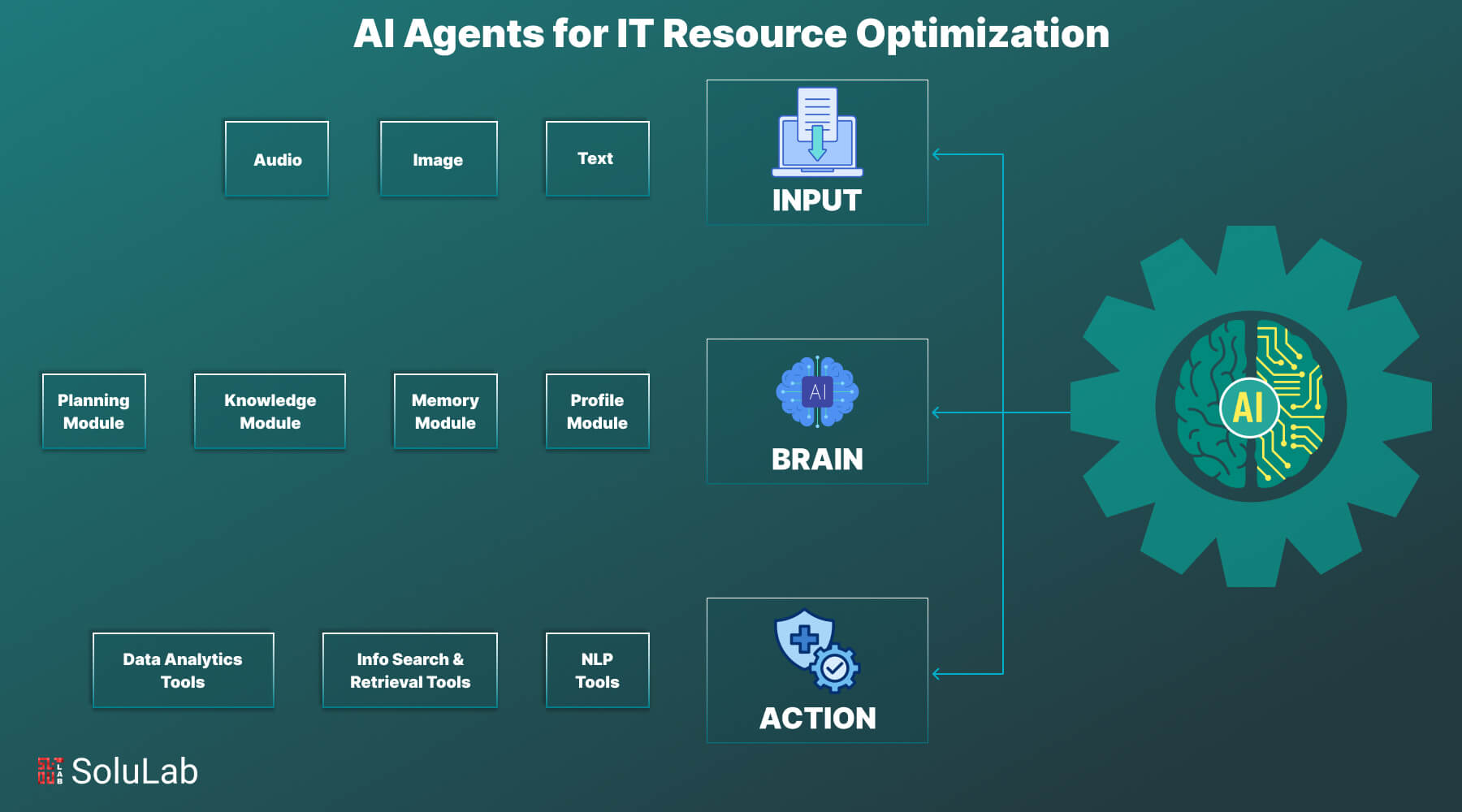
An AI agent for IT is made up of important components such as input processing, cognitive thinking, and strategy execution, all of which help to improve IT operations with exceptional efficiency and precision.
- Input: This component collects and processes many forms of data from systems and users, including text, audio, and images. These inputs provide the basis for the agent’s choices and actions inside IT operations.
- Brain: The brain is the key hub for cognitive functioning. It drives thinking and decision-making through linked modules.
- Profiling: It specifies the agent’s job and scope, like network management or cybersecurity issues.
- Memory: Memory stores previous interactions and data, allowing the agent to learn from them and improve over time.
- Knowledge: Contains specialized, domain-specific information required for IT activities, allowing for informed decision-making and successful issue solutions.
- Planning: It identifies the optimum path of action by assessing incoming data and aligning it with set goals, resulting in efficient job execution.
- Action: This component implements the agent’s plans, carrying out activities such as system monitoring, incident response, and performance optimization. The agent ensures that IT activities run smoothly and efficiently by utilizing tools from its specialized toolbox.
These interconnected components allow AI agents to provide accuracy, flexibility, and scalability, making them important in current IT contexts.
The Role of AI Agents in IT
With their capacity to traverse complex technical environments and decipher enormous volumes of data, AI agents for IT infrastructure are changing operations. These AI agents are designed to perform a variety of tasks, from regular system monitoring to intricate cybersecurity analysis, in contrast to typical language models that produce text.
They are capable of complex problem-solving and decision-making, going beyond simple automation. AI agents in IT have the ability to automatically identify network traffic irregularities, anticipate system faults before they happen, and suggest the best configurations based on real-time data. By anticipating and reducing threats, this insight and agility improve security posture in addition to streamlining IT processes.
Additionally, by effectively managing repetitive chores, AI agents free up IT personnel to concentrate on important objectives. They increase system dependability, decrease downtime through predictive maintenance, and speed up issue reaction times. Organizations in the IT industry may increase operational efficiency, optimize resource consumption, and eventually create a more robust infrastructure that can adapt to changing technological needs by utilizing AI agents.
In the digital age, AI agents for IT are essential instruments that improve performance standards, reduce operational risks, and open the door for further innovation. Their capacity for large-scale data assimilation and analysis gives companies useful insights for the development to change as per the new technological norms.
Use Cases of AI Agents in the IT Industry
AI agents in IT are transforming the industry by streamlining processes, enhancing security, and improving overall efficiency. Here are some key use cases where AI agents add value:
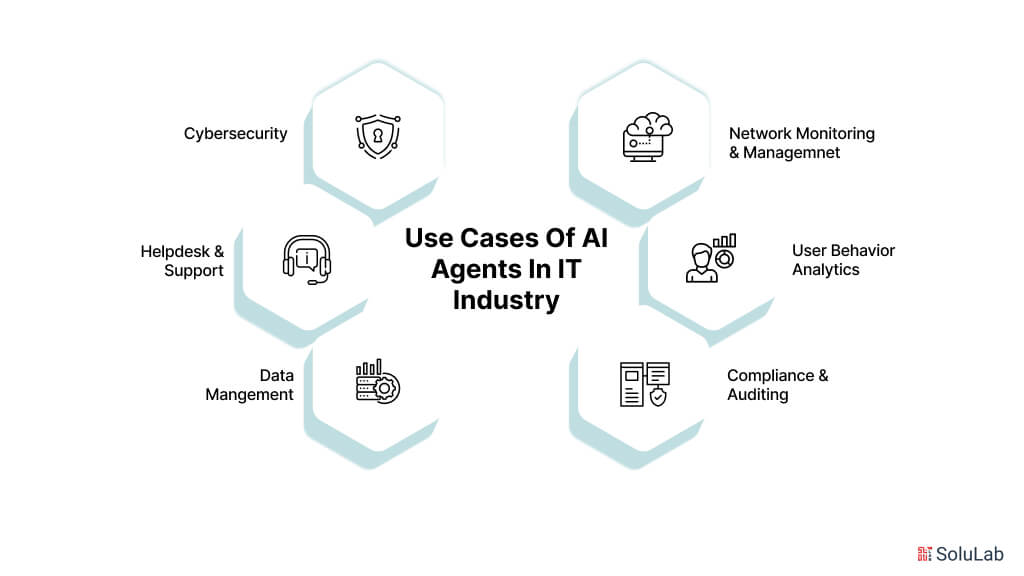
1. Network Monitoring and Management
- AI agents are constantly monitoring network traffic to discover and fix abnormalities such as unexpected spikes, bottlenecks, and latency issues.
- They improve network setups to maintain continuous connectivity and reduce downtime.
- Predictive analytics foresee network faults, allowing for preemptive interventions to preserve dependability.
2. Cybersecurity
- AI agents detect possible dangers in real time, such as malware, phishing attempts, and unauthorized access.
- They conduct automated vulnerability evaluations and suggest fixes or upgrades to close security vulnerabilities.
- Incident response systems driven by AI agents reduce the time between threat discovery and resolution, hence lowering damage.
3. System Performance Optimization
- Artificial intelligence agents improve resource allocation by evaluating system parameters such as CPU use, memory utilization, and disk activity.
- They detect and fix performance bottlenecks, resulting in high system availability.
- Automated diagnostics enable IT workers to resolve issues more quickly, minimizing the need for manual intervention.
4. Helpdesk & Support
- AI agents manage client inquiries via intelligent AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants, giving immediate assistance.
- They automate issue classification, assignment, and resolution, resulting in faster response times and better service quality.
- AI agents recommend solutions to reoccurring issues based on prior support data, increasing problem resolution efficiency.
5. Data Management and Analysis
- AI agents evaluate and organize huge datasets, extracting useful insights to improve decision-making.
- They manage data cleansing and transformation, which increases data quality and accuracy.
- Predictive modeling helps to uncover trends and patterns, which helps in strategic planning.
6. DevOps and CI/CD Automation
- AI agents simplify code integration, testing, deployment, and monitoring inside DevOps pipelines.
- They detect flaws in software builds, resulting in speedier debugging and release cycles.
- Continuous learning enables them to optimize procedures and shorten time-to-market for IT solutions.
7. IT Asset Management
- AI agents monitor the lifespan of IT assets, including hardware and software, to ensure optimal use.
- They anticipate maintenance needs, minimizing downtime and unforeseen repair expenses.
- By tracking asset performance, AI agents assist IT teams in making educated decisions regarding upgrades and replacements.
8. Compliance & Auditing
- AI agents automate compliance inspections, assuring compliance with industry laws including GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO standards.
- They produce thorough audit reports, saving time and effort for IT departments.
- Real-time monitoring ensures that firms meet growing regulatory obligations.
9. Incident Management
- AI agents identify, categorize, and prioritize events based on severity to provide prompt answers.
- They give actionable insights and propose strategies to minimize service interruptions.
- Historical data analysis assists in finding underlying causes and averting future occurrences.
10. User Behavior Analytics
- AI agents monitor user activities to detect anomalous behavior, such as illegal access or insider threats.
- They assist IT staff in understanding consumer preferences, allowing for more efficient delivery of IT services.
- Behavior patterns are utilized to improve security protocols and the user experience.
11. IT Project Management
- AI agents help with work scheduling, resource allocation, and real-time project progress tracking.
- They offer predictive insights that help detect future project delays or resource limits.
- Integrated reporting ensures that stakeholders receive up-to-date information.
12. Data Privacy and Governance
- AI agents control data privacy standards by tracking data access and use.
- They assure adherence to global data protection requirements such as the CCPA and GDPR.
- Automated notifications advise IT teams of potential privacy violations or illegal data use.
Thus, AI agents’ applications in IT cover several sectors, providing exceptional efficiency, accuracy, and scalability. By automating repetitive activities, boosting security, and giving insightful insights, AI agents allow IT teams to zone in on strategic goals and innovation, resulting in business success.
Benefits of AI Agents in IT
The incorporation of AI agents into IT operations provides organizations with transformative benefits, including the ability to optimize processes, improve security, and increase efficiency. The following is an example of how AI agents have a substantial effect:
1. Enhanced Efficiency: AI agents automate repetitive and time-consuming duties, including system monitoring, patch updates, and ticket administration. This enables IT teams to concentrate on strategic initiatives, thereby reducing manual errors and saving time.
2. Improved Cybersecurity: AI agents detect and respond to hazards in real time by perpetually monitoring systems. To guarantee a secure IT environment, they prevent data intrusions, identify vulnerabilities, and provide proactive protection against evolving cyber threats.
3. Cost Optimization: By automating routine processes, optimizing resource allocation, and predicting system failures, AI agents assist in the reduction of operational costs. This reduces latency and eliminates unnecessary expenditures that are linked to system outages or manual intervention.
4. Decision-Making Based on Data: AI agents analyze immense quantities of data to offer actionable insights, thereby enabling IT teams to make well-informed decisions. Predictive analytics facilitate the alignment of IT strategies with business objectives, expedite resource planning, and anticipate potential issues.
5. Scalability: AI agents are capable of managing escalating duties without sacrificing performance. They guarantee the smooth operation of businesses as they expand, effectively scaling IT resources and adapting to new challenges.
6. Accelerated Incident Resolution: AI agents are proficient in the rapid identification, classification, and resolution of IT incidents. Their capacity to offer immediate solutions minimizes delay and guarantees consistent system performance.
7. Customized User Experience: AI agents customize IT services and support by employing user behavior analytics. They enhance user contentment by offering customized solutions, whether it involves resolving tickets or recommending system enhancements.
8. Governance and Compliance: AI agents generate comprehensive audit reports and automate compliance checks to guarantee regulatory compliance. They mitigate the risk of non-compliance, thereby shielding businesses from potential legal challenges or penalties.
9. Continuous Improvement and Learning: Machine learning is employed by AI agents to enhance their performance over time. They ensure that IT operations remain at the forefront of the industry by refining processes, adapting to new data, and providing increasingly effective solutions.
10. Constant Accessibility: AI agents are operational 24/7, guaranteeing continuous monitoring, assistance, and incident response. This is particularly important for global organizations that necessitate consistent performance across various time zones.
How to Build an AI Agent for IT?
The development of an AI agent for IT necessitates a structured approach that commences with explicit objectives and concludes with ongoing optimization. Here is a comprehensive guide to the development of a customized AI agent that is capable of managing a wide range of IT duties and enhancing operational efficiency.
-
Define Your Objectives
Begin by defining the objectives of your AI agent in IT. Ascertain whether it will optimize system performance, automate cybersecurity responses, manage network monitoring, or improve user support. The development process will be effectively guided by clear objectives.
-
Select the Most Suitable Frameworks and Libraries
It is essential to choose the appropriate frameworks and libraries. For the development of machine learning models, it is imperative to utilize tools such as sci-kit-learn, PyTorch, and TensorFlow. Furthermore, to guarantee compatibility and efficiency, IT-specific libraries should be utilized for duties such as infrastructure administration or anomaly detection.
-
Choose an Appropriate Programming Language
Python continues to be the dominant language in the field of AI development due to its extensive library support and adaptability. Alternatively, specialized frameworks may suggest specific languages that are specifically designed for IT tasks, thereby guaranteeing optimal performance and integration.
-
Data Collection and Preparation
In the field of IT, the training of an effective AI agent is contingent upon the availability of high-quality data. Accumulate datasets, such as user interaction data, security incident records, system performance metrics, and network logs. Ensure that the data is pertinent, clear, and representative of operational scenarios.
-
Develop a Scalable Architecture
Develop a modular architecture that is capable of accommodating the expansion of IT operations. Guarantee the ability to integrate existing cloud platforms, ticketing systems, and monitoring tools with ease. Modify architectures to accommodate large-scale deployments and real-time data streams.
-
Initiate Model Training
Employ suitable methodologies, including reinforcement learning for dynamic environments or supervised learning for classification tasks. Specialized frameworks may provide customized environments for the training of IT-specific models, thereby enhancing accuracy and performance.
-
Deploy the AI Agent
Use cloud services or containerized environments to deploy the AI agent, which will provide scalability and flexibility. Guarantee compatibility with IT infrastructure and adherence to security protocols. Frameworks offer simplified deployment options that facilitate integration into existing IT ecosystems.
-
Conduct a Thorough Examination
Validate the AI agent’s functionality, performance, and security across a variety of IT operations through rigorous testing. In order toTo guarantee reliable performance in production environments, incorporate scenarios regarding scalability, reliability, and responsiveness.
-
Consistently Monitor and Optimize
Adapt the AI agent to the changing IT environments and emergent hazards by monitoring it post-deployment. Performance, responsiveness, and alignment with IT objectives are all improved by consistent updates and optimizations.
These procedures can assist in creating a sophisticated AI agent specifically designed for IT. These agents have the potential to optimize operational efficiency, increase security measures, and automate tasks. They enable IT teams to proactively address challenges, enhance service delivery, and foster innovation within organizational IT frameworks.
Implementation Challenges of AI Agents in the IT Industry
While adopting AI agents in IT offers numerous benefits, implementing them comes with several challenges. Organizations must address these obstacles to ensure successful integration into their systems. Here are some of the key challenges:
-
Integration with Legacy Systems
Many IT infrastructures rely on outdated systems that do not easily work with AI technologies. Integrating AI agents into these environments can be complicated, requiring customization and upgrades that may disrupt operations.
-
Data Quality and Availability
To operate efficiently, AI agents necessitate high-quality data. Poor data quality or incomplete datasets can reduce their accuracy and effectiveness. Ensuring clean, accurate, and relevant data is a significant challenge for many IT teams.
-
High Implementation Costs
Deploying AI agents often involves significant upfront investments in hardware, software, and skilled personnel. Smaller organizations, in particular, may find these costs prohibitive if the financial benefits are not immediately evident.
-
Skill Gap
AI implementation requires machine learning, data science, and AI operations expertise. A shortage of skilled professionals can slow down deployment and limit the effectiveness of AI systems.
-
Change Management
Introducing AI agents often requires a shift in processes and workflows. Resistance to change, fear of job loss, and a lack of understanding about AI’s role can create barriers to adoption within IT teams and organizations.
-
Security Concerns
While AI agents enhance cybersecurity, their implementation can introduce new vulnerabilities. Misconfigured systems or reliance on external APIs can lead to risks such as data breaches or unauthorized access.
-
Ethical and Regulatory Issues
AI agents must comply with legal and ethical standards, especially when handling sensitive data or automating decision-making. Solving regulations such as GDPR or CCPA can be challenging for organizations.
-
Scalability Issues
Scaling AI agents across diverse IT operations can be complex. Organizations must ensure that their infrastructure can support the computational demands of AI solutions as operations grow.
-
Unrealistic Expectations
Organizations sometimes expect immediate and significant results from AI agents. Misaligned expectations can lead to disappointment if outcomes are not as impactful as initially envisioned.
Future Trends of AI Agents in IT Resource Management
The role of AI agents in IT resource management is rapidly evolving, with emerging trends shaping how businesses optimize their operations. These trends highlight the growing sophistication of AI solutions and their potential to redefine IT strategies. Here’s a look at the future of AI agents for IT resource management:
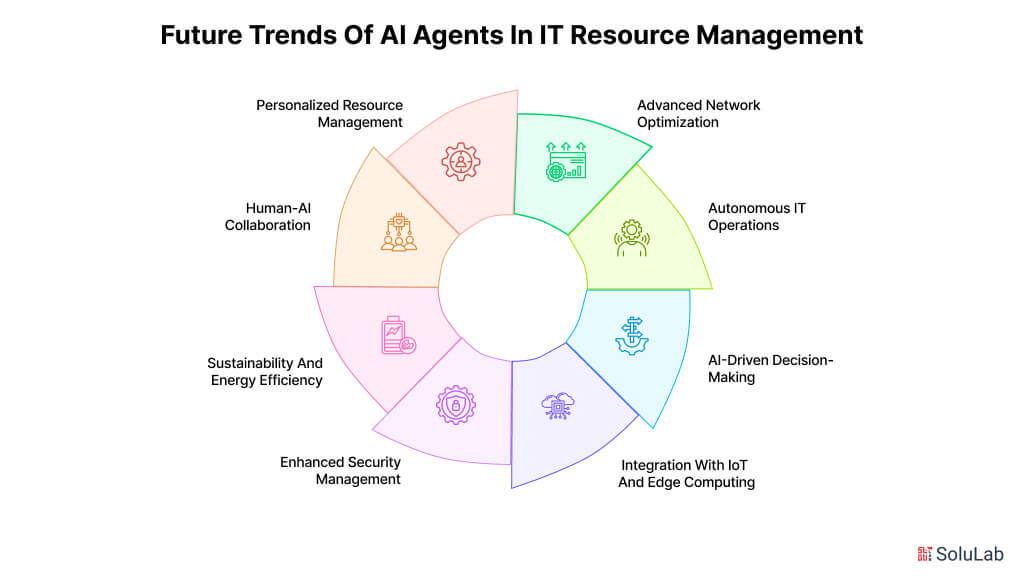
1. Advanced Network Optimization
AI agents are increasingly being used for network optimization, enabling real-time monitoring and dynamic resource allocation. In the future, AI agents for network optimization will leverage predictive analytics to anticipate network demands, reduce latency, and enhance bandwidth utilization. These capabilities will ensure seamless connectivity in complex, multi-cloud environments.
2. Autonomous IT Operations
As AI technologies mature, AI agents are expected to operate with minimal human intervention. They will autonomously manage IT resources, including provisioning, scaling, and performance tuning. This trend will reduce operational costs while enhancing efficiency and reliability.
3. AI-Driven Decision-Making
AI agents will evolve to provide more nuanced and strategic recommendations. By analyzing vast datasets and incorporating contextual business objectives, they will guide decision-making for IT resource allocation, project prioritization, and budget management.
4. Integration with IoT and Edge Computing
With the rise of IoT and edge computing, AI agents will play a critical role in managing distributed resources. They will optimize data flow between devices, edge servers, and cloud infrastructures, ensuring efficient processing and minimal latency.
5. Enhanced Security Management
AI agents will increasingly integrate with IT security frameworks to manage resources securely. Future AI agents will predict and mitigate threats proactively, ensuring IT resources remain protected against changing cybersecurity risks.
6. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
AI agents for enterprises will help organizations meet sustainability goals by optimizing energy consumption in IT operations. They will identify inefficiencies in data centers and recommend changes to reduce carbon footprints, supporting greener IT practices.
7. Human-AI Collaboration
The future of AI agents in IT resource management will focus on enhancing human-AI collaboration. AI agents will provide IT teams with real-time insights, intuitive dashboards, and actionable recommendations, allowing professionals to focus on strategic tasks rather than routine operations.
8. Personalized Resource Management
AI agents will become more adaptive, customizing IT resource management to specific business needs. They will adjust resource allocation for different departments, projects, and workflows, ensuring optimal utilization and productivity.
The Bottom Line
AI agents are redefining how IT teams manage resources, offering solutions that streamline operations, enhance security, and drive data-driven decisions. From automating repetitive tasks to optimizing system performance, these intelligent systems empower organizations to focus on innovation and strategic growth.
Recently, a travel company partnered with SoluLab to overcome challenges like high query volumes, slow response times, and limited personalization in customer service. By integrating an AI-powered chatbot, the company transformed its customer support operations, providing faster responses and customized travel recommendations.
Looking to improve your IT operations or deliver better customer experiences? We being an AI agent development company have a team of experts who are ready to help you take the next step. Reach out to us today and let’s explore how AI-powered solutions can make a real difference for your business.
FAQs
1. What are AI agents in IT resource optimization?
AI agents in IT resource optimization are intelligent systems designed to automate and improve the allocation, utilization, and management of IT resources. They use advanced algorithms, machine learning, and data analytics to monitor systems, predict resource needs, and optimize performance, reducing costs and enhancing efficiency.
2. How do AI agents benefit IT operations?
AI agents streamline IT operations by automating repetitive tasks, such as system monitoring and incident management, freeing IT teams to focus on strategic initiatives. They also enhance cybersecurity, optimize network performance, and provide data-driven insights for better decision-making, leading to more efficient and scalable IT systems.
3. Can AI agents work with legacy IT systems?
Yes, AI agents can integrate with legacy IT systems, though it may require additional customization or middleware solutions. While some older systems may pose challenges, AI agents can often be tailored to ensure compatibility and improve overall functionality without overhauling the existing infrastructure.
4. What are common use cases of AI agents in IT?
AI agents are used in network optimization to improve performance and reduce latency, cybersecurity to detect threats and automate vulnerability management, and system performance monitoring to identify bottlenecks. They also streamline helpdesk operations by automating ticket resolution and enhancing compliance by automating regulatory checks and generating audit reports.
5. How can businesses get started with AI agents for IT resource optimization?
To begin, businesses should assess their current IT infrastructure and identify areas where AI agents can add value, such as automating tasks or optimizing performance. Partnering with an experienced AI development company, like SoluLab, can simplify implementation and ensure tailored solutions that meet specific business needs. Contact us today to explore how AI can transform your IT operations.






