Overview
Data is the lifeline in every medicare system and can dramatically improve the efficiency of the system. Every industry is optimistic about blockchain but when it comes to healthcare system, there is skeptcism. Blockchain in healthcare today is a big transformation and a vibrant ecosystem is being developed. Along with government policy and compilance issues, there are headwinds fueled by those who may be reluctant to buy in. Technology is a Pandora box and once it has opened, it can’t be shut down. Thus the transformation of medical healthcare system is inevitable.
Emeregence of blockchain in the field of healthcare is an alternative to the existing slow and bloated system of various stakeholders unable to work together in real time. While implementation of blockchain between industry partners and companies can improve the interoperability and transparency, the widesread distrust among the stakeholders is a big blockade for the implementation in healthcare.
“I believe in huge potential for healthcare moving to a blockchain world,”
says Marta Pierkarska, director of ecosystem at Hyperledger.

Source: PWC
Who are the major stakeholders in the healthcare ecosystem?
- Hospitals, Medical Clinics, Specialized Health Care Centres
- Pharmaceutical/Chemist Shops
- Hospital Administration and IT Infrastructure
- Insurance Providers
- Patients and their family members
- Government verification/regulatory systems
Let’s understand the implementation of blockchain applications in a simple medical system.
What are the major benefits of blockchain in the medical healthcare?
Advantages of blockchain in healthcare is based on the core competencies of the blockchain platform –
- Immutable store of informationand Super-Secure
- Decentralization of transactions
- Gamification-enabled system
Let’s understand these core competencies in a more detailed way –
Immutable store of information
The notorious NHS hacking incident by WannaCryhas exposed the vulnerabilities in open daylight. It has crippled more than 300,000 computers all over the world. Medical professionals and organizations can freely collaborate with the data in real-time without being threatened from pervasive hacking and dangerous ransomware.
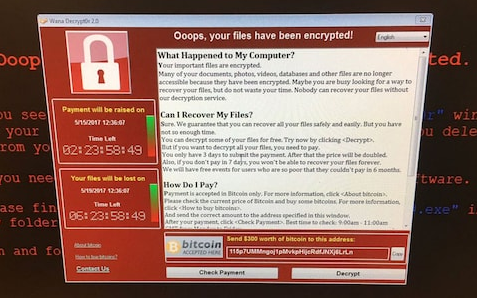
A computer at Greater Preston CCG Credit: @fendifille/Twitter
Once properly implemented, the blockchain system will enable any barrier in the free flow of information and remove any necessity to go over the same set of information from time-to-time.
Read More-: How to use blockchain and cryptos to improve dental practice?
Decentralization of transactions
Multiple stakeholders are involved across the healthcare industry using the distributed ledger infrastructure which is decentralised and more efficient than existing and securing the data. However, due to regulations like HIPPA, PIPEDA, GDPR etc. there is a necessity for a few strong intermediate diagnostic centers, research labs and medical registries to oversee the entire ecosystem. As the intermediaries are less in number, the unnecessary delays between the patients and service provider will be considerably reduced.
Built-in Gamification
Presently, insurance and healthcare companies provide incentives to policyholders/patients for leading a better lifestyle. Reward points are there for walking, exercising, meditation hours etc. This also incentivise healthcare stakeholders to undertake activities that ensures the well-being of the patients in the longer run. Users who actively share their health data with the medical community will be given perks.
Gamification techniques have proven to be effective for specific medical cases where positive behavior reduce friction between the components and the end users get the maximum benefit. However, it is still not used at scale.
Implementation of Blockchain: Use Cases
1-Patients with personalized prescriptions
Patients are generally used as a collective group of individuals with specific set of symptoms for a particular disease in most of the cases. However, if extensive diagnostics are carried out, then there may be other reasons to explain the condition. Such extensive diagnostic testing will take too much time and resources.
However, when patients data is collected from their day-to-day activities it become much easier for the medical community to carry out proper research before advising a proper set of medicines.
Read More-: How Blockchain Projects Battle for Healthcare Data Protection
2-Industry Proof-of-Concept and Authenticity of Drugs
In the pharmaceutical industry medicines are regularly returned by the wholesaler when it is excess supply. Now all these shipments worth almost $7-10 billion.
In order to re-sell the medicines in the open market again, the companies need to go through several compliances. All drugs need to be serialized and barcoded so that their sales and activity during transit can be tracked.
A time-stamp need to be added every time the drug package change hands until it reaches the end customer. This is a robust problem as the package need to be tracked across boundaries and need to comply with laws of various countries.
Industry Example
SAP has developed such a system for Merck Sharp &Dohme (US) that helps them to accelerate the supply chain by 10x.
3-Tracking Users’ Consent during Clinical Trials
In US, the FDA conducts pharmaceutical tests for the companies and receive funding for these kind of research tests.
Here we can see a clear conflict of interests where FDA is getting funded from those companies where it also has the responsibility to certify the new drugs after trials.
Using blockchain in healthcare, patients, healthcare workers, government and other stakeholders can keep a check on various activities. The collected data will also bring down the cost of hiring clinical trial patients and companies has the information to select a sampled set of patients with a particular set of health parameters for a drug trial.
The decentralized property of blockchain empower the patients, grant control over their data, and allow them to give consent and its revocation.
Industry example
Exochain – a startup working pharma blockchain sector is working towards creating an ecosystem on blockchain where it can be automated and patients’ health records and consent are easy to manage.
Source: Exochain
Cybersecurity in Internet of Medical Things
Collected data automatically gets stored at various locations in blockchain technology. To maintain the accountability and auditability, private blockchain is used which authorize users to make access to the network. The private blockchain networks take user’s sign before they are enabled to make any change to the database.
Blockchain also provides integrity solutions at its core. It maintains the chain of events (you can say log to each transaction), even if anyone deletes or update the data over the network. This is very helpful to scale up a IoT Infrastucture and reduce time and cost.
Read More-: 5 healthcare startups monetizing health and wellness via blockchain
Challenges to Blockchain in Healthcare
Several challenges are there to blockchain adoption in healthcare. The number of blockchain professional are few and there is a high compliance resistance. Even if these problems are resolved then there is a huge initial cost involved that is still funded by private stakeholders where they consider every investment from the point of good profit. As the technology advances, technical challenges like the speed of processing and the massive duplication of data will be resolved. The main obstruction is the ownership of the blockchain whether it will stay in the private or government hands. As a potential solution, Estonia’s government-backed blockchain initiative, it allow companies to build dapps and the data infrastructure is secured due to government’s role. Therefore, Estonia is slowly becoming the powerhouse of blockchain startups in Europe. It is the only country where citizens can vote for the government online.
WHO WILL PAY?
Even though the US government has funded several blockchain initiatives, uncertainty persists over who will ultimately fund blockchain’s implementation costs.
Who will fund the other infrastructure?
Companies or consortium of commerce bodies and if they do how much ownership or real power they will actually hold.