
A recent Deloitte survey revealed that 78% of participating companies have implemented or are in the process of implementing Robotic Process Automation (RPA). Additionally, 16% of respondents plan to adopt RPA robotic process automation in the near future. A 2022 survey conducted by Robocorp indicated that 67% of its respondents had invested in RPA technologies during 2021. In terms of market valuation, the global RPA market was estimated to be worth $5.63 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to experience significant growth, reaching $54.57 billion by 2032, representing an impressive yearly growth rate of 28.7%.
RPA’s roots can be traced back to the 1980s and 1990s when macro technologies for automating tasks in applications like Excel were developed. In the 1990s, RPA evolved further with the automation of user interface testing. The term “RPA” was coined in 2012, and its popularity exploded in 2018. RPA is particularly useful for organizations with complex systems that need to interact seamlessly. Traditional automation software would require human intervention to complete tasks, whereas RPA technology can adapt to interact with systems without human assistance.
What is Robotic Process Automation?
Robotic process automation (RPA) is a technology that simulates human interactions with software to perform high-volume, repeatable tasks. It involves creating software programs or bots that can log into applications, input data, complete tasks, and transfer data between applications. RPA automates repetitive business processes in industries such as banking, IT, human resources, and healthcare, making them faster and more efficient.
RPA is gaining popularity because it offers several benefits:
- Reduced costs: RPA bots can automate tasks that would otherwise require human labor, resulting in significant cost savings.
- Streamlined processing: RPA bots can process large volumes of data quickly and accurately, improving operational efficiency.
- Enhanced customer experiences: RPA can help organizations provide better customer service by automating routine tasks and freeing up human employees to focus on more strategic initiatives.
When combined with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, RPA can capture more context from the content it’s working with. This includes reading text or handwriting using optical character recognition (OCR), extracting entities like names, invoice terms, or addresses using natural language processing (NLP), and capturing more context from images, such as automatically estimating accident damage in an insurance claim picture.
Why Do Companies Invest in RPA?
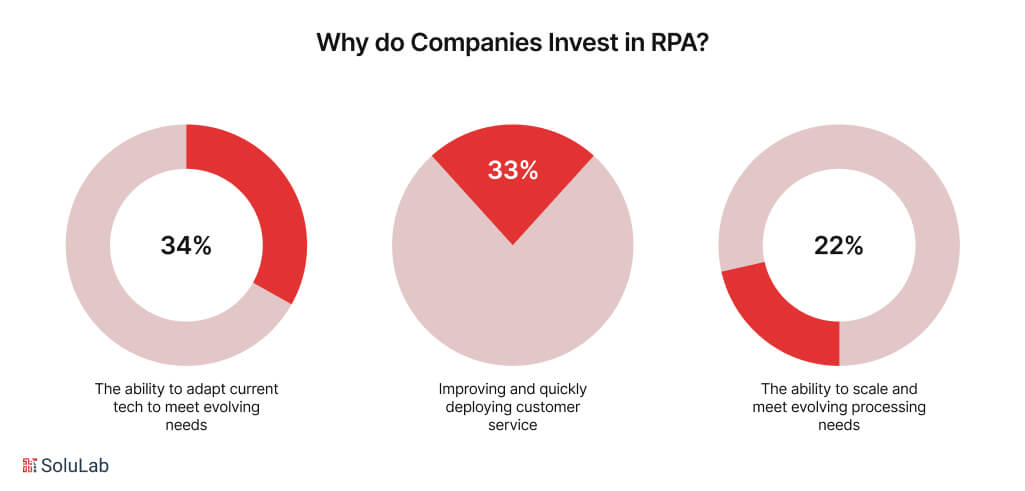
Companies invest in Robotic Process Automation (RPA) to enhance efficiency, reduce operational costs, and improve accuracy across various business processes. By automating repetitive and rule-based tasks, RPA allows organizations to free up human resources for more strategic activities, leading to increased productivity. Additionally, RPA ensures consistency in task execution, minimizes errors, and provides scalability, making it easier for businesses to adapt to changing demands. Investing in RPA also accelerates process times, enhances compliance with regulations, and offers a quick return on investment (ROI), making it a strategic choice for companies aiming to stay competitive.
How Does RPA Work?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) mimics human interaction with software applications. It differs from automation tools like APIs and low-code development by replicating how humans execute computerized processes. Simple RPA bots are created by recording user clicks and keystrokes. These basic recordings serve as templates for more advanced bots that can adapt to changes. More sophisticated RPA tools use machine vision to interpret on-screen elements and adjust accordingly. Hybrid bots record existing processes and dynamically generate workflow automation. RPA tools combine the simplicity of RPA development with the scalability of workflow automation.
Legacy enterprise systems with RPA may require front-end integrations if back-end systems are inaccessible. Process mining and task mining tools can capture business process workflows as templates for RPA automation. RPA tools integrate with other systems and include orchestration and administration tools for configuration, monitoring, and security. RPA tasks can be run attended (responding to employee requests) or unattended (running on a schedule). RPA tools can be enhanced with AI modules like OCR, machine vision, natural language understanding, or decision engines, creating intelligent process automation. These capabilities may be packaged into cognitive automation modules tailored to specific industries or business processes.
RPA and its Industries
In various industries, RPA (Robotic Process Automation) finds extensive application, especially in sectors characterized by repetitive tasks. Key industries leveraging RPA include insurance, banking, finance, healthcare, and telecommunications. These industries benefit from RPA’s ability to automate routine and repetitive processes, enhancing efficiency and accuracy. Some examples include the following:
- Finance: Robotic automation process automates financial processes like governance, account reconciliation, invoice processing, payment exchange, account opening/closing, audit request management, and insurance claim processing, resulting in improved efficiency and accuracy.
- Supply Chain Management: Organizations leverage RPA to automate data entry, procurement, predictive maintenance, order processing, and payments for after-sales service support, shipment tracking, and inventory level monitoring, leading to optimized supply chain operations.
- Telecommunications: Telecommunications companies employ RPA to configure new services and billing systems for new accounts, as well as gather data from multiple sources to troubleshoot equipment outages and anticipate potential issues, enhancing customer satisfaction and network reliability.
- Banking: Banks utilize robotic process automation RPA to automate customer onboarding, account closing, customer service, credit card processing, and fraud detection, providing faster and more secure banking services.
- IT: Robotic process automation RPA facilitates data collection, regulatory compliance, automated network management, data transformations, and onboarding/offboarding processes in the IT sector, streamlining operations and ensuring data integrity.
- Human Resources (HR): HR teams leverage RPA for recruiting, employee onboarding/offboarding, training, employee data management, expense management, employee information updates, and timesheet submissions, enhancing HR efficiency and accuracy.
- Insurance: In the insurance industry, RPA automates claims processing, regulatory compliance, fraud detection, customer service, and policy administration/cancellations, improving the overall customer experience and reducing operational costs.
- Healthcare: RPA robotic process automation in healthcare automates appointment scheduling, account management, claims administration, billing, regulatory compliance, electronic record management, and data processing, ensuring accurate and efficient patient care.
- Customer Service: RPA enhances customer service by automating contact center tasks such as e-signature verification, scanned document uploading, and information verification for automatic approvals or rejections, resulting in faster resolution times and improved customer satisfaction.
- Accounting: Organizations employ robotics process automation for general accounting, operational accounting, transactional reporting, and budgeting, leading to increased accuracy, timeliness, and efficiency in financial operations.
Benefits Of RPA
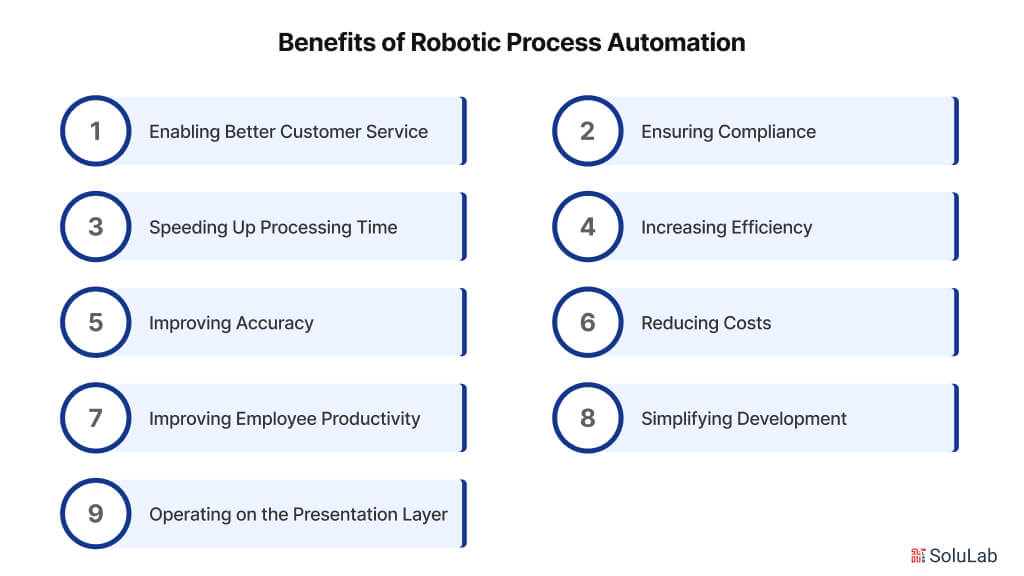
Robotic process automation technology can help organizations on their digital transformation journeys by doing the following:
1. Enabling Better Customer Service:
RPA can streamline customer service processes, allowing businesses to respond to customer inquiries faster and more efficiently. This can improve customer satisfaction and loyalty. For example, RPA bots can be used to automate tasks such as answering FAQs, processing customer orders, and tracking shipments. This can free up customer service representatives to focus on more complex and value-added tasks, such as building relationships with customers and resolving complex issues.
2. Ensuring Compliance:
RPA can help businesses stay compliant with regulations and compliance standards by automating tasks such as data entry, document processing, and reporting. This can reduce the risk of fines and penalties. For example, robotic process automation services bots can be used to automate the process of collecting and reporting customer data, such as names, addresses, and phone numbers. This can help businesses comply with data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
Check Out Our Blog: Generative AI for Compliance
3. Speeding Up Processing Time:
RPA can dramatically speed up processing time for tasks such as invoice processing, order fulfillment, and claims processing. This can improve operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. For example, RPA bots can be used to automate the process of extracting data from invoices and purchase orders. This can help businesses process invoices faster and get paid sooner.
4. Increasing Efficiency:
RPA can increase efficiency by automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks. This can free up employees to focus on more strategic and value-added activities. For example, RPA bots can be used to automate tasks such as data entry, data processing, and reporting. This can free up employees to focus on more creative and innovative tasks, such as developing new products and services.
5. Improving Accuracy:
RPA can improve accuracy by eliminating the risk of human error. This is especially important for tasks that require precision and attention to detail. For example, robotic automation process bots can be used to automate the process of calculating taxes and discounts. This can help businesses avoid errors that could result in lost revenue or fines.
6. Reducing Costs:
RPA can reduce costs by decreasing manual and repetitive tasks. This can free up resources that can be invested in other areas of the business. For example, robotics process automation bots can be used to automate the process of collecting and processing expense reports. This can help businesses reduce the cost of processing expenses and free up employees to focus on more productive tasks.
7. Improving Employee Productivity:
RPA can improve employee productivity by focusing on more important or complicated tasks. This can boost morale and job satisfaction. For example, RPA bots can be used to automate tasks such as scheduling appointments and sending reminders. This can free up employees to focus on more challenging and rewarding tasks, such as providing customer service and developing new products.
8. Simplifying Development:
RPA can simplify development by using low-code tools to make RPA scripts. This makes it easier for businesses to automate processes without having to invest in extensive coding resources. For example, robotic process automation services bots can be developed using drag-and-drop interfaces and pre-built templates. This can help businesses quickly and easily automate processes, without the need for specialized coding skills.
9. Operating on the Presentation Layer:
RPA operates on the presentation layer of apps, which doesn’t disturb inner systems. This makes it a safe and non-invasive way to automate processes. For example, RPA bots can be used to automate tasks such as filling out forms and clicking buttons. This can help businesses automate processes without having to make changes to their underlying systems.
Challenges Of RPA
There are also several challenges related to RPA that have limited its use:
-
Scalability
Enterprises have faced challenges in scaling their RPA automation initiatives due to several factors. While RPA robotic process automation software bots are relatively straightforward to implement, governing and managing them can be challenging, particularly when scaling up operations. This complexity arises from the need to ensure that RPA bots are operating in a consistent and efficient manner, adhering to organizational policies and regulations, and integrating seamlessly with existing IT infrastructure.
-
Limited Abilities
Critics have pointed out that while RPA tools automate tasks, they often fall short of automating complete processes. This is because RPA bots are typically designed to handle specific, repetitive tasks within a process. However, when multiple tasks need to be stitched together to form a cohesive process, additional work is required. Furthermore, there are inherent limitations to RPA bots’ capabilities. For instance, they may struggle when required to make more than five decisions, manipulate more than five applications, or perform more than 500 clicks. These limitations can hinder the automation of complex processes.
-
Security
Robotic process automation RPA bots often require access to sensitive information to complete their tasks. This poses an additional security risk for organizations if the bots are compromised. RPA bots may become vulnerable to unauthorized access, manipulation, or data theft if not properly secured. Organizations must implement robust security measures, such as access control, encryption, and regular security audits, to mitigate these risks.
Read Blog: The Role of AI in Modern Cybersecurity
-
Limited Resiliency
RPA failures can occur when applications change in ways that aren’t anticipated by the software developers. This is because RPA bots rely on the stability and consistency of the applications they interact with. When applications undergo updates, modifications, or redesigns, RPA bots may no longer function correctly. This lack of resilience can lead to disruptions in automated processes and impact operational efficiency.
-
New Quality Assurance (QA) Issues
Bots introduce a new set of QA challenges that need to be addressed to ensure they continue to work as intended. Traditional QA practices may not be sufficient for robotics process automation bots, as they require specialized testing methodologies and tools. organizations need to establish robust QA processes to validate the accuracy, reliability, and performance of RPA bots throughout their lifecycle.
-
Privacy
RPA bots often work with personally identifiable information (PII) governed by privacy requirements. Organizations need to ensure that this data is processed in compliance with local data protection laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Failure to do so could result in legal and reputational risks. For example, moving data outside of a specific country without encryption would constitute a GDPR violation. To address these concerns, RPA vendors are seeking ISO 27701 certification from the International Organization of Standardization (ISO) as a foundation for managing sensitive information.
-
Efficiency
RPA bots often manually navigate through applications in a similar manner to humans. This approach may not be as efficient as automating applications through application programming interfaces (APIs) or integrating workflow automations directly into the applications themselves. APIs can provide faster and more direct access to application data and functionality, enabling more efficient automation.
RPA Vendors
The following are examples of RPA vendors:
ABBYY:
- Develop OCR tools to enhance back-office applications.
- Recently expanded to offer automation capabilities for diverse use cases.
Automation Anywhere:
- Provides a digital workforce platform for various back-office processes, including procure-to-pay, quote-to-cash, HR, and claims processing.
Blue Prism:
- Focuses on assisting regulated industries to automate processes.
- Offers desktop-aligned and AI-powered bots managed centrally.
NICE:
- Traditionally focused on improving customer interactions in call centers.
- Expanded automation capabilities to support RPA with an emphasis on enhancing customer experience across multiple channels.
Nintex:
- Provides comprehensive automation capabilities, including process mining, governance, and AI modules to extend RPA functionalities.
Pegasystems:
- Initially known for business process management tools.
- Expanded into robotic process automation services by acquiring OpenSpan in 2016, offering Pega Robotic Automation.
UiPath:
- Provides an open platform to assist organizations in automating business processes efficiently.
The Future Of the RPA
Robotic process automation (RPA) is experiencing significant market growth due to its ability to enhance organizational capabilities, boost performance, and drive cost savings. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) capabilities into RPA products has contributed to this growth, enabling RPA bots to learn from data, automate complex tasks, and extend their usability. Future growth of RPA is further anticipated due to trends such as cloud-based RPA, RPA as a service model, no-code RPA for efficient development, and the use of process and task mining to uncover automation opportunities.
RPA’s growth is anticipated to be accelerated by hyper automation. Hyperautomation combines RPA with various automation tools, such as low-code and no-code development platforms, BPM tools, and decision engines. IPA and cognitive automation modules further enhance the integration of AI capabilities into this automation. Organizations should adopt a strategic approach to identify and generate automation opportunities and manage processes across the enterprise as hyper-automation gains traction. Some have established an automation center of excellence to effectively coordinate and scale automation projects.
Conclusion
In conclusion, robotic process automation (RPA) is transforming business operations by automating repetitive tasks, enhancing efficiency, and reducing costs. Understanding what is robotic process automation and its potential allows organizations to optimize their processes and stay competitive. The benefits of robotic process automation are substantial, from increased accuracy to better compliance, making it a critical tool in today’s fast-paced environment.
Exploring robotic process automation use cases helps identify opportunities for RPA to drive significant improvements. However, addressing robotic process automation challenges like implementation costs and ongoing management is essential for maximizing its potential. Integrating artificial intelligence services and robotic process automation can further enhance decision-making and process automation.
For businesses looking to fully leverage RPA, partnering with an experienced provider like SoluLab can be invaluable. SoluLab offers comprehensive robotic process automation services, guiding companies through every step of the automation journey. Whether you’re starting out or expanding your RPA initiatives, SoluLab’s expertise ensures that your process automation RPA efforts are successful and sustainable, paving the way for future growth and innovation.
FAQs
1. What is robotic process automation (RPA)?
Robotic process automation (RPA) refers to the technology that automates repetitive, rule-based tasks typically performed by humans. RPA robots, or “bots,” can mimic human interactions with digital systems, such as data entry, form filling, and processing transactions.
2. What are the benefits of robotic process automation?
The benefits of robotic process automation include increased efficiency, reduced errors, cost savings, and enhanced compliance. By automating repetitive tasks, organizations can free up human resources to focus on more strategic initiatives.
3. What are some common robotic process automation use cases?
Common robotic process automation use cases include invoice processing, customer service automation, HR onboarding, and data migration. These tasks, which are repetitive and time-consuming, are ideal for automation through RPA.
4. What are the challenges of implementing RPA robotic process automation?
Implementing RPA robotic process automation can present challenges such as initial setup costs, resistance to change from employees, and the need for ongoing maintenance. It’s important to address these challenges to maximize the benefits of RPA.
5. How does artificial intelligence enhance robotic process automation?
Artificial intelligence and robotic process automation can be integrated to create more intelligent robotic process automation systems. This combination allows RPA to handle more complex tasks, such as decision-making, data analysis, and pattern recognition, enhancing the overall capabilities of RPA bots.






