The way that blockchain technology as the basis of all significant cryptocurrencies is being used has changed since the first cryptocurrency was created. Since then, the developers have realized how drastically it can transform industries that have relied on lengthy paper trails and that stand to gain from greater security, transparency, and lower prices when exchanging anything. The trade finance industry has been identified as the one that stands to gain significantly from this technology.
According to 54% of banks polled, disruptive technologies like blockchain, digital commerce, and online trading platforms are important areas for the development of tactical attention in the future to ensure future growth. Additionally, over half of the respondents indicated that both paper and digital documents may become more common in trade.
Cooperation between businesses that are more often competitors is necessary to advance the digitization of trade finance. Banks can effectively cooperate and agree on conducting business digitally for their mutual benefit through blockchain platforms such as SoluLab solutions for finance trade
What is Trade Finance?
The financial goods and mechanisms used by companies to support global trade and commerce are collectively referred to as trade finance. It eases the complexity of cross-border operations and is an essential facilitator for importers and exporters. Notably trade finance is found to be responsible for 80% to 90% of global trade according to WTO. Trade financing reduces the risks associated with international trade, including credit risk, currency volatility, and geopolitical concerns, while addressing the financial gaps between importers and exporters.
A wide range of financial products are available through trade finance, such as supply chain financing, export credit insurance, documentary credits, and letters of credit. These tools ensure on-time payments and minimize possible losses by facilitating seamless transactions and offering financial protection. Through its ability to reduce risk and its wide range of products, trade finance is essential for promoting job creation, economic expansion, and international connections.
Key Components of Trade Finance
Another key facilitator of international trade is the medium of trade financing. Numerous financial products and instruments mitigate risks and expedite trading for importers and exporters alike.
-
A Letter of Credit
LC is a bank guarantee provided by a bank to an exporter on the importer’s behalf. It greatly enhances security for both parties because this ensures that the exporter will be paid when all requirements are met.
-
Export Credit Agency
Export Credit Agencies are government-backed organizations that provide loans, guarantees, and insurance for exports. It minimizes risks such as default from the buyer, volatility in exchange rates, and political uncertainty.
-
Insurance
Provides a wide range of covers regarding international trade, including credit, political, and cargo damage risks. Insurance financial cover is available to both importers and exporters.
-
Forfaiting
It is a special financing method wherein the exporters sell forfeiture at the discount price of their export receivables. It is the transfer of the credit risk to the forfaiter and free working cash for the exporter.
-
Supply Chain Finance
Supply chain finance consists of various financial options that enhance cash flow and expense reduction across the supply chain. This can include working capital loans, factoring, and invoice discounting.
How does Blockchain and Trade Finance Work Together?
1. Trade finance generally means giving assurance from a financial aspect to ensure the effective performance of the transfer of goods. None of the parties to this international trade wish to assume their responsibility without sufficient assurance from the counterparty. Here is how blockchain in trade finance works:
2. The letter of credit issued by the importer’s bank promises reimbursement for the exporter’s costs of transferring the goods. Once the importer receives the letter of credit and signs the bill of lading upon actual receipt of the goods, the law places him on the hook for the full amount due on the cargo.
3. The use of distributed ledger technology, also referred to as DLT, allows banks, trading houses, and other network members, such as insurance companies, to exchange documents securely and transparently. Every transaction is time-stamped and contains a unique or distinctive cryptographic signature that is recorded permanently in the blockchain. To be completely transparent, the correct or the same information will always be available to anyone with the permission right, thereby building trust and preventing fraud.
4. An independent set of rules defines risk and dispute management processes and how banks and dealers may be able to trade with each other. Shipping and commercial terms agreed upon by parties are recorded by smart contracts. Smart contracts issue payment notifications when some pre-set criteria such as shipping of products are fulfilled.
In a trade finance blockchain transaction, there are usually two banks: the collection bank of the buyer and the remitting bank of the seller. The check is handled by both of them during the trade finance process as an actual payee while monitoring whether all parties to the transaction have fulfilled their obligations in the process.
One giant step toward the modernization of this sector would be the introduction of blockchain technology into trade finance, transforming entirely how companies conduct international trade to provide improvements in transparency, security, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness, unlocking the door to a much more integrated global economy.
What is the Role of Banks in Trade Finance?
Banks are necessary for blockchain trade finance because they simplify international trade and further the enhancement of the economy worldwide. They make complicated transactions more manageable, expose fewer risks, and ensure that there is liquidity. Here are five reasons why banks provide functionality in trade finance:
1. Credit Letter Provision (LCs)
Among the primary responsibilities that banks play in trade finance is the issuance of letters of credit. An LC is, in effect, a credit instrument that reduces the risk associated with cross-border transactions for both the parties involved. It ensures that there is indeed an obligation on the part of the buyer to pay the seller. Essentially, it acts as a bank guarantee between the buyer’s bank that undertakes reimbursement, in case the goods delivered strictly live up to the requirements or obligations contained in the agreement. This arrangement helps provide confidence between the importer and the exporter when the parties may not know each other.
2. Availment of Loans for Trade Finance
Banks offer trade finance to importers and exporters through lending. These are short-term loans primarily meant to finance the working capital required to close the gap between manufacturing and the actual sale of goods. Importers and exporters rely on banks to provide them with access to capital that will help them pay shipping costs, raw materials purchases, and any other typical related costs involved in a transaction.
3. Banks Facilitate Documentary Collections
Another important service that banks offer in trade finance is documentary collection. In this, the exporter’s bank collects payment on behalf of the exporter by sending relevant documentation to the importer’s bank. When the importer makes the payment or accepts a bill of exchange, then he keeps the documents liable for clearing the consignments.
4. Minimizing Risk Through Trade Credit Insurance
A bank provides trade credit insurance as a measure of protecting businesses against their trading partners’ inability or insolvency. This particular type of insurance helps exporters minimize risks within foreign markets, especially unstable areas. Trade credit insurance provides a safety net for all exchange rate transactions and reduces the possible financial impact of default while encouraging business exploration of new markets.
5. Aiding Exchange Rate Transactions
Cross-border trade has been characterized by the use of many currencies and the related risks associated with fluctuating foreign exchange rates. Commercial banks play a key role in providing foreign exchange services such as forward contracts, and hedging facilities that enable firms to ‘lock in’ favorable exchange rates to protect against adverse fluctuations of currency. This way, through offering foreign exchange services, banks help reduce the risks that characterize international trading.
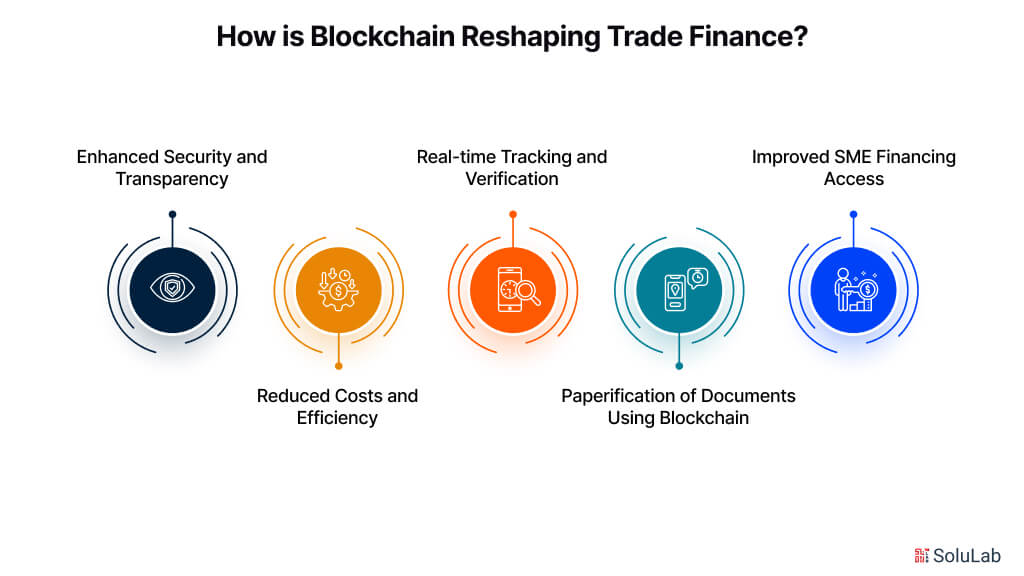
How is Blockchain Reshaping Trade Finance?
The benefits of blockchain in trade finance are solving persistent issues related to dependability, efficiency, security, and transparency. The tireless, paper-based processes along with the several intermediaries used in conventional trade finance create inconveniences, expensive costs, and the threat of fraud. Blockchain technology, through its decentralized and impenetrable ledger system and blockchain consulting company,
introduces a new way for trade finance upgrades through the digitization of papers, the reduction of intermediaries, and transparency in real-time recordings of transactions. Blockchain is transforming trade finance in many ways:
-
Enhanced Security and Transparency
Transparency is one of the advantages of blockchain, and this is one of the reasons why it has the solution needed for trade finance, which more often than not includes complex transactions involving multiple parties. It is for this reason that any transaction entered into a blockchain will be available to network users. For instance, since any alteration to the transaction data would become immediately clear to all, it reduces the likelihood of fraud or errors. For example, blockchain technology may record the entire lifecycle of a trade transaction, from when the buyer and seller first agreed to the final payment, ensuring accountability at each stage.
-
Reduced Costs and Efficiency
There are now several inefficiencies that conventional trade financing procedures entail, such as the trudging and time-consuming process that involves a lot of documentation and paperwork involving go-betweens such as banks, insurance companies, and shipping companies. The use of smart contracts through blockchain technology may automatically reduce these inefficiencies because they are self-executing contracts with the terms of an agreement explicitly put into code. Under specific conditions, these smart contracts trigger alterations and payouts on their own. Because manual interventions are less frequent, this automation promises correctness, speeds the transaction process, and reduces administrative costs. Costs are similarly decreased, and settlement times are significantly reduced when less or no intermediary is involved.
-
Real-time Tracking and Verification
With blockchain, the progress of items involved in a trade transaction will be visible in real time to every party associated with the transaction. This is very handy in international trade, especially where it is challenging to retain visibility over the goods since they may pass through so many countries and different customs procedures. Every checkpoint can be safely recorded by blockchain, thus allowing stakeholders to track how a shipment is going at every turn. This live tracking increases the efficiency of a supply chain and builds confidence among trade participants. They can identify and remove bottlenecks much faster, hence clearing delays and strengthening relationships between trading partners.
-
Paperification of Documents Using Blockchain
Digitalization of trade documents like invoices, bills of lading, and letters of credit can only be enabled through blockchain. It changes them into digital assets that can be easily transmitted safely across the network. Since digital artifacts are cryptographically encrypted and individually authenticated, digital paper is susceptible to loss and forgery of papers. This digitization, therefore, speeds up the approval process and eliminates the handling of physical documentation.
-
Improved SME Financing Access
Access to trade finance is not easy for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) since they undergo complicated documentation requirements or lack credit histories. B: By giving safe, transparent records like a digital record of a business’s transaction history, blockchain bridges this gap and makes it easier for financial institutions to assess risks and extend funding. Alternative financing options, such as tokenized trade assets available to investors, facilitate the growth of blockchain-based trade finance platforms and drive further inclusiveness of international trade finance by offering SME liquidity.
Real-World Use Cases
Blockchain technology has already been applied to trade finance in several cases. Around 65% of the world’s largest banks are predicted to employ blockchain technology in some capacity. Numerous institutions have already teamed up with blockchain companies to conduct trials. Here are the most effective blockchain use cases:
-
HSBC
With a comparable letter of credit exchange in May 2018, HSBC went one step further and asserted that it was the first trade finance transaction to use blockchain technology in a commercially viable manner. They asserted that while earlier proof-of-concept transactions had been successful, however, theirs was the first that had been used commercially.
The letter of credit was issued to financier ING on behalf of US food and agriculture company Cargill. It involved a deal over the shipment of soybeans from Argentina to Malaysia.
-
Barclays
Barclays believes that blockchain is the future and has coined the phrase “the new operating system for the planet.” As per their claims, they are the first bank to use the technology of blockchain for trade finance. This was done to accelerate international transactions as well as improve the processes that were occurring currently at the supply change.
They employed a technology named Wave, which was specifically designed to support the secure signing and blockchain-based exchange of bills of lading as well as other paper for trade transactions, just like the insurance certificates.
The seller receives a receipt of goods from the goods carrier when the goods are onboard the ship. Then, the receipt needs to be physically couriered to all parties concerned in the deal so that it is signed by each of them.
Other Banks
Other banks, aside from RBS and Barclays, test blockchain technology. Several major European banks contracted IBM in 2017 for the creation of a cross-border orders financing platform for small firms.
They have started to partner with Maersk to develop an online blockchain platform for the container shipping industry to shift the supply chain process online.
The Most Suitable Cryptocurrencies
Theoretically, it could exploit any cryptocurrency that supports direct transactions without involving third-party identification to reduce transaction costs. All of them can be counted practically.
The blockchain technology on which cryptocurrencies rely with financial Software development companies is much more important to trade finance than cryptocurrencies themselves are. Several blockchain applications used in trade finance, including Corda and Wave, work without using any cryptocurrency token.
Most advanced applications of blockchain include those specifically designed for trade finance. In such a way, an increasingly large number of blockchain applications are now developed for particular use cases, such as Ripple which partnered with a number of top banks.
How does SouLab promise the Efficiency of blockchain technology?
Blockchain and trade finance have changed complex trades in industries such as trade finance through internally built-up advantages of efficiency, security, and openness. In this regard, blockchain facilitates cross-border payments, minimizes fraud risks, and enhances the accuracy of data by lowering the reliance on middlemen. As such, it reduces transaction costs and time of settlement by a significant margin. For these reasons, blockchain is a very useful tool for financing trade, simplifying procedures that were previously cumbersome and opaque.
NovaPay Nexus, such as in the remarkable potential of Solulab a blockchain development company in delivering efficiency to blockchain digital transactions, enables users to accept Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies directly from their fully self-hosted and automated cryptocurrency payment processor. There is no cost, no transaction expenses, nor any middlemen. Besides its function as a payment processor, it also allows businesses to create their own ecosystems, giving clients safe and easy digital choices for payments. NovaPay Nexus offers a fine opportunity for companies to use blockchain technology to make transactions safer and raise user engagement all with a plethora of applications that extend from crowdfunding, loyalty programs, and even donation platforms.
Take it to the next level with SoluLab and create a safe, self-sufficient blockchain environment that best serves your company’s needs.
FAQs
1. How does trade finance use blockchain technology?
By lowering risk and simplifying international trade for buyers and sellers as they develop their businesses and enter new markets, the resultant blockchain-based trade network is intended to enhance the trade finance lending process and assist banks in reaching new markets with new products.
2. What is blockchain in trade finance?
A decentralized record of every transaction made across a network of peers is called blockchain in trade finance. Participants can verify transactions using this technique without a central clearing body being required.
3. What does the future of blockchain in finance look like?
Blockchain technology in finance promises to increase efficiency in the future by facilitating quicker, less expensive transactions and lowering the need for middlemen. Blockchain also simplifies access to monetary services on a global scale.
4. How is SoluLab making blockchain easier to use for users?
Solulab creates user-friendly applications and intuitive interfaces that improve accessibility, it is also making blockchain easier for users by automating procedures with the help of smart contracts.
5. What does trade finance cover?
It strives to guarantee that trade occurs in a seamless, effective, and trouble-free way. It includes all of the financial tools, goods, and services that support commercial activities, these consists of supply chain finance, Letters of Credits, and factoring insurance.






