Artificial Intelligence (AI) is one of our time’s most transformative forces in this digital era. From virtual assistants to autonomous vehicles, AI has seamlessly integrated into our daily lives, revolutionizing industries and reshaping societal norms. However, with great power comes great responsibility, and the ethical implications of AI’s proliferation cannot be overstated. As AI systems become increasingly sophisticated and pervasive, we must adopt responsible practices to ensure ethical development and deployment.
AI’s emergence presents a wide range of benefits as well as difficulties, so it’s critical to move cautiously and strategically into this new digital frontier. A comprehensive approach to AI governance that prioritizes openness, responsibility, equity, privacy, and safety is embodied in responsible AI practices. By abiding by these guidelines, we may use AI’s potential to promote good while minimizing risks and negative effects. We will examine the importance of moral AI practices, dig into important concepts, and talk about the issues and factors influencing AI governance going forward in this guide to responsible AI.
So, let’s get started!
What is Responsible AI?
Responsible AI refers to the ethical development, deployment, and use of artificial intelligence technologies in a manner that upholds ethical principles and values. At its core, responsible AI embodies a commitment to transparency, accountability, fairness, privacy, and safety throughout the AI lifecycle. This entails considering the ethical implications of AI algorithms and systems, addressing biases and discrimination, protecting individuals’ privacy rights, and ensuring the safety and reliability of AI-driven outcomes. Responsible AI practices aim to mitigate potential risks and harms associated with AI technologies while maximizing their positive impact on society and promoting equitable access to AI-driven innovations.
Key to understanding responsible AI is recognizing the intersection of technology and ethics. AI ethics encompasses a broad spectrum of considerations, including fairness, transparency, accountability, privacy, and human autonomy. Responsible AI requires thoughtful deliberation and decision-making to navigate complex ethical dilemmas inherent in AI development and deployment. By integrating ethical principles into every stage of the AI lifecycle, from data collection and algorithm design to deployment and monitoring, we can foster trust among stakeholders, mitigate potential risks and harms, and ensure that AI technologies benefit society responsibly.
What is Ethical AI?
Ethical AI refers to the development, deployment, and use of artificial intelligence technologies in a manner that aligns with moral principles and values. At its core, ethical AI seeks to uphold human dignity, promote fairness and justice, and mitigate potential risks and harms associated with AI-driven systems. This involves adhering to ethical frameworks and guidelines that prioritize transparency, accountability, fairness, privacy, and safety throughout the AI lifecycle. Ethical AI goes beyond technical considerations to encompass broader societal impacts, including issues such as bias and discrimination, societal inequalities, and human autonomy. By integrating ethical principles into AI design and decision-making processes, ethical AI aims to ensure that AI technologies benefit individuals and society while upholding fundamental rights and values.
Key to understanding ethical AI is recognizing the complex interplay between technology and human values. Ethical AI requires thoughtful deliberation and decision-making to navigate ethical dilemmas inherent in AI development and deployment. This involves balancing competing interests and priorities, considering the potential consequences of AI-driven decisions on individuals and communities, and promoting transparency and accountability in AI systems. Ethical AI also entails ongoing reflection and evaluation to adapt to evolving ethical standards and societal norms, ensuring that AI technologies continue to uphold ethical principles and contribute to positive social outcomes. Ultimately, ethical AI strives to create a future where AI technologies enhance human well-being, empower individuals, and promote a more just and equitable society.
Ethical Uses of AI
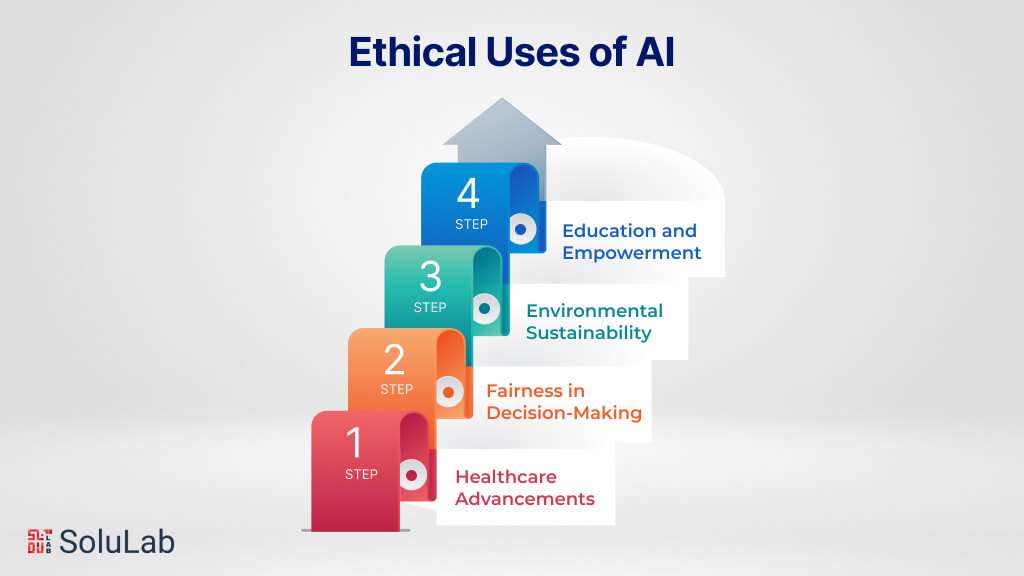
Ensuring the ethical use of AI is paramount to harnessing its potential for positive impact while mitigating potential risks and harms. Ethical use of AI entails deploying AI technologies in a manner that upholds moral principles and respects fundamental human rights. Here, we delve into key considerations for ensuring the ethical uses of AI:
1. Healthcare Advancements: Ethical AI applications in healthcare hold the promise of improving patient outcomes, enhancing diagnostics, and personalizing treatment plans. From medical imaging analysis to predictive analytics for disease prevention, AI-driven innovations have the potential to revolutionize healthcare delivery. However, ethical considerations such as patient privacy, data security, and informed consent must be carefully addressed to ensure that AI technologies benefit patients without compromising their rights or autonomy.
2. Fairness in Decision-Making: Ethical AI promotes fairness and transparency in decision-making processes, particularly in contexts such as lending, hiring, and criminal justice. By mitigating biases and ensuring algorithmic fairness, AI-driven decision-making can help reduce discrimination and promote equality. Ethical considerations such as fairness metrics, bias detection, and algorithmic transparency play a crucial role in ensuring that AI systems make decisions that are equitable and just.
3. Environmental Sustainability: Ethical AI can contribute to environmental sustainability by optimizing resource allocation, reducing energy consumption, and mitigating environmental risks. From optimizing energy grids to predicting climate change impacts, AI-driven solutions have the potential to address pressing environmental challenges. Ethical considerations such as environmental impact assessments, ethical sourcing of data, and stakeholder engagement are essential for ensuring that AI technologies promote sustainability without causing harm to the environment or communities.
4. Education and Empowerment: Ethical AI applications in education have the potential to empower learners, personalize learning experiences, and improve educational outcomes. From adaptive learning platforms to intelligent tutoring systems, AI-driven innovations can enhance student engagement and support educators in delivering tailored instruction. Ethical considerations such as data privacy, algorithmic transparency, and inclusive design are critical for ensuring that AI technologies promote equity and empower learners from diverse backgrounds.
The ethical use of AI encompasses a range of considerations, including healthcare advancements, fairness in decision-making, environmental sustainability, and education empowerment. By prioritizing ethical principles such as fairness, transparency, and accountability, we can harness the transformative potential of AI technologies to create a more equitable, sustainable, and inclusive future for all.
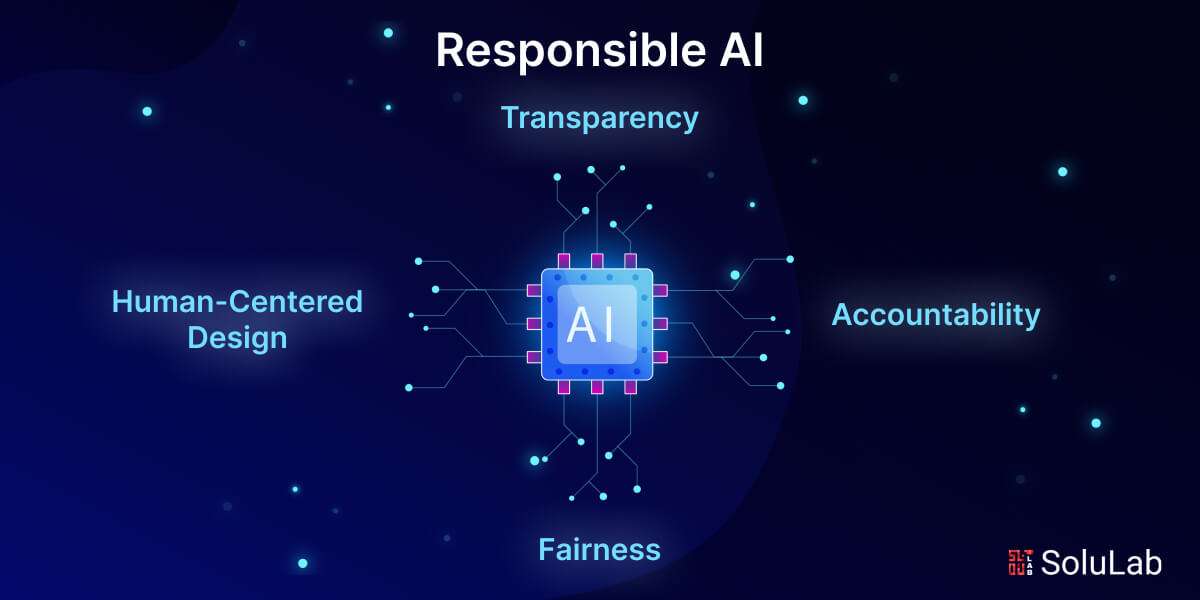
The Foundations of Responsible AI
Transparency and accountability are the fundamental tenets of responsible AI, which is essential to use AI responsibly. These guidelines aid in the development of morally sound, socially conscious, and efficient AI systems.
1. Transparency
The foundation for fostering mutual respect and understanding between AI systems and those who utilize them is transparency. The ‘why,’ ‘how,’ and ‘what’ of AI choices and functions are explained. As AI systems make judgments that impact more and more facets of society, including employment, healthcare, and personal privacy, transparency becomes essential. Users are better able to comprehend and have faith in transparent AI, which encourages wider adoption and moral use.
Transparency implementation in AI requires many phases. Making sure that the core algorithms and data handling methods are transparent is the first step in properly describing AI processes and choices. As demonstrated by Google’s AI Principles, which highlight the significance of justice, privacy, and safety in AI research, this is further enhanced by putting ethical standards and governance frameworks into place.
Utilizing interpretable machine learning models is one of the tools and techniques that promotes transparency in AI by making it simpler to comprehend the decision-making process. To help with this process, Google, for example, has created a TensorFlow Constrained Optimization Library and a Responsible AI toolbox. Furthermore, interacting with a variety of stakeholders and carrying out thorough ethical evaluations are essential to guaranteeing that AI systems remain transparent and compliant with social standards.
2. Accountability
AI accountability is a crucial factor that determines the ethical implications and reliability of AI systems. In AI, accountability guarantees a distinct accountability for the results of AI systems. It is essential because it preserves moral principles and confidence in artificial intelligence, particularly as these systems become increasingly ingrained in our daily lives and ways of making decisions. Accountability in AI also guarantees responsible usage of AI technologies in compliance with legal and ethical requirements.
There are several ways to create accountability in AI. This supervision covers decision-making and the creation and application of AI systems in a transparent manner. AI systems are created and applied ethically and responsibly thanks to this oversight.
Organizations may use AI governance frameworks and responsible AI training modules, as proposed by Microsoft Learn. These lessons provide insights into responsible AI ideas and practices, assisting enterprises in better understanding and implementing responsibility in their AI systems.
3. Fairness
Fairness in AI is a critical component of Responsible AI, assuring equal outcomes and preventing biases in AI systems.
Fairness in AI addresses the requirement to prevent biased outputs from AI systems. This is significant because AI biases can result in prejudice and unjust treatment of specific groups, jeopardizing the legitimacy and ethical position of AI applications. Maintaining fairness in AI helps to develop confidence among users and stakeholders.
Fairness in AI is implemented in phases, beginning with the design of the AI system and continuing through its evolution after deployment. Microsoft, for example, offers an AI fairness checklist that guides users through steps such as envisioning, prototyping, building, launching, and evolving. This checklist offers due diligence efforts at each level to reduce unfairness in the system.
There are several methods and approaches available to ensure justice in AI. Microsoft’s Fairlearn Python module is an example of how data scientists and developers may examine and improve the fairness of AI systems. Azure Machine Learning offers tools for understanding and improving AI system behavior, including model interpretability and counterfactual what-if scenarios, which help in fairness evaluation.
4. Human-Centered Design
Human-centered design in AI systems considers user experience and varied viewpoints to guarantee that AI technologies are helpful and equitable to people. This method for AI system design is important for a variety of reasons.
AI systems are becoming more common in all parts of society, from healthcare to transportation. However, there remains a gap in the design process since many AI systems have yet to thoroughly examine their influence on people. Human-centered design attempts to create AI systems that benefit users, communities, and society.
Human-centered design in AI requires many fundamental methods. First, systems must be designed and analyzed at three levels: user, community, and society. For example, in the case of self-driving automobiles, designers must consider drivers’ requirements, the influence on non-drivers such as cyclists and pedestrians, and larger social implications like as traffic congestion.
Utilizing human-centered metrics, that go beyond standard measures like accuracy, is one of the key practices of human-centered design. Given the greater power dynamics that underpin these measurements, they should represent what people require and value.
Human-centered design in AI requires many fundamental methods. First, systems must be designed and analyzed at three levels: user, community, and society. For example, in the case of self-driving automobiles, designers must consider drivers’ requirements, the influence on non-drivers such as cyclists and pedestrians, and larger social implications like as traffic congestion.
Utilizing human-centered metrics, that go beyond standard measures like accuracy, is one of the key practices of human-centered design. Given the greater power dynamics that underpin these measurements, they should represent what people require and value.
Implementing Responsible AI Practices
Implementing responsible AI practices requires a concerted effort across various stakeholders, including researchers, developers, policymakers, and end-users. Ethical considerations should be integrated into every stage of the AI lifecycle, from conception to deployment and beyond. Here’s a detailed breakdown of how responsible AI practices can be implemented effectively:
- Ethical AI Design and Development: The foundation of responsible AI begins with ethical design and development practices. This involves incorporating ethical considerations into the design process, such as identifying potential biases in training data, ensuring transparency in algorithmic decision-making, and prioritizing fairness and inclusivity. Developers should also implement robust testing procedures to evaluate AI systems for ethical implications and biases before deployment.
- Ethical Data Collection and Usage: Data lies at the heart of AI systems, making it crucial to prioritize ethical data collection and usage practices. This includes obtaining informed consent from individuals whose data is being collected, ensuring data privacy and security through encryption and anonymization techniques, and adhering to relevant data protection regulations such as GDPR or CCPA. Additionally, developers should be mindful of the potential consequences of data misuse and take steps to minimize risks accordingly.
- Fairness and Bias Mitigation: Addressing biases in AI algorithms is paramount to ensuring fairness and equity in AI-driven decision-making. Developers should employ techniques such as bias detection and mitigation algorithms, diverse training data representation, and regular audits to identify and mitigate biases throughout the AI lifecycle. Furthermore, ongoing monitoring and evaluation are essential to ensure that AI systems remain fair and unbiased in real-world applications.
- Transparency and Explainability: Transparency and explainability are essential components of responsible AI, enabling users to understand how AI systems work and why specific decisions are made. Developers should strive to make AI systems transparent and interpretable by providing clear explanations for algorithmic decisions and making underlying data and algorithms accessible to relevant stakeholders. This fosters trust and accountability, allowing users to assess the reliability and fairness of AI-driven outcomes.
- Privacy and Data Security: Protecting the privacy and security of individuals’ data is paramount in responsible AI practices. Developers should implement robust data security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and data anonymization, to safeguard sensitive information from unauthorized access or misuse. Additionally, developers should ensure compliance with relevant privacy regulations and standards, such as GDPR or HIPAA, to uphold individuals’ rights to privacy and data protection.
- Safety and Reliability: Ensuring the safety and reliability of AI systems is critical to mitigating potential risks and harms. Developers should prioritize safety considerations in the design and development of AI systems, including fail-safe mechanisms, robust testing procedures, and adherence to industry standards and best practices. Additionally, developers should conduct thorough risk assessments and scenario planning to anticipate and mitigate potential safety hazards associated with AI deployment in real-world environments.
By implementing these responsible AI practices, skilled developers can uphold ethical standards and mitigate potential risks and harms associated with AI technologies. Through collaboration, transparency, and a commitment to ethical principles, we can harness the transformative power of AI to drive positive change and build a more inclusive and equitable future for all.
Benefits of Responsible AI
Adopting responsible AI practices not only aligns with ethical principles but also yields numerous benefits for individuals, organizations, and society at large.
1. Enhanced Trust and Credibility: Upholding a robust AI code of ethics builds trust among users and stakeholders. When individuals perceive that AI systems operate transparently, accountably, and fairly, they are more likely to trust and engage with these technologies. This trust fosters positive relationships between users and AI-driven systems, ultimately enhancing credibility and acceptance.
2. Fairness and Equity: Responsible AI practices prioritize fairness and equity by mitigating biases and discrimination in AI algorithms. By proactively addressing biases in data and algorithms, responsible AI ensures that AI-driven decisions are fair and unbiased, regardless of individuals’ demographic characteristics. This commitment to fairness promotes inclusivity and equality, benefiting marginalized groups and promoting social cohesion.
3. Privacy Protection and Data Security: Embracing responsible AI includes safeguarding individuals’ privacy and ensuring data security. By implementing robust data protection measures and adhering to privacy regulations, organizations demonstrate their commitment to respecting individuals’ privacy rights. This not only enhances trust among users but also minimizes the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access, safeguarding sensitive information from exploitation or misuse.
4. Compliance and Risk Mitigation: Adhering to ethical AI principles helps organizations comply with legal and regulatory requirements governing AI technologies. By following established AI codes of ethics and standards, organizations mitigate legal risks and liabilities associated with non-compliance. This proactive approach to risk management protects organizations from potential legal challenges and reputational damage, ensuring long-term sustainability and resilience.
5. Positive Social Impact: Responsible AI practices contribute to positive social impact by addressing societal challenges and promoting the well-being of communities. By leveraging AI technologies for social good initiatives, organizations can address pressing issues such as healthcare disparities, environmental sustainability, and access to education. This alignment with social values and priorities fosters goodwill and strengthens organizational reputation, ultimately benefiting society as a whole.
Thus, the benefits of responsible AI extend beyond ethical considerations to encompass enhanced trust and credibility, fairness and equity, privacy protection and data security, compliance and risk mitigation, and positive social impact. By embracing responsible AI practices and adhering to established AI codes of ethics, organizations can maximize the potential of AI technologies while promoting ethical values and contributing to a more equitable and inclusive future.
Challenges of Using Responsible AI

Adopting Responsible AI presents various problems, including data bias, a lack of legislation, and technical limits. These issues are more obvious when creating and implementing generative AI systems.
-
Data Bias
One of the most major issues is data bias. Machine learning models, particularly those employed in AI, learn from previously acquired data from the actual world. This data may contain pre-existing prejudices based on race, gender, religion, or other qualities that the AI may learn or reinforce.
-
Lack of Regulation
Another difficulty is the necessity for extensive regulation of artificial intelligence. While self-regulation is important, such as Google’s AI Principles, governments, universities, and civil society must also provide balanced direction. This comprises rules and laws that encourage advancement while lowering the possibility of misuse. Developing and implementing policies needs collaboration from several parties.
-
Technical Limitations
Technical limitations also provide a difficulty, notably in the analysis of data by AI systems. AI models frequently require assistance recognizing the distinction between correlation and causation. Because of this shortcoming, AI systems may reach inaccurate conclusions and take inappropriate actions. Improving the interpretability of AI systems is crucial for maintaining their intended functionality and user benefits.
-
Vulnerabilities in AI Systems
Responsible generative AI must handle particular flaws, such as data used for training poisoning and model denial of service assaults. Proactive steps and testing procedures can assist in reducing these hazards. It simulates assaults on AI systems in order to detect and resolve weaknesses before they are exploited in real-world circumstances.
-
Limitations of Datasets and Models
Finally, the constraints of datasets and models underline the importance of cautious planning in AI development. AI interpretations based on poor data or wrong assumptions might provide undesirable results. Understanding the difference between correlation and causality in AI interpretations is critical for creating systems that make ethical and correct judgments.
Final Words
Following responsible AI principles while creating and implementing AI technology is critical. It fosters trust, ensuring that AI’s benefit is achieved efficiently and responsibly. To overcome perceived hazards linked with AI, responsible AI concepts must be realistically implemented rather than just defined.
Organizations and people must be aware and involved with the latest advances in AI ethics and regulations. Understanding new legislation and ethical issues is critical as the AI environment changes. This involves comprehending the effects of AI choices on people’s lives, addressing concerns such as prejudice and discrimination, and ensuring openness and accountability in AI systems.
SoluLab, as an AI development company, is committed to promoting Responsible AI by adhering to ethical principles and best practices in AI development and deployment. We prioritize transparency, fairness, and accountability in our AI solutions, ensuring that they uphold human rights, mitigate biases, and protect individuals’ privacy. Our team of AI experts is dedicated to integrating responsible AI practices into every stage of the AI lifecycle, from data collection and algorithm design to deployment and monitoring. By partnering with SoluLab, clients can trust that their AI initiatives will not only deliver innovative solutions but also uphold ethical standards and contribute to positive social impact. Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you navigate the ethical complexities of AI and build responsible AI solutions for a better future.
FAQs
1. What is Responsible AI, and why is it important?
Responsible AI refers to the ethical development, deployment, and use of artificial intelligence technologies. It is crucial because it ensures that AI systems operate transparently, accountably, and fairly, mitigating potential risks and harms associated with AI technologies while maximizing their positive impact on society.
2. What are the key principles of Responsible AI?
The key principles of Responsible AI include transparency, accountability, fairness, privacy, and safety. These principles guide the ethical design, development, and deployment of AI technologies, ensuring that they uphold human rights, mitigate biases, and promote trust among users and stakeholders.
3. How can organizations implement Responsible AI practices?
Organizations can implement Responsible AI practices by integrating ethical considerations into every stage of the AI lifecycle, from data collection and algorithm design to deployment and monitoring. This includes prioritizing transparency, fairness, and accountability in AI systems and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations and standards.
4. What are the potential benefits of adopting Responsible AI practices?
Adopting Responsible AI practices can yield numerous benefits, including enhanced trust and credibility, fairness and equity, privacy protection and data security, compliance and risk mitigation, and positive social impact. By prioritizing ethical principles and values, organizations can maximize the potential of AI technologies while promoting ethical values and contributing to a more equitable and inclusive future.
5. How can SoluLab help organizations navigate Responsible AI?
SoluLab is committed to promoting Responsible AI by adhering to ethical principles and best practices in AI development and deployment. We prioritize transparency, fairness, and accountability in our AI solutions, ensuring that they uphold human rights, mitigate biases, and protect individuals’ privacy. Our team of experts is dedicated to integrating responsible AI practices into every stage of the AI lifecycle, providing clients with innovative and ethical AI solutions that contribute to positive social impact.






