The number of individuals using blockchain technology is rapidly increasing from a small group to millions. Research experts reveal that around 420 million individuals worldwide are cryptocurrency owners as of early 2023. While this remarkable rise is admirable, it creates an infrastructure bottleneck that hinders the functionality of blockchain networks. This is where blockchain scalability becomes relevant. Blockchain cannot become widely used if we cannot achieve great scalability.
To address this challenge, developers have devised a range of solutions aimed at enhancing blockchain scalability. Among these solutions, Layer-1 blockchain scaling and Layer-2 blockchain scaling mechanisms have gained prominence, each offering unique approaches to improving the throughput and performance of blockchain networks.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the differences between Layer-1 and Layer-2 scaling solutions, dissecting their respective advantages, drawbacks, and real-world applications. By the end of this discussion, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of these critical components in the quest to achieve scalable, efficient, and accessible blockchain infrastructure.
Importance of Scalability in Blockchain Technology
Scalability is a crucial consideration in blockchain technology due to its direct impact on the network’s performance, user experience, and potential for mass adoption. Several key reasons underscore the importance of scalability:
- Transaction Throughput: Scalability directly affects the number of transactions a blockchain network can process per second (TPS). Higher throughput enables faster transaction confirmation times and smoother user experiences, essential for applications requiring real-time interactions or high transaction volumes.
- Cost Efficiency: Scalability solutions that reduce transaction fees or energy consumption make blockchain technology more accessible and cost-effective for users and businesses. Lower transaction costs encourage broader adoption and support the viability of blockchain-based applications across various industries.
- Network Stability and Reliability: Scalability improvements enhance the stability and reliability of blockchain networks by reducing the risk of congestion, network delays, and transaction backlogs during periods of high demand. A scalable blockchain can accommodate growing user bases and fluctuating transaction volumes without compromising performance or security.
- Ecosystem Growth and Innovation: Scalability unlocks new opportunities for innovation and ecosystem growth by enabling the development of complex decentralized applications (DApps), decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, and other blockchain-based solutions. As scalability improves, developers can explore novel use cases and functionalities that were previously hindered by network limitations.
Types of Blockchain Layers
1. Layer-1 (On-Chain Scaling)
Layer-1 Scaling: This refers to scaling solutions implemented directly within the underlying blockchain protocol to enhance its capacity for processing transactions and supporting a larger user base. These solutions aim to optimize the protocol’s core components, such as the consensus mechanism, block size, and data structure, to improve scalability and performance.
2. Layer-2 (Off-Chain Scaling)
Layer-2 Scaling: Layer-2 solutions operate on top of the Layer-1 blockchain and focus on improving scalability by handling transactions off-chain or via secondary protocols. These solutions aim to alleviate congestion on the main chain and enhance transaction throughput without modifying the underlying protocol.
What is Layer-1 Blockchain Scaling?
Layer-1 blockchain scaling solutions are pivotal in the quest to enhance the scalability of blockchain networks. These solutions focus on refining the core protocol to augment transaction processing capabilities and improve overall network efficiency. Here’s a deeper exploration of Layer-1 scaling:
Layer-1 scaling revolves around making foundational adjustments to the underlying blockchain protocol to bolster its capacity for handling transactions and accommodating a larger user base. These modifications typically target key aspects of the protocol, such as the consensus mechanism, data structure, or block validation processes. By optimizing these elements directly within the protocol, Layer-1 scaling solutions aim to lay a robust foundation for scalability and sustainable network growth.
- Targeted Protocol Enhancements: Layer-1 scaling solutions focus on optimizing the core aspects of the blockchain protocol to streamline transaction processing and enhance network scalability.
- Foundational Changes: Unlike Layer-2 scaling solutions, which operate above the base protocol, Layer-1 solutions involve making fundamental modifications directly within the blockchain’s architecture.
Examples of Layer-1 Scaling Solutions
Layer-1 scaling encompasses various strategies and techniques aimed at fortifying the underlying protocol. Here are some prominent examples of Layer-1 scaling solutions:
1. Sharding
Sharding is a technique that divides the blockchain network into smaller, manageable segments known as shards. Each shard operates independently, processing a subset of transactions. This parallel processing significantly boosts transaction throughput, enabling the network to handle a larger volume of transactions concurrently. Sharding has been proposed as a solution to address Ethereum’s scalability issues, with Ethereum 2.0 aiming to implement sharding to enhance its transaction processing capabilities.
2. Consensus Algorithm Optimization
Consensus algorithm optimization plays a crucial role in enhancing Layer-1 scalability. Traditional consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) require substantial computational resources for block validation, limiting scalability. Transitioning to more efficient consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Stake (PoS) or Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), can significantly improve scalability by reducing the computational overhead and energy consumption associated with block validation. Projects like Cardano (PoS) and EOS (DPoS) have adopted alternative consensus mechanisms to enhance scalability and network efficiency.
Pros and Cons of Layer-1 Scaling Solutions
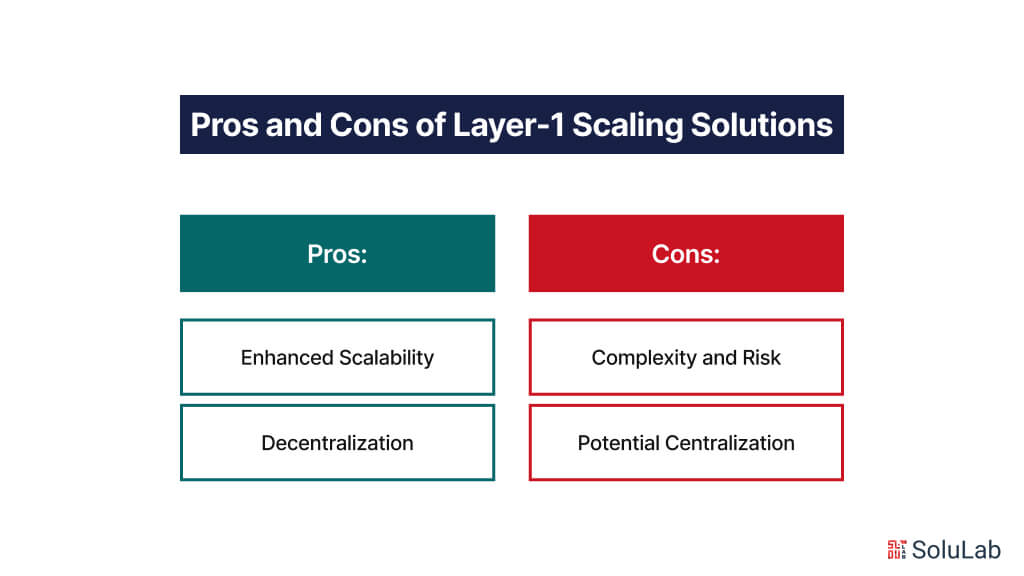
Layer-1 scaling solutions offer both advantages and challenges. Let’s examine the pros and cons:
Pros:
- Enhanced Scalability: Layer-1 scaling solutions directly address scalability concerns at the protocol level, resulting in substantial improvements in transaction throughput and network performance. By optimizing core protocol components, Layer-1 solutions lay the groundwork for long-term scalability and sustainable network growth.
- Decentralization: Many Layer-1 solutions prioritize maintaining or enhancing decentralization, ensuring the network remains secure and resistant to censorship. By implementing scalable solutions that preserve decentralization, blockchain projects can uphold the core principles of transparency, immutability, and trustlessness.
Cons:
- Complexity and Risk: Implementing Layer-1 scaling solutions often involves making fundamental changes to the blockchain protocol, which can introduce complexities and potential vulnerabilities. Modifying core protocol components requires careful planning and extensive testing to ensure compatibility, stability, and security. Additionally, the introduction of new features or consensus mechanisms may introduce unforeseen risks or attack vectors, necessitating thorough risk assessment and mitigation strategies.
- Potential Centralization: Some Layer-1 solutions may inadvertently lead to increased centralization if they favor certain nodes or validators over others. For example, consensus mechanisms like Proof of Stake (PoS) or Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) rely on token ownership or voting power to determine block validators, potentially concentrating control in the hands of a few large stakeholders. This centralization risk undermines the network’s decentralization and security, necessitating measures to promote inclusivity, fairness, and decentralization.
Read Also: Layer 3 Blockchain
What is Layer-2 Blockchain Scaling?
Layer-2 scaling solutions operate above the base Layer-1 protocol and aim to improve blockchain scalability by handling transactions off-chain or through secondary protocols. Unlike Layer-1 scaling solutions, which involve making fundamental changes to the underlying protocol, Layer-2 solutions focus on enhancing scalability without directly modifying the core blockchain architecture. Instead, Layer-2 solutions enable faster and more efficient transaction processing by conducting transactions off-chain and settling them on the main chain only when necessary. This approach reduces congestion on the main chain, increases transaction throughput, and improves overall network performance.
- Scalability Enhancement: Layer-2 scaling solutions aim to enhance blockchain scalability by processing transactions off-chain or via secondary protocols, alleviating congestion on the main chain and improving transaction throughput.
- Off-Chain Transactions: Layer-2 solutions enable participants to conduct transactions off-chain, allowing for faster and more cost-effective transactions while maintaining security and trustlessness through cryptographic mechanisms.
- Main Chain Settlement: Transactions conducted off-chain are settled on the main chain only when necessary, reducing the burden on the main chain and enhancing overall network efficiency.
Different Types of Layer-2 Scaling Solutions
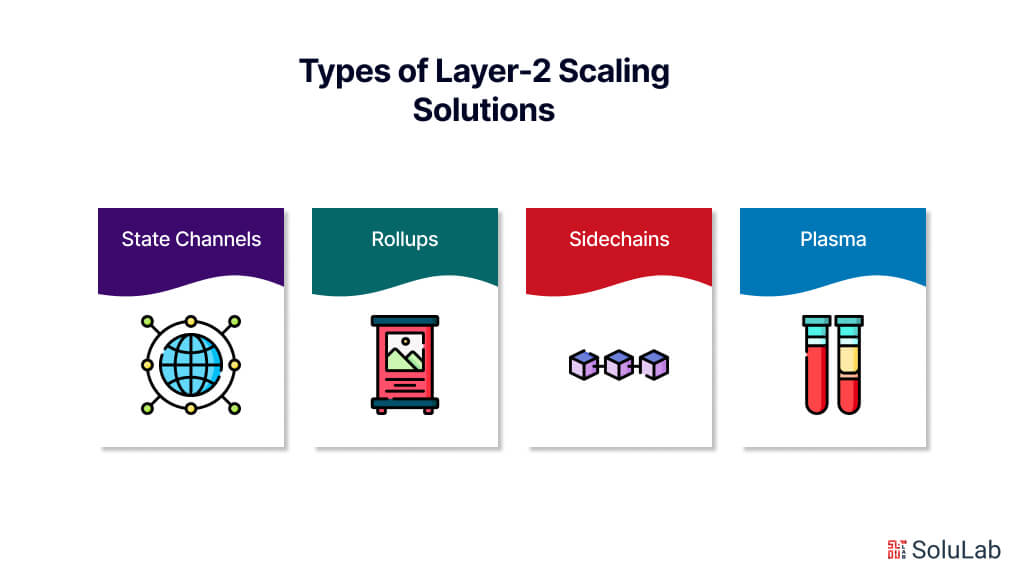
Layer-2 scaling encompasses various techniques and protocols designed to improve scalability through off-chain transaction processing and secondary protocols. Here are some common types of Layer-2 scaling solutions:
1. State Channels
State channels enable participants to conduct multiple transactions off-chain while preserving security and trustlessness through cryptographic mechanisms. Participants exchange signed messages off-chain, updating the state of their transactions, and settling the final outcome on the main chain when necessary. State channels are well-suited for use cases requiring frequent interactions and real-time transaction processing, such as micropayments and gaming.
2. Rollups
Rollups are a Layer-2 scaling solution for blockchain networks. They work by processing transactions off-chain, aggregating them into a single compressed data structure, and then periodically settling the aggregated data on the main blockchain. Rollups come in two main types: optimistic rollups, which rely on optimistic execution and dispute resolution, and zk-rollups, which use zero-knowledge proofs to provide cryptographic assurances of transaction validity without revealing sensitive data. Rollups significantly enhance blockchain scalability, reduce transaction costs, and improve overall network efficiency while maintaining security and trustlessness.
3. Sidechains
Sidechains are independent blockchains connected to the main blockchain, allowing for faster transaction processing and experimentation with different consensus mechanisms or features without congesting the main chain. Sidechains enable participants to transfer assets between the main chain and the sidechain, providing scalability benefits while maintaining interoperability with the main chain.
4. Plasma
Plasma is a framework for creating hierarchical tree structures of sidechains (child chains) anchored to the main blockchain (parent chain). Plasma enables high-throughput transaction processing by aggregating multiple transactions into blocks on the child chain and periodically settling the state on the main chain. Plasma is suitable for applications requiring high scalability and security, such as decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and tokenized assets.
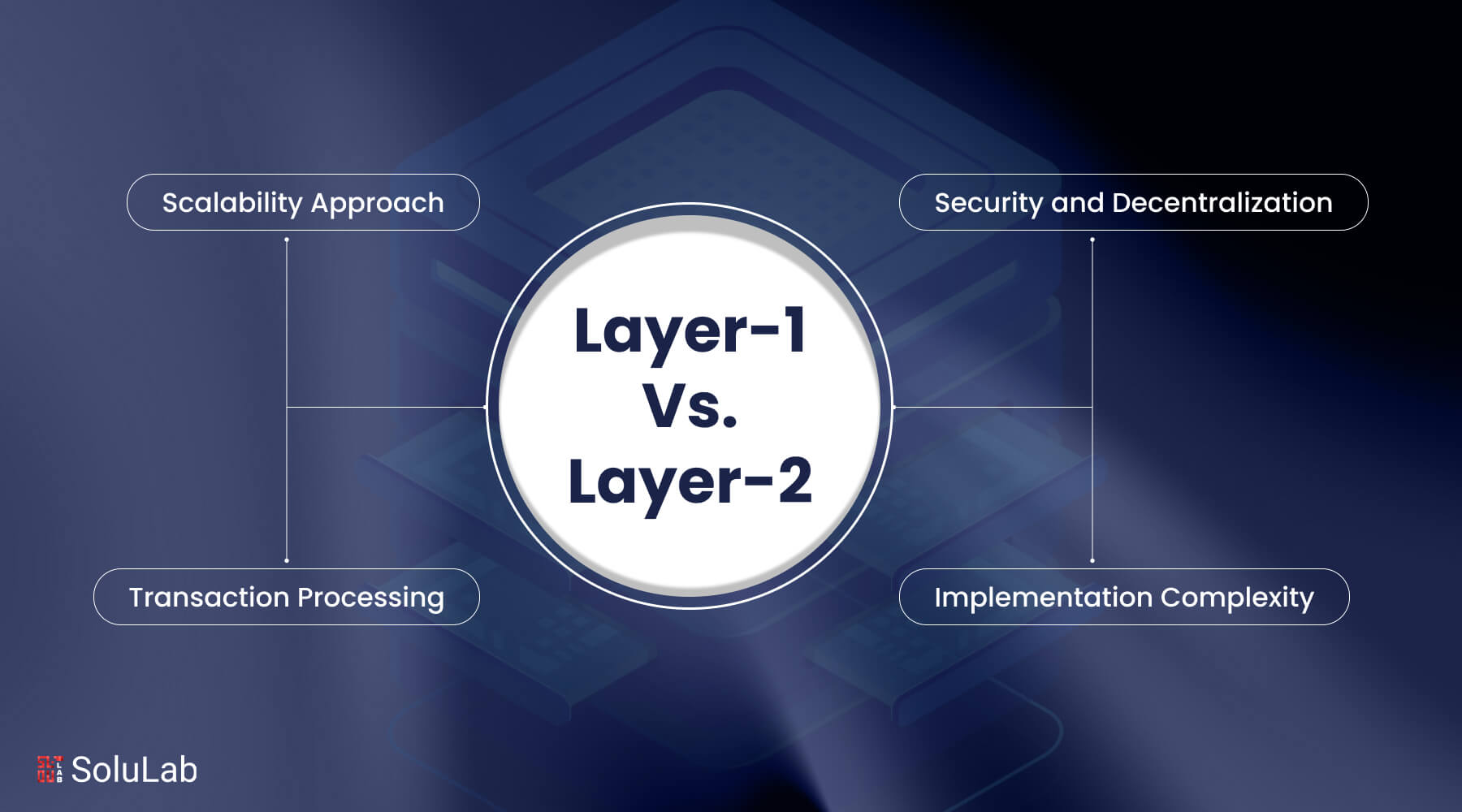
A Comparative Analysis Between Layer-1 Blockchains vs. Layer-2 Blockchains
Layer-1 and Layer-2 scaling solutions each offer unique approaches to addressing blockchain scalability challenges. Here’s a comparative analysis of their key characteristics:
Scalability Approach
- Layer-1: Layer-1 scaling solutions involve making fundamental changes to the underlying blockchain protocol to directly improve scalability. These solutions aim to optimize core protocol components, such as consensus mechanisms and block size limits, to increase transaction throughput and improve network performance.
- Layer-2: Layer-2 scaling solutions operate above the base protocol and focus on improving scalability through off-chain transaction processing and secondary protocols. By handling transactions off-chain or via secondary layers, Layer-2 solutions alleviate congestion on the main chain and enhance transaction throughput without modifying the underlying protocol.
Transaction Processing
- Layer-1: Transactions on Layer-1 are processed directly on the main chain, which may lead to congestion and slower transaction speeds during periods of high network activity. Layer-1 scaling solutions aim to improve transaction processing efficiency at the protocol level.
- Layer-2: Layer-2 solutions enable transactions to be processed off-chain or via secondary protocols, reducing congestion on the main chain and enabling faster transaction speeds. Off-chain processing allows for more scalable and cost-effective transactions, particularly for use cases requiring frequent interactions and real-time processing.
Security and Decentralization
- Layer-1: Layer-1 solutions typically prioritize maintaining or enhancing security and decentralization, as changes to the core protocol can impact the network’s integrity and trustlessness. Ensuring robust security and decentralization is crucial for maintaining user trust and network reliability.
- Layer-2: Layer-2 solutions introduce additional security considerations, such as channel disputes and data availability challenges, which must be addressed to maintain the integrity and trustworthiness of off-chain transactions. While Layer-2 solutions offer scalability benefits, ensuring security and decentralization remains paramount.
Implementation Complexity
- Layer-1: Implementing Layer-1 scaling solutions often requires making fundamental changes to the blockchain protocol, which can be complex and require coordination among network participants. Changes to the core protocol may also introduce risks and require extensive testing and validation.
- Layer-2: Layer-2 solutions may involve less complexity in implementation compared to Layer-1 solutions, as they operate above the base protocol and focus on improving scalability through off-chain processing. However, ensuring compatibility, security, and interoperability with the main chain and other Layer-2 solutions is still essential.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Layer-1 and Layer-2 Scaling
When evaluating whether to implement Layer-1 or Layer-2 scaling solutions, several factors should be considered:
1. Scalability Requirements: Assess the specific scalability needs of the blockchain network, including transaction throughput, latency, and cost considerations. Determine whether Layer-1 or Layer-2 solutions are better suited to address the scalability challenges based on the network’s requirements.
2. Security and Trustlessness: Consider the security and trustlessness implications of implementing Layer-1 versus Layer-2 scaling solutions. Evaluate the trade-offs between scalability, security, and decentralization, and prioritize solutions that maintain the integrity and reliability of the network.
3. Implementation Complexity: Assess the complexity and feasibility of implementing Layer-1 versus Layer-2 scaling solutions. Consider factors such as development effort, coordination among network participants, and risks associated with modifying the core protocol versus implementing off-chain solutions.
4. Use Case and Application Requirements: Consider the specific use cases and application requirements that the blockchain network aims to support. Evaluate whether Layer-1 or Layer-2 scaling solutions are better aligned with the performance, functionality, and user experience needs of the applications running on the network.
Use Cases Where Layer-1 or Layer-2 Scaling Might be More Suitable
The suitability of Layer-1 or Layer-2 scaling solutions depends on the specific use cases and requirements of the blockchain network. Here are some scenarios where each approach might be more suitable:
Layer-1 Scaling Use Cases
1. High-Volume Financial Transactions:
Blockchain networks supporting high-volume financial transactions, such as cryptocurrency exchanges or payment processing platforms, require fast and efficient transaction processing directly on the main chain. Implementing Layer-1 scaling solutions like sharding or consensus algorithm optimizations can increase transaction throughput and reduce latency, enabling the network to handle a larger volume of transactions without sacrificing security or decentralization. Layer-1 scaling solutions ensure that high-volume financial transactions are processed quickly and securely on the main chain, enhancing the overall efficiency and reliability of financial applications.
2. Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Protocols
DeFi protocols, including decentralized exchanges (DEXs), lending platforms, and liquidity pools, require fast and cost-effective transaction processing to support complex financial transactions and interactions. Enhancing Layer-1 scalability through protocol optimizations or consensus algorithm upgrades can improve transaction throughput and reduce transaction fees, making DeFi protocols more accessible and efficient for users. Layer-1 scaling solutions empower DeFi protocols to support a larger user base and handle a greater volume of transactions, fostering greater adoption and liquidity within the decentralized finance ecosystem.
Layer-2 Scaling Use Cases
1. Microtransactions and Micropayments
Applications requiring frequent microtransactions or micropayments, such as online gaming platforms, content monetization systems, or pay-per-use services, need fast and inexpensive transaction processing to provide a seamless user experience. Implementing Layer-2 scaling solutions like state channels or payment channels allows users to conduct off-chain transactions quickly and cost-effectively, reducing transaction fees and latency associated with on-chain transactions. Layer-2 scaling solutions enable applications to support microtransactions and micropayments at scale, unlocking new revenue streams and business models while minimizing transaction costs and delays for users.
2. Privacy-Preserving Applications
Applications handling sensitive data or requiring transaction privacy, such as healthcare record management, supply chain tracking, or identity verification systems, need robust privacy-preserving mechanisms to protect user confidentiality and data integrity. Leveraging Layer-2 solutions like zk-rollups, which use zero-knowledge proofs to provide cryptographic privacy guarantees, enables applications to maintain transaction privacy while ensuring transaction validity and integrity. Layer-2 scaling solutions enhance the privacy and confidentiality of transactions and data, enabling applications to comply with regulatory requirements and protect user privacy without sacrificing scalability or performance.
Which Blockchain Layer Will Rule the Future?
It is justifiable to assume that layer 2 blockchains will be the most widely used in the future given the facts provided above. They facilitate interoperability and increased blockchain adoption by offering cheaper transaction speeds. Although a layer 2 blockchain still requires a layer 1 to support it, it will prosper as long as it can maintain its increased efficiency and feature set.
But the solution is not that straightforward. The blockchain world is constantly expanding and changing at a fast pace. While Solana and other more recent third-generation blockchains provide hundreds of transactions per second, Cosmos’ distinctive network design allows for efficient interoperability and scalability. Ethereum is also going through major changes that will deal with its speed and scalability
Ultimately, layer 2 blockchains are significant because they address a gap in layer 1 blockchain development. Layer 2 scaling solutions might not be necessary if layer 1s can meet user demand on their own. If enough people choose layer 1 blockchains with interoperability and scalability built in, that will be determined over time.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the trade-offs of Layer 1 and Layer 2 blockchains must be understood in order to select the best option for your use case. Although Layer 1 blockchains offer a high degree of decentralization and security, they could have issues with scalability and transaction speed. However, Layer 2 blockchains can forgo decentralization and security in favor of speed.
Blockchain technology is continually developing, with new developments appearing on a regular basis. At the moment, layer 2 blockchains are the most widely used method for increasing scalability and cutting expenses. But it’s crucial to keep a watch on more recent third-generation blockchains since they’re expanding the scope of what can be done on Layer 1.
SoluLab, a leading blockchain development company, specializes in offering innovative solutions to both Layer-1 and Layer-2 scaling issues. We provide personalized solutions to improve the scalability and performance of blockchain networks by using our blockchain technology experience and unique approach. Our experienced blockchain engineers focus on Layer-1 protocol advancements like sharding and consensus algorithm optimizations, as well as Layer-2 scaling solutions like state channels and zk-rollups. Whether you want to improve the scalability of your blockchain network or deploy off-chain scaling solutions, SoluLab is your reliable partner. Contact us today to hire blockchain developers and maximize the potential of your blockchain project.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between Layer-1 and Layer-2 scaling solutions?
Layer-1 scaling solutions involve making fundamental changes to the underlying blockchain protocol to directly improve scalability, while Layer-2 scaling solutions operate above the base protocol and focus on improving scalability through off-chain transaction processing and secondary protocols.
2. How do Layer-1 scaling solutions improve blockchain scalability?
Layer-1 scaling solutions improve blockchain scalability by optimizing core protocol components, such as consensus mechanisms and block size limits, to increase transaction throughput and improve network performance directly at the protocol level.
3. What are some examples of Layer-2 scaling solutions?
Examples of Layer-2 scaling solutions include state channels, sidechains, Plasma, rollups, and other off-chain scaling techniques that enable faster and more cost-effective transactions by processing transactions off-chain or via secondary protocols.
4. What are the advantages of Layer-2 scaling solutions?
Layer-2 scaling solutions offer several advantages, including improved scalability, reduced transaction fees, faster transaction speeds, enhanced privacy, and the ability to support a larger volume of transactions without congesting the main chain.
5. How do I choose between Layer-1 and Layer-2 scaling solutions for my blockchain project?
When choosing between Layer-1 and Layer-2 scaling solutions, consider factors such as scalability requirements, security and decentralization, implementation complexity, and specific use cases and application requirements to determine which approach is more suitable for addressing your project’s scalability challenges.






