If you have been monitoring the blockchain sector lately, it is likely that you have encountered discussions on TON Blockchain, which stands for The Open Network. Originating from Telegram’s concept of a decentralized internet, TON is gaining prominence because of its rapid transactions, minimal fees, and effortless integration with a leading messaging platform. TON is not only another blockchain; it is a whole ecosystem engineered to facilitate payments, NFTs, decentralized applications, and storage.
As per the recent data, the TON network has processed over 3.4 billion user transactions, averaging 123 transactions per second. With Telegram’s user base surpassing 900 million monthly active users, TON is distinctly positioned to introduce cryptocurrency to the general populace, integrated into an application that individuals utilize daily.
In this guide, we will provide complete information on TON, its functionality, and its potential as the future of Web3.
What is TON?
TON (The Open Network) is a blockchain engineered to enable rapid transactions and support the development of diverse decentralized applications (dApps). This community-oriented initiative was launched by the founders and proprietors of Telegram.
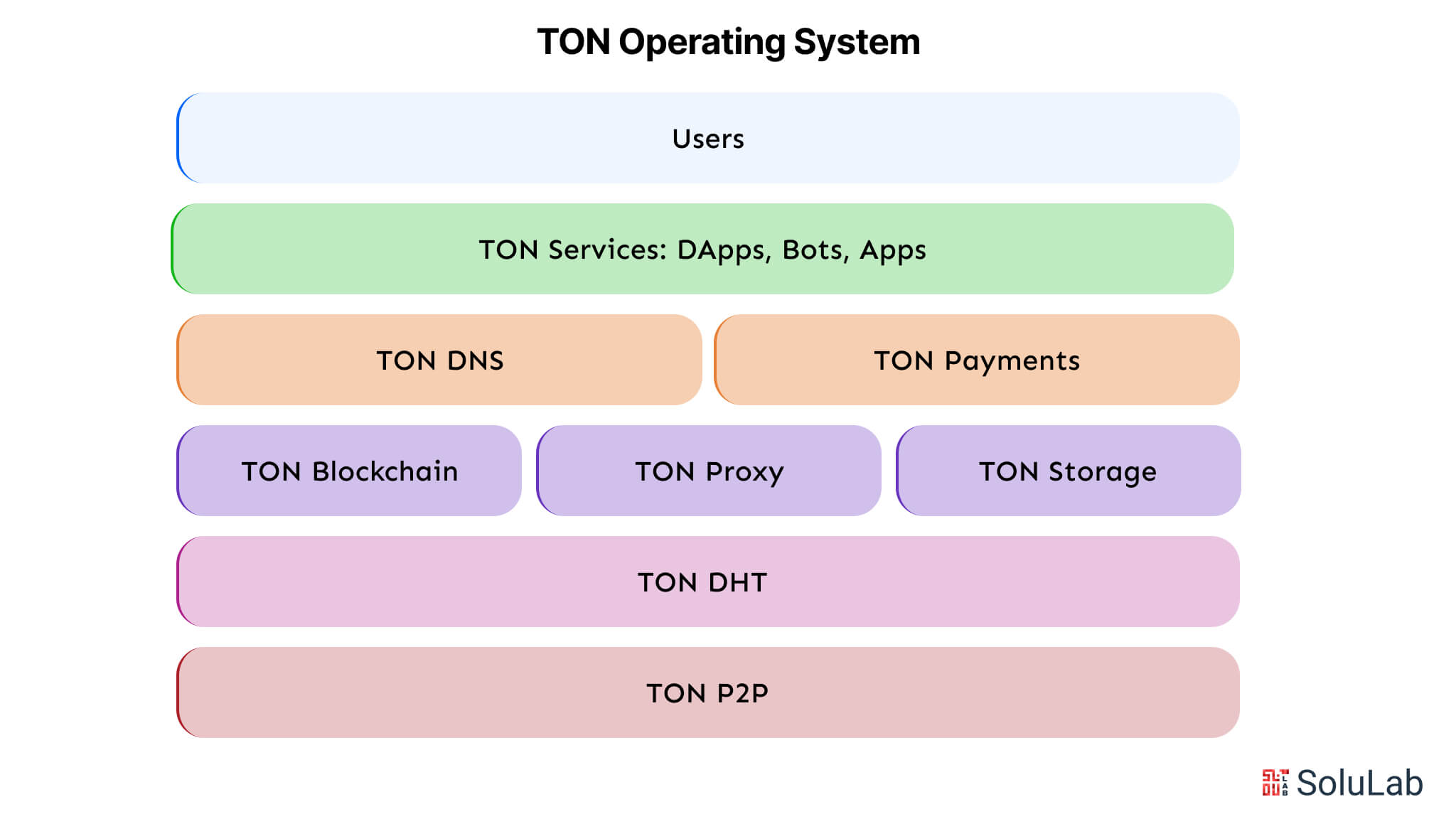
The network consists of many components, including the TON Blockchain, TON DNS, TON Storage, and TON Sites.
- TON DNS: Facilitates user engagement by allocating human-readable designations to accounts and decentralized applications (dApps).
- TON Storage: Provides decentralized file storage, enhancing data retrieval and
- TON Sites: Enables users to deploy a web server for their website, rendering it accessible on the TON network.
- TON Proxy: Facilitates connectivity to TON Sites.
- TON Payments: Enables immediate transactions without requiring block confirmation or incurring transaction fees.
- TON Space: Integrates with Telegram, offering a user-friendly interface that facilitates convenient access to wallets within the chat network.
- TON DHT: Operates as a decentralized storage system, enabling each network participant to store personal information or other data.
TON blockchain telegram mini-app platform constitutes not only a blockchain but a comprehensive ecosystem that includes essential participants:
- users who hold assets;
- validators, who maintain the fundamental consensus to preserve the blockchain’s integrity; and
- application developers, who create and enhance services on the TON platform.
The substantial user population of Telegram, which has direct access to The Open Network, enhances its adoption potential.
Current State of TON Development
The Open Network (TON) has seen notable progress recently, demonstrating its dedication to improving scalability, security, and user involvement. The following is a summary of the current status of TON’s development:
Recent Advancements:
- Network Updates: In March 2025, TON launched the 2025.03 Update, which introduced additional extracurrency functionality and enhanced the validation process, with special emphasis on CellStorageStat. These upgrades intend to augment network efficiency and performance.
- Security Enhancements: In late 2024, patches v2024.10 and FunC 0.4.5 were released, rectifying significant vulnerabilities and introducing performance enhancements. The modifications concentrated on system optimization, synchronization velocity, and minimizing network traffic, consequently augmenting the overall resilience of the network.
Expansion of Ecosystem:
- Wallet Expansion: In 2024, TON experienced the establishment of 36.2 million new wallets, signifying a considerable rise in user adoption and participation within the ecosystem.
- USDt Integration: The integration of USDt on TON has led to a net circulation of $1.4 billion and more than 26 million transactions, highlighting the network’s expanding significance in decentralized finance (DeFi) operations.
- DeFi Expansion: The DeFi sector of TON had a 55-fold surge in Total Value Locked (TVL) in 2024, alongside the introduction of several new initiatives, underscoring the network’s burgeoning financial environment.
Developer Resources:
- Comprehensive Toolkits: TON offers substantial tools for developers, comprising Software Development Kits (SDKs), thorough documentation, and community assistance, hence easing the development of decentralized apps (dApps) and smart contracts.
- Incentive Programs: Initiatives like The Open League provide enduring incentives, motivating developers to enhance the ecosystem’s development and innovation.
Strategic Alliances and Integrations:
- Telegram Connection: TON has intensified its connection with Telegram, utilizing the platform’s extensive user base to facilitate the adoption of Toncoin and related services, therefore augmenting the network’s exposure and functionality.
- Collaborations: Strategic alliances with other enterprises have been formed to enhance TON’s infrastructure and broaden its service offerings, thereby strengthening a more resilient and adaptable blockchain ecosystem.
These advancements highlight TON’s commitment to creating a scalable, secure, and user-centric blockchain platform, establishing it as a prominent entity in the decentralized technology arena.
How Does TON Work?
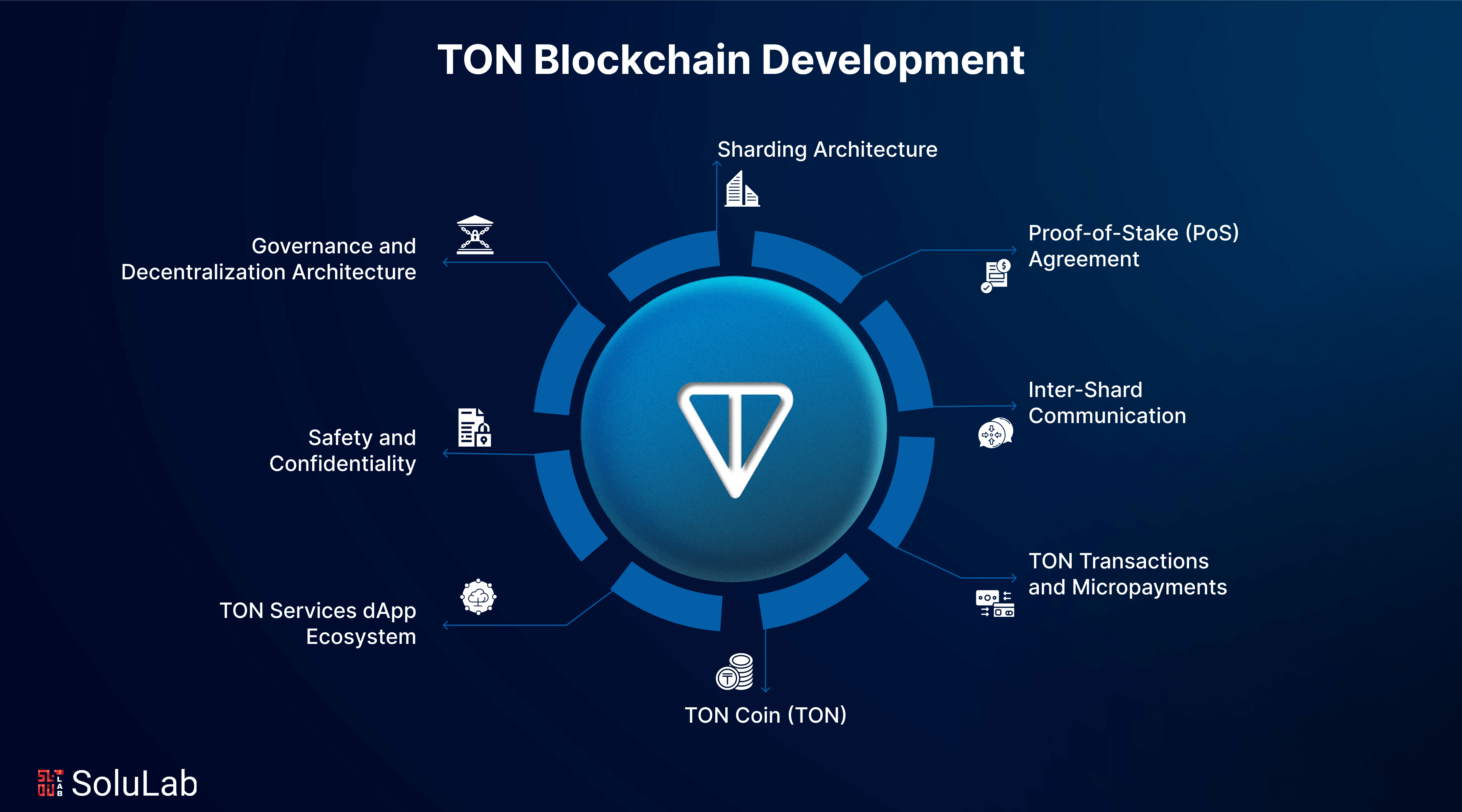
The TON blockchain network aims to overcome the primary constraints of conventional blockchain networks, including scalability, transaction speed, and user experience; a unique initiative should be introduced. The proof-of-stake method and multi-layered design, in conjunction with sharding, enhance the prospects for the TON blockchain.
1. Sharding Architecture: TON employs a multi-blockchain framework with sharding as a fundamental component. Sharding is the process of partitioning the blockchain into smaller, concurrent chains known as shards. Each shard functions as an autonomous blockchain, processing transactions independently and concurrently across the shards, hence improving scalability and performance. In contrast to conventional blockchain networks, Sharding enables TON to process millions of transactions per second. Each shard operates independently and may validate transactions using a synchronized communication mechanism. This enhances performance and reduces network congestion.
2. Proof-of-Stake (PoS) Agreement: TON blockchain telegram uses a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus method to provide decentralized and secure transactions while reducing the energy expenditures linked to conventional Proof-of-Work (PoW) systems. In Proof of Stake (PoS), validators engage in the verification and addition of new blocks by staking a certain quantity of TON currency as collateral. The more tokens a validator stakes, the increased the probability of their selection for validating fresh blocks.
3. Inter-Shard Communication: A primary obstacle with multi-shard blockchains is inter-shard communication. TON has addressed this issue via an inter-shard communication protocol, facilitating smooth interaction among the network’s many shards. It facilitates the transmission of assets, data, and smart contract calls between shards, ensuring the TON blockchain functions as an integrated system.
4. TON Transactions and Micropayments: TON apps and dApps facilitate immediate and scalable transactions via the TON Payments system. The network is engineered to enable rapid and economical payments, making it suitable for micropayments and low-value transactions that are generally impractical on other blockchains due to elevated transaction costs.
5. TON Coin (TON): The native token of the TON blockchain is TONcoin (TON), utilized for several functions within the ecosystem, including the payment of transaction fees, staking for transaction validation, and involvement in governance decisions. TON holders are permitted to stake their coins to become validators, contributing to network security and earning incentives in the process. The TON coin is vital for the network’s economy, powering its operations and allowing users to utilize different services inside the ecosystem.
6. TON Services dApp Ecosystem: It includes decentralized finance (DeFi), tokenized assets, gaming, social media, and other sectors. The TON blockchain facilitates the development of dApps with its adaptable smart contract mechanism. TON further provides TON DNS, a decentralized domain name system enabling users to register human-readable addresses for blockchain resources, hence enhancing platform usability.
7. Safety and Confidentiality: TON blockchain development prioritizes security and privacy at an elevated protocol level. The network’s decentralized architecture renders it resilient to central sources of failure and censorship. Furthermore, it employs cryptographic methods to guarantee the confidentiality of user data and transactions.
8. Governance and Decentralization: TON operates under a decentralized paradigm wherein the community of validators actively participates in decision-making. The governance framework is structured to be transparent and inclusive, enabling token holders to vote on various proposals for network enhancements, protocol modifications, and other significant choices. This guarantees the network’s decentralization.
Key Features of TON Blockchain
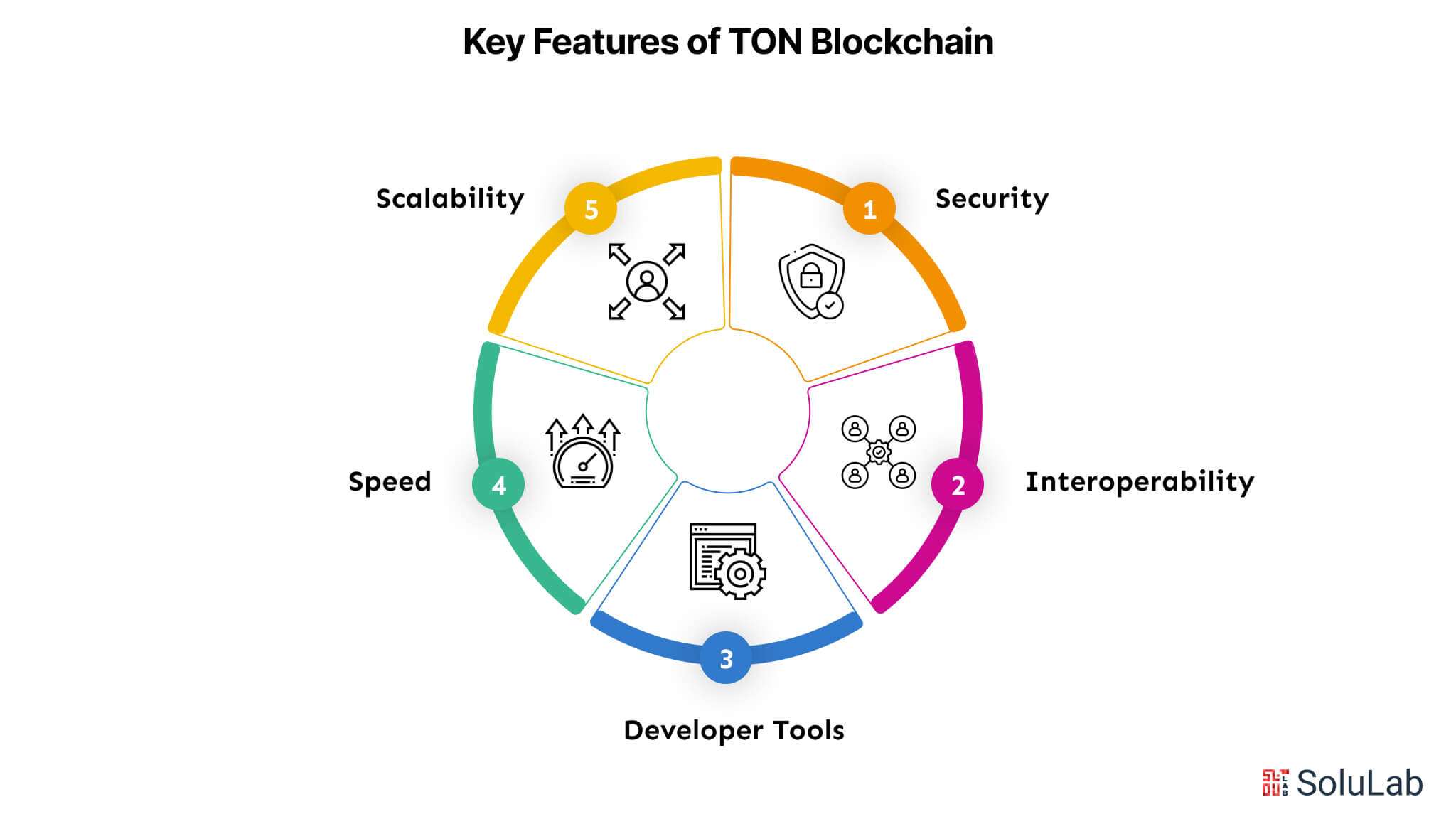
The TON blockchain has unique features and advantages.
-
Scalability
TON may shard the whole network, enhancing its performance as the user base expands, particularly for applications anticipated to grow rapidly.
-
Security
The TON blockchain employs contemporary cryptographic techniques and a decentralized design to provide high security for all users and developers. Previous users especially appreciate the network’s exceptional durability during attacks.
-
Interoperability
TON facilitates collaboration and innovation with developers across several blockchain networks due to its compatibility with different protocols. This facilitates interaction with other dApps, providing a degree of freedom.
-
Developer Tools
TON facilitates platform navigation for novice and seasoned users by offering comprehensive developer tools, including software development kits (SDKs) and libraries. This also accelerates the development process.
-
Speed
The TON blockchain enhances user experience by facilitating real-time data processing and providing rapid confirmation times.
By utilizing these capabilities, beginners who are learning to design a dApp on TON will be capable of constructing new dApps with superior user experience and functions.
Principles of TON Design
TON blockchain is engineered to offer a scalable foundation for decentralized applications. TON guarantees flexibility, scalability, security, and efficiency in decentralized applications by isolating contracts, facilitating asynchronous processes, and employing a sharded proof-of-stake consensus mechanism.
TON operates as a ledger of state transitions. It documents alterations in the status of various accounts, each functioning as a smart contract with distinct storage and an individual address. These accounts maintain TON currency balances and program code, enabling developers to formulate the logic of smart contracts performed on the TON Virtual Machine (TVM).
The primary design ideas of TON include:
- Asynchronous Operations
TON functions asynchronously, indicating that a contract cannot instantaneously access the state of another contract. It transmits a message and awaits a reply. This approach resembles the communication method of separate machines on the internet, preserving their data and state while transmitting and receiving messages asynchronously. It guarantees that no individual entity must access the complete global state of the blockchain at any moment.
- Flexibility and Isolation
TON contracts provide significant freedom to developers, enabling them to alter data, revise contract code, and transmit money and data messages to other contracts. Each contract is autonomous and segregated, inhibiting direct access to the states of other contracts, hence enabling the TON blockchain to scale indefinitely. Contracts autonomously process incoming information, adjust their status, and dispatch outbound messages.
- Guarantees and Consensus
The TON blockchain enables developers to authenticate the address of any message sender. Likewise, messages dispatched to an address are accompanied by cryptographic guarantees about the receiving code. The network ensures message delivery, albeit the timeframe may differ among shards and blocks.
TON employs a proof-of-stake mechanism to avoid double-spending and uphold unanimity within the network. In this architecture, validators are selected according to their stake or the quantity of cryptocurrency they own. Validators are tasked with authenticating transactions and are motivated to behave ethically, as their share is subject to penalties for fraudulent verification. The presence of several validators facilitates the detection and rejection of fraudulent activities in each transaction. This preserves the integrity of the TON network by dissuading malevolent entities from tampering with transactions.
Validators may be categorized into groups to handle elevated loads, facilitating horizontal scalability of the system. For instance, one group may manage even account numbers, while another group may oversee odd accounts.
- Latency in Transaction Processing
A transaction requires around 5 to 6 seconds to be committed to the base chain and a further 5 to 6 seconds for the master chain. The network requires around 10 to 12 seconds to present new data. Transactions of greater complexity, which involve several messages, may require additional time; nonetheless, the majority of transactions are uncomplicated, exhibiting predictable future actions following the confirmation of the first transaction.
- Independent Contracts
Every contract in TON functions as a distinct account containing its data and code. They provide information through message transmission. Validator consensus guarantees message transmission and mitigates replay attacks and double-spending. Although operations sometimes entail several transactions across diverse contracts, the initial transaction confirmation occurs within only seconds.
Architecture of TON Blockchain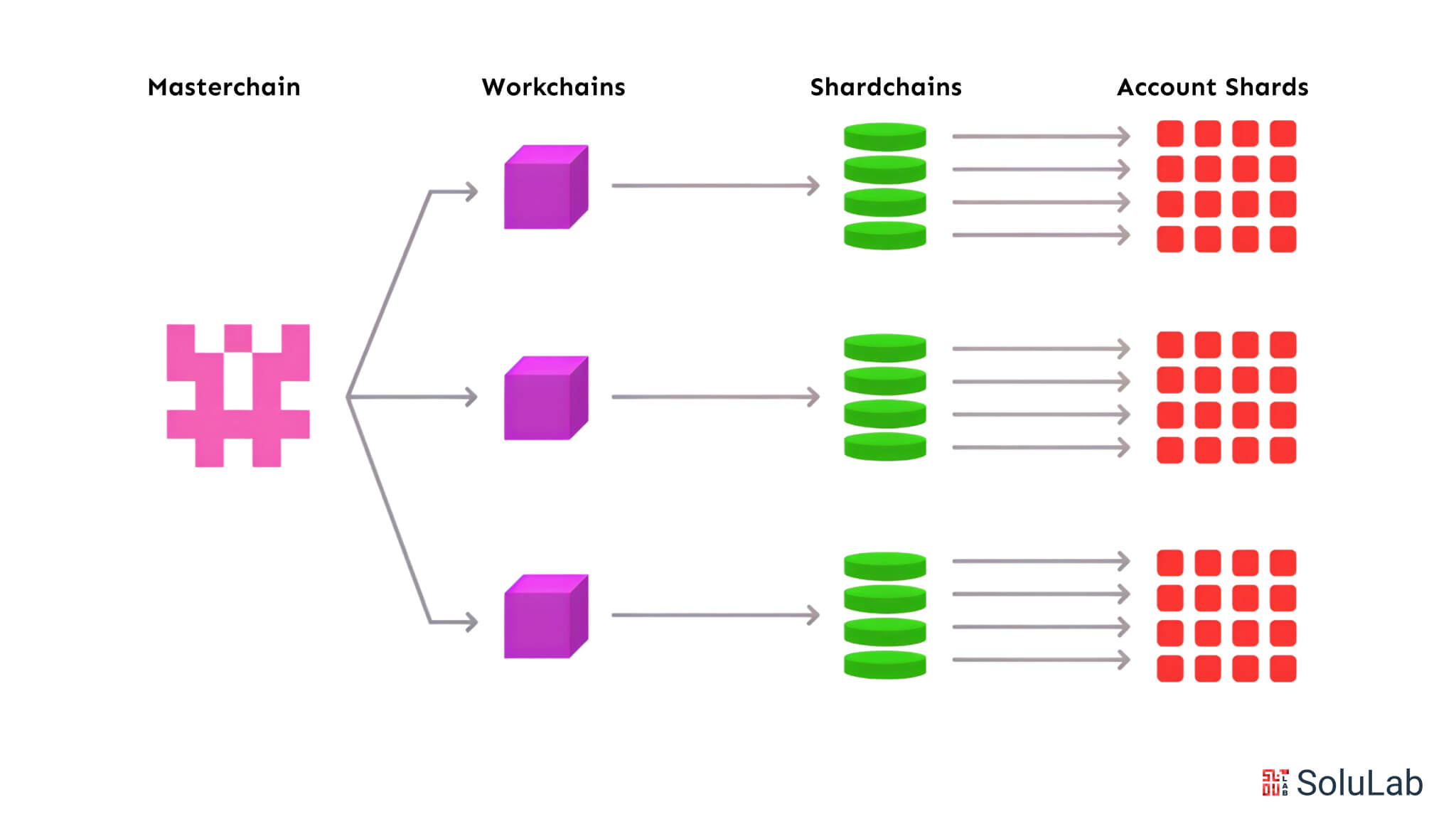
The TON blockchain comprises a masterchain and up to 2^32 workchains, each governed by its regulations. These workchains can be further subdivided into 2^60 shardchains. Now, just the basechain is functional.
- Masterchain: This principal chain retains network settings, the conclusive status of all workchains, protocol details, active validators, and block hashes, hence maintaining network consensus.
- Workchain: Tailored blockchains for certain transactions or applications, operating concurrently within the TON network. Every workchain possesses distinct rules, consensus processes, and tokenomics, yet synchronizes alongside the masterchain for validation and interoperability.
- Shardchain: Sub-chains of workchains, distinguished by a 60-bit shard prefix that denotes certain accounts. Shardchains can dynamically divide or merge to equilibrate the burden.
A. Dynamic Sharding
TON’s dynamic sharding facilitates the distribution of transactions over several workchains and shardchains, hence minimizing bottlenecks. Shardchains communicate their status to the masterchain and employ Hypercube route for intershard communication, facilitating fast transaction processing throughout the ecosystem.
B. Validators
Validators uphold the network’s integrity, security, and functionality by supplying computational power and staking Toncoin. They authenticate new blocks, verify transactions, and engage in the consensus mechanism. Validators are crucial to the whole ecosystem, encompassing both the masterchain and smaller shardchains. They are frequently reorganized to prevent collusion. This hierarchical, sharded design guarantees that TON can accommodate diverse use cases and exceptionally large transaction volumes.
What Distinguishes TON From Other Blockchains?
The primary differentiator of TON is its remarkable scalability and rapid performance. Due to its multi-layered, multi-blockchain design, TON can process millions of transactions per second, establishing it as a formidable competitor in the future of blockchain technology. To fully understand its benefits, let us simply examine its the throughout time:
-
Bitcoin: Fundamental and Rigid
Bitcoin, the trendsetter of blockchain technology, was launched approximately 14 years ago. Although groundbreaking at its inception, it provides restricted capabilities. The programming language accommodates only basic smart contracts, with limitations in storage and state management. Furthermore, Bitcoin’s architecture is predicated on a finite block limit, which is approaching its capacity, affording less opportunity for future expansion or flexibility.
-
Ethereum: Adaptable but Constrained
Ethereum represented the second generation of blockchain, offering enhanced flexibility via intricate smart contracts. Nonetheless, Ethereum has challenges with scalability, as each node in the network must retain the complete blockchain state and sequentially execute transactions. This leads to diminished speeds and more congestion as the network expands.
-
TON: Scalable, Adaptable, and Prepared for the Future
TON illustrates the third generation of blockchain, integrating Ethereum’s contractual versatility with unparalleled scalability. In contrast to earlier models, each account in TON possesses a distinct state and can engage asynchronously with other accounts. This approach facilitates the efficient routing of messages and transactions without necessitating access to the complete blockchain state.
TON employs sharding, a technique that divides contracts into smaller segments that may communicate fluidly throughout the network. This, together with its concurrent execution of smart contracts and application of logical time, ensures that transactions remain conflict-free irrespective of processing sequence. Consequently, TON provides a strong framework for extensive decentralized applications.
The network’s architecture facilitates speed, stability, and future scalability, rendering it an exceptional option for developing dApps or managing assets via TON wallets among contemporary blockchain platforms.
What are TON Accounts and Contracts?
In the TON (The Open Network) ecosystem, accounts and smart contracts are integral elements that collaborate to provide robust decentralized apps and services.
TON Accounts
Each user or smart contract on TON is denoted by an account. These accounts extend beyond only retaining monies, like conventional wallets; they also maintain their own state and may autonomously communicate with other accounts throughout the network. TON accounts have far greater versatility in comparison to those on preceding blockchains such as Bitcoin or Ethereum.
TON comprises two categories of accounts:
- Externally Owned Accounts (EOAs): Governed by private keys—utilized by users to administer TON wallets, execute transactions, and engage with contracts.
- Smart Contract Accounts: These are self-executing programs residing on the blockchain that react to incoming messages according to predetermined logic.
Smart Contracts
In TON, smart contracts are asynchronous, streamlined programs that manage logic and data. Each smart contract operates inside its own isolated environment and interacts with others through the transmission of messages, rather than by invoking functions directly. This is a significant advance that enables contracts to function concurrently, enhancing efficiency and throughput.
Significance of TON Blockchain
TON facilitates expedited transaction processing, reduced network congestion, and enhanced scalability by separating the global state and permitting asynchronous interactions. Comprehending TON accounts and contracts is crucial for effectively utilizing the network’s full capabilities, whether you are maintaining a TON wallet, installing a decentralized application, or constructing a DeFi platform.
What is the Functionality of a Contract?
Contracts can execute the following functions:
- Management of Internal Messages: Receive and handle incoming communications from other smart contracts.
- External Message Management: Acquire and handle incoming communications originating from outside the blockchain.
- Modifying the Status: Modify the data within the contract storage and the contract code.
- Transmit Messages: Dispatch messages, including associated money and data, to alternative contracts.
Typically, complex systems comprise several smart contracts, and interactions with these systems need to invoke an entry point contract, which then transmits messages to other contracts that do intermediate computations and modify their state accordingly.
The TON Token & Its Value
Toncoin (TON) serves as the native token of the TON blockchain. It facilitates transactions, smart contracts, and decentralized services throughout the network. Toncoin serves as a fundamental utility token, facilitating efficient interaction between developers and consumers within the TON ecosystem.
Functionality and Applications
Toncoin performs many roles inside the TON network:
- Transaction Fees: These are utilized for the execution of transactions and smart contracts.
- Staking and Validation: Validators stake Toncoin to fortify the network and get incentives.
- Governance: Token holders may engage in decision-making procedures and protocol enhancements.
- Access to Services: Toncoin is necessary for utilizing services such as TON DNS, TON Storage, and TON Proxy.
Monetary Worth and Expansion
The value of Toncoin is underpinned by tangible use cases and an expanding ecosystem of decentralized apps. The architecture facilitates elevated transaction throughput and scalability, rendering it appropriate for extensive blockchain use. As the demand for TON-based services escalates, the usefulness and prospective worth of Toncoin also rise.
Enterprises aiming to enhance this ecosystem may partner with a reputable TON blockchain development firm to construct scalable, token-driven systems for decentralized finance, gaming, identification, and more applications.
Use Cases of TON Blockchain
The TON blockchain development provides a robust and scalable architecture that accommodates a diverse range of real-world applications. Its rapidity, minimal costs, and adaptable framework render it suitable for both consumer-oriented and enterprise-level applications. Here are some of the TON blockchain use cases:
1. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
TON facilitates the creation of DeFi applications, including decentralized exchanges (DEXs), lending platforms, stablecoins, and staking systems. Its elevated throughput and concurrent processing render it optimal for developing rapid and cost-effective financial services.
2. Encrypted Communication and Transactions
Users may transmit Toncoin immediately within conversations because to its profound interaction with Telegram. TON is ideal for micro-payments, tipping, subscription models, and worldwide peer-to-peer transactions without middlemen.
3. Web3 Decentralized Applications
Developers may utilize TON to create scalable and efficient decentralized apps across many industries, including gaming, social networking, identity verification, and NFT markets. Its asynchronous smart contract framework facilitates real-time, user-centric decentralized application experiences.
4. Tokenized Loyalty Initiatives
Brands and enterprises may establish tokenized reward programs on TON to enhance client engagement. These loyalty tokens may be acquired, exchanged, or utilized inside a specified ecosystem, providing greater flexibility than conventional point-based systems.
5. Cross-Border Transactions
TON’s rapid settlement timeframes and minimal transaction fees make it an excellent option for remittance solutions and international payment platforms. Businesses may optimize overseas payments utilizing Toncoin, circumventing banks and sluggish middlemen.
6. Gaming and Digital Assets
Game creators may create blockchain-based games in which assets such as skins, weaponry, or characters are minted as NFTs. Players may possess, exchange, and profit from their in-game items inside a safe and scalable TON ecosystem.
Future Outlook of TON Blockchain
TON is rapidly attracting interest as a highly potential blockchain platform for the forthcoming generation of Web3 apps. The robust foundation and expanding ecology of TON indicate a promising and potential-filled future.
- More Speed, More Users
TON is always concentrating on scalability, intending to enhance the network’s speed and efficiency. Future enhancements will accommodate even bigger transaction volumes, rendering it optimal for applications with millions of users, particularly due to its seamless connection with Telegram.
- Layer-2 Payment Solution
TON intends to implement a Layer-2 solution for instantaneous, economical transactions. This is ideal for microtransactions, game prizes, or tipping creators in chat applications.
- Enhanced Smart Contracts
Enhancements are forthcoming to augment the capabilities of TON smart contracts. Developers will have the capability to create more sophisticated decentralized applications in sectors such as banking, gaming, and identification, while ensuring speed and security.
- Bitcoin Compatibility
TON is investigating methods to integrate with the Bitcoin network, enabling users to transfer BTC within TON’s ecosystem. This creates exhilarating new opportunities for cross-chain financial and decentralized finance technologies.
- Expanding Ecosystem and Investment
The TON ecosystem is experiencing fast expansion, drawing in developers, entrepreneurs, and significant investors. This impetus is propelling the development of more tools, applications, and practical use cases based on TON.
- Telegram Integration Equals Extensive Reach
As Telegram rapidly expands towards one billion users, TON is poised to become the preferred blockchain for routine digital interactions. The transmission of tokens, engagement in games, or direct access to services via chat may soon become instinctive for millions.
TON’s future encompasses not just technology but also the development of a seamless, accessible, and robust experience for both users and enterprises. Regardless matter whether you are a developer or an investor, the present moment is opportune for examining the offerings of TON.
Conclusion
TON is not only another blockchain; it is an innovative ecosystem designed for scalability, rapidity, and practical implementation. Through its seamless connection with Telegram, asynchronous smart contracts, and emphasis on user-friendly decentralized services, TON is facilitating the emergence of the next generation of Web3 apps. It provides the necessary capabilities for developers and users to engage in on-chain interactions seamlessly, spanning finance, gaming, and routine transactions.
SoluLab is dedicated to assisting businesses in using advanced blockchain technologies such as TON. As a leading blockchain development company, we recently partnered on the OBORTECH Smart Hub, a project that exemplifies the capabilities of Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS). OBORTECH enables organizations to develop scalable blockchain applications via cloud-based networks, facilitating deployment on AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure. This idea demonstrates how enterprises may implement blockchain technology without substantial infrastructure expenditures.
If you are investigating TON or strategizing your forthcoming blockchain-based solution, SoluLab is available to assist. Our specialists can actualize your concept from strategy and development to launch and scale. Let’s build something transformative together—reach out to us today!
FAQs
1. Why is TON considered a third-generation blockchain?
TON is classified as a third-generation blockchain because it addresses the core limitations of earlier blockchains—scalability, speed, and flexibility. It introduces features like asynchronous smart contracts, multi-sharding, and parallel transaction execution, allowing it to handle millions of transactions per second efficiently. These advancements make it well-suited for mass adoption and real-world decentralized applications.
2. What are TON accounts, and how do they work?
TON accounts are individual entities on the network that can either be user-controlled wallets or smart contracts. Each account maintains its state and communicates asynchronously with other accounts. This design allows for parallel execution and faster transactions without the need to access the global blockchain state.
3. What is the TON token (Toncoin) used for?
Toncoin is the native token of the TON blockchain. It is used to pay transaction fees, interact with smart contracts, stake for network validation, and participate in governance. It also powers services like decentralized payments and applications within the TON ecosystem.
4. Can businesses build on TON, and how?
Yes, businesses can build scalable and secure decentralized apps (dApps) on TON. By partnering with a TON blockchain development company like SoluLab, companies can create enterprise-grade blockchain solutions tailored to their needs, leveraging services such as smart contract development, tokenization, and integration with platforms like Telegram.
5. What does the future look like for TON?
TON’s roadmap includes major upgrades like Layer-2 payments, enhanced smart contracts, and Bitcoin interoperability. With growing adoption, investment, and integration into apps like Telegram, TON is positioned to become a leading blockchain platform for both developers and everyday users.






